Final ID: MDP1037
Applying artificial intelligence chatbot to increase heart disease awareness and knowledge in women
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Heart disease is the leading cause of death (LOCD) in women in the United States. Despite public campaigns, women's awareness of heart disease as the LCOD of death for women significantly decreased from 65% in 2009 to 44% in 2019. Significant declines were observed in Black, Hispanic, and young women.
Aims: This pilot trial aims to evaluate the acceptability/usability and potential efficacy of the fully automated artificial intelligence (AI) HeartBot program to increase awareness and knowledge of heart attacks in women.
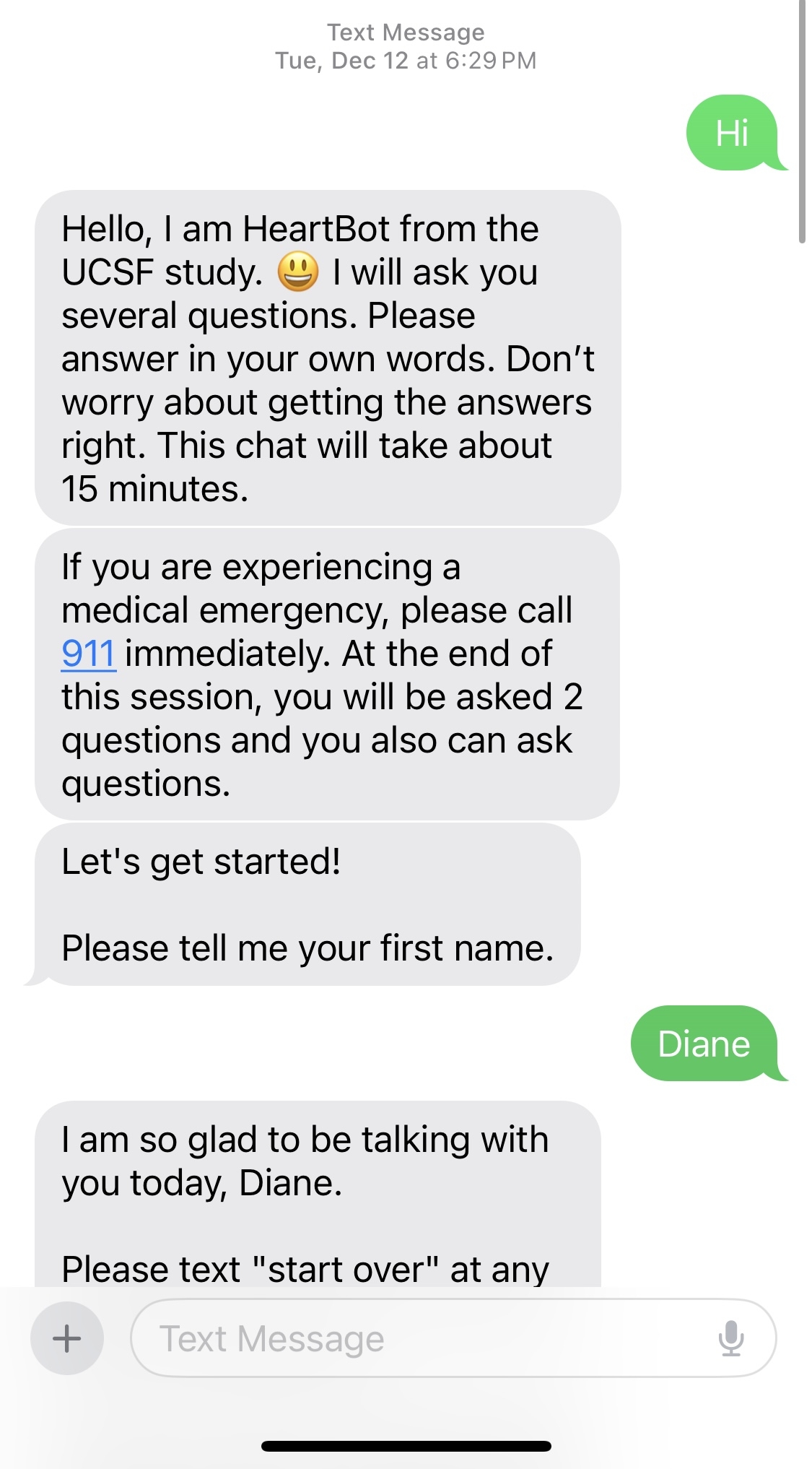
Methods: In this pre-and post- trial, 102 women were asked to complete the baseline survey and then interact with the HeartBot. The HeartBot is an AI-based text-driven conversational agent, available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, and fully automated (Figure 1). After 4 weeks of the interaction, women were asked to complete the post-survey. The primary outcomes include four questions (recognizing the signs and symptoms of a heart attack, telling the difference between the signs or symptoms of a heart attack and other medical problems, calling an ambulance or dialing 911, and getting to an emergency room within 60 minutes after the onset of your symptoms of a heart attack). Wilcoxon signed rank tests and ordinal logistic regression models were used to evaluate the HeartBot program.
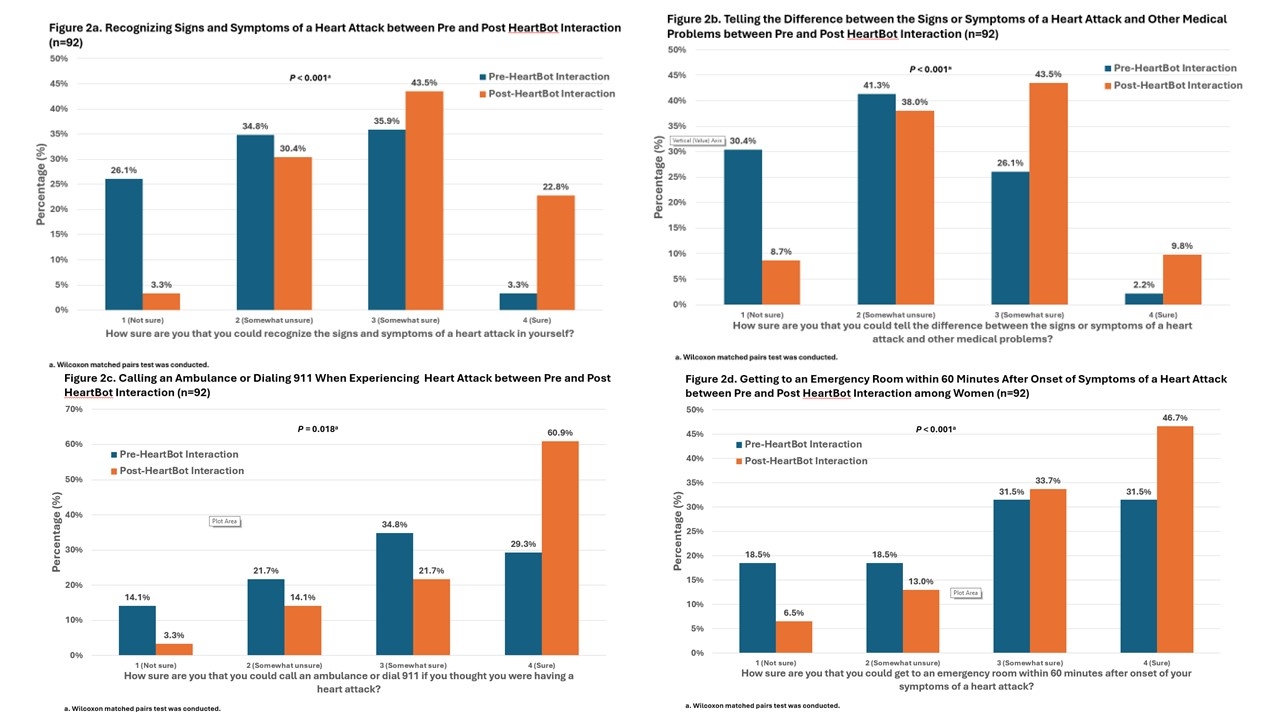
Results: The mean (SD) age was 46 (12) years; 60.6% of the sample was women with racial/ethnic backgrounds; 41.3% reported commercially available chatbot use (i.e. Siri) in the past 30 days. 88.5% of the sample completed the trial and the majority accepted HeartBot use. The mean (SD) length of the HeartBot interaction was 13 (11) minutes. Overall, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test indicated a significant increase in all outcomes of heart attack awareness and knowledge from the baseline and the post-Heartbot interaction (p < 0.05) (Figure 2). In the ordinal regression model, this significance of the outcomes remains even when controlling for potential confounding factors (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: To the best of our knowledge, this was the first pilot trial to demonstrate the potential efficacy of the HeartBot program in the short term in women with diverse racial/ethnic backgrounds. However, a full-scale randomized controlled is warranted.
Aims: This pilot trial aims to evaluate the acceptability/usability and potential efficacy of the fully automated artificial intelligence (AI) HeartBot program to increase awareness and knowledge of heart attacks in women.
Methods: In this pre-and post- trial, 102 women were asked to complete the baseline survey and then interact with the HeartBot. The HeartBot is an AI-based text-driven conversational agent, available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, and fully automated (Figure 1). After 4 weeks of the interaction, women were asked to complete the post-survey. The primary outcomes include four questions (recognizing the signs and symptoms of a heart attack, telling the difference between the signs or symptoms of a heart attack and other medical problems, calling an ambulance or dialing 911, and getting to an emergency room within 60 minutes after the onset of your symptoms of a heart attack). Wilcoxon signed rank tests and ordinal logistic regression models were used to evaluate the HeartBot program.
Results: The mean (SD) age was 46 (12) years; 60.6% of the sample was women with racial/ethnic backgrounds; 41.3% reported commercially available chatbot use (i.e. Siri) in the past 30 days. 88.5% of the sample completed the trial and the majority accepted HeartBot use. The mean (SD) length of the HeartBot interaction was 13 (11) minutes. Overall, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test indicated a significant increase in all outcomes of heart attack awareness and knowledge from the baseline and the post-Heartbot interaction (p < 0.05) (Figure 2). In the ordinal regression model, this significance of the outcomes remains even when controlling for potential confounding factors (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: To the best of our knowledge, this was the first pilot trial to demonstrate the potential efficacy of the HeartBot program in the short term in women with diverse racial/ethnic backgrounds. However, a full-scale randomized controlled is warranted.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Community Outreach Program Focused on Hypertension Awareness Reaches 600+ People in Rural Georgia and Works to Build the Next Generation of Biomedical Scientists
Dent Elena, Ilatovskaya Daria, Pinkerton Brittany, Crider Emily, Ryan Michael, Sullivan Jennifer
Adverse Maternal and Offspring Outcomes in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat Pregnancies: Impact of a Maternal Hypertensive High-Fat DietGomes Viviane, Watts Stephanie, Fink Gregory, Kim Lauren, Lopez Krystal, Gilbert Bryce, Bailey Victoria, Marques Bruno, Garver Hannah, Mckenzie Mckenzie, Lauver Adam