Final ID: MDP1639
Trends in Rheumatic Heart Disease Mortality in India (2010-2021) and Projections to 2030
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction: In 2021, India reported an estimated 166,017 deaths related to Rheumatic Heart Disease (RHD). Since 2010, the Indian government has implemented various initiatives to reduce this burden. The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) launched the "Jai Vigyan Mission Mode Project," focusing on raising awareness, early detection, treatment, and infrastructure strengthening. The National Programme for Prevention & Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases & Stroke (NPCDCS) and Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram (RBSK) programs have established NCD clinics and cardiac care units, conducted health education campaigns, and trained medical staff for RHD prevention and control. Key initiatives include using RHD registers, regular penicillin prophylaxis, and promoting early diagnosis and treatment. The development of the low-cost Sree Chitra Valve has also increased treatment affordability. This study aims to evaluate the impact of these government efforts on reducing RHD-related mortality in India.
Methods: Data from the Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx) for the 2021 Global Burden of Disease was analyzed to assess the global burden of RHD cases from India and the death rates per 100,000 population between 2010 and 2021 and predictive models adopted for estimates till 2030.
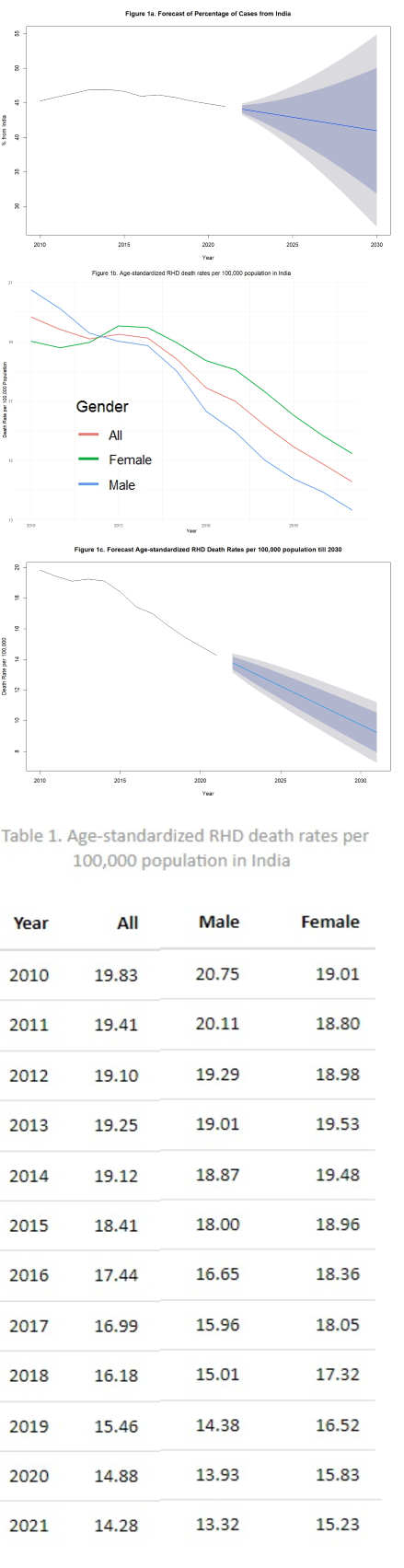
Results Between 2010 and 2014, the global mortality linked to RHD from India increased from 45.23% to 46.94%, then decreased gradually to 44.47% in 2021. Our predictive model estimates that India will contribute around 40.96% of global RHD deaths by 2030. Initially, the age-standardized RHD death rate per 100,000 population was lower among females than males, but it rose higher than males from 2013 onwards. A continuous reduction in the rate was observed in females from 2013 to 2021. Meanwhile, a declining trend was seen among males and combined (male + female) over the study period. By 2030, the overall death rate per 100,000 population is estimated to reach 9.23 (95% CI 7.24-11.22)(Figure 1).
Conclusion Our study confirms the downward trend of RHD mortality rates in India, likely linked to the multiple health initiatives. This highlights the need for sustained public health efforts to continue reducing RHD mortality.
Introduction: In 2021, India reported an estimated 166,017 deaths related to Rheumatic Heart Disease (RHD). Since 2010, the Indian government has implemented various initiatives to reduce this burden. The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) launched the "Jai Vigyan Mission Mode Project," focusing on raising awareness, early detection, treatment, and infrastructure strengthening. The National Programme for Prevention & Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases & Stroke (NPCDCS) and Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram (RBSK) programs have established NCD clinics and cardiac care units, conducted health education campaigns, and trained medical staff for RHD prevention and control. Key initiatives include using RHD registers, regular penicillin prophylaxis, and promoting early diagnosis and treatment. The development of the low-cost Sree Chitra Valve has also increased treatment affordability. This study aims to evaluate the impact of these government efforts on reducing RHD-related mortality in India.
Methods: Data from the Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx) for the 2021 Global Burden of Disease was analyzed to assess the global burden of RHD cases from India and the death rates per 100,000 population between 2010 and 2021 and predictive models adopted for estimates till 2030.
Results Between 2010 and 2014, the global mortality linked to RHD from India increased from 45.23% to 46.94%, then decreased gradually to 44.47% in 2021. Our predictive model estimates that India will contribute around 40.96% of global RHD deaths by 2030. Initially, the age-standardized RHD death rate per 100,000 population was lower among females than males, but it rose higher than males from 2013 onwards. A continuous reduction in the rate was observed in females from 2013 to 2021. Meanwhile, a declining trend was seen among males and combined (male + female) over the study period. By 2030, the overall death rate per 100,000 population is estimated to reach 9.23 (95% CI 7.24-11.22)(Figure 1).
Conclusion Our study confirms the downward trend of RHD mortality rates in India, likely linked to the multiple health initiatives. This highlights the need for sustained public health efforts to continue reducing RHD mortality.
More abstracts on this topic:
Aortic Valve Neocuspidization Using Autologous Insertion Of Pulmonary SinusTm: A Proof Of Concept
Faateh Muhammad, Raees Muhammad Aanish, Ahmed Hosam, Almiqlash Bushray, Villalobos Lizardi Jose, Ricci Marco, Ashfaq Awais
Artificial intelligence-guided screening of rheumatic heart disease from single-view two-dimensional echocardiographyOikonomou Evangelos, Nascimento Bruno, Pedroso Aline, Lombo Bernardo, Mcnamara Robert, Karnik Ruchika, Sable Craig, Ribeiro Antonio, Khera Rohan