Final ID: Sa2071
Catheter Ablation Outperforms Medical Therapy in Management of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Enhanced Cardiac Function, Reduced Mortality, and Lower Hospitalizationion Rates
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) presents a significant management challenge, particularly in patients with concurrent heart failure. The effectiveness of catheter ablation compared to medical therapy for these patients remains under debate.
Aim
This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the outcomes of catheter ablation versus medical therapy for managing persistent AF.
Research Question
How does catheter ablation compare to medical therapy in managing persistent AF considering outcomes like arrhythmia recurrence, hospitalizations, cardiac function, exercise capacity, and mortality?
Methods
We performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing catheter ablation with medical therapy in patients with persistent AF. Data sources included PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Clinicaltrial.gov, Google Scholar, and CINAHL/EBSCOHOST, with studies selected based on predefined inclusion criteria. Primary outcomes assessed were recurrence of atrial arrhythmias, hospitalizations, changes in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), changes in 6-minute walk test (6MWT) distance, and all-cause mortality. The data extraction was done using a spreadsheet, and the data analysis was done using RevMan 5.4.1: for meta-analysis
Results
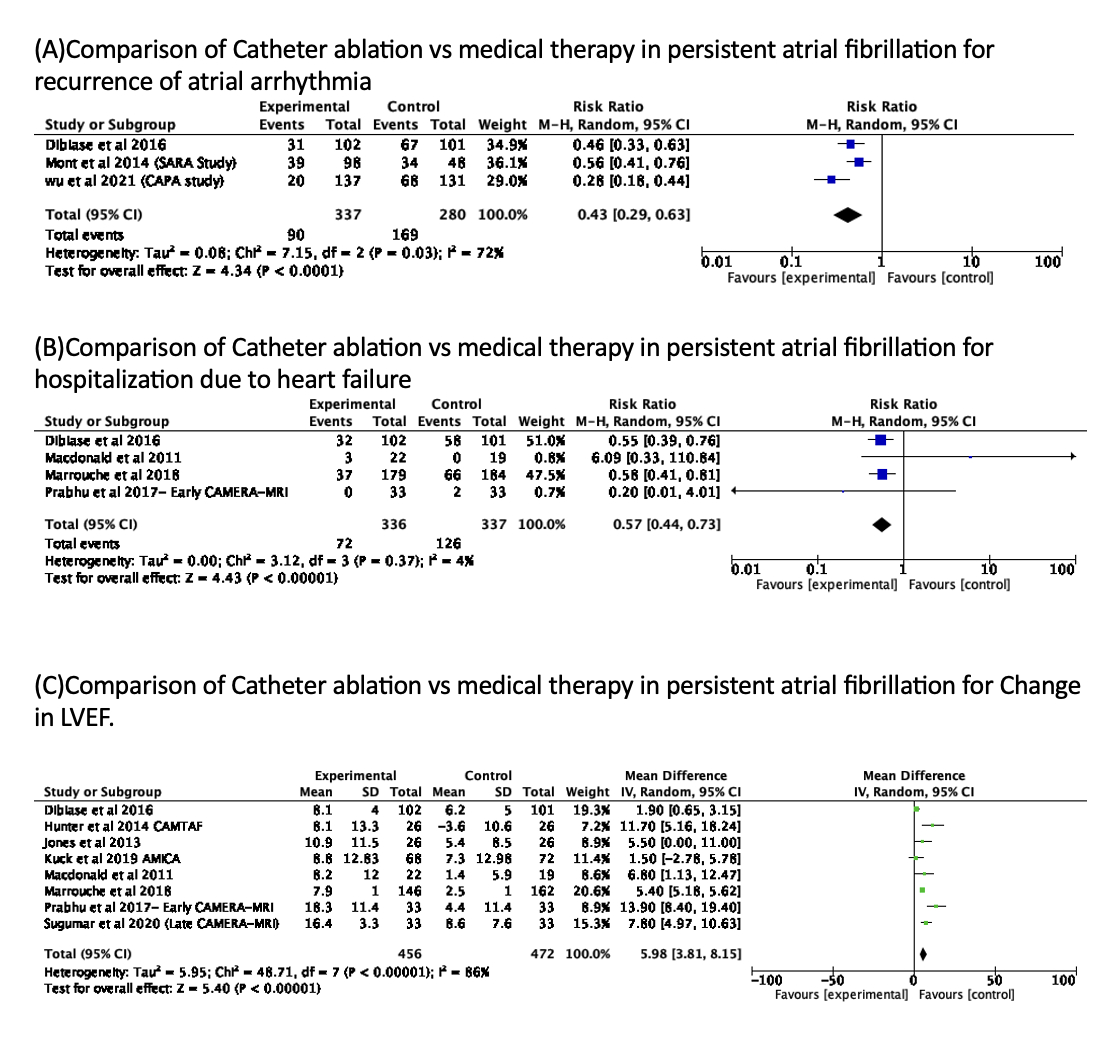
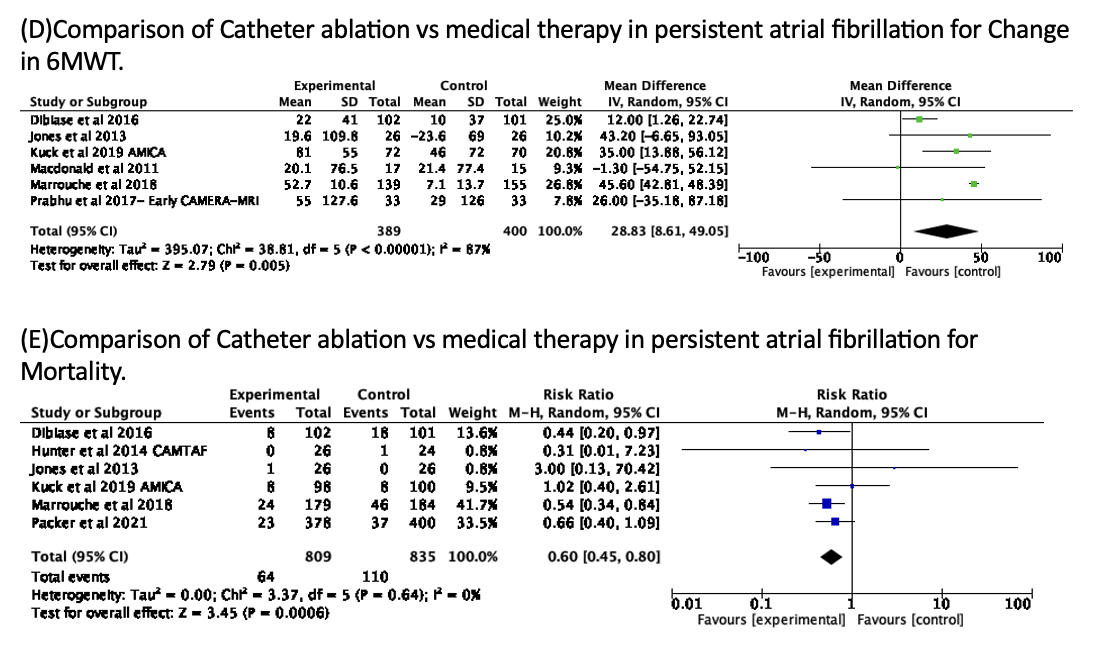
A total of 10 RCTs involving 1812 patients were included in the analysis. Compared to medical therapy, catheter ablation significantly reduced the recurrence of atrial arrhythmias (risk ratio [RR] = 0.43, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.29-0.63, P < 0.0001). Hospitalization rates due to heart failure were also lower in the ablation group (RR = 0.57, 95% CI: 0.44-0.73, P < 0.001). Improvements in LVEF were observed with a mean difference (MD) of 5.98% (95% CI: 3.81% to 8.15%, P < 0.00001). The performance on the 6MWT was better in the catheter ablation group, with an MD of 28.83 meters (95% CI: 8.61 to 49.05 meters, P = 0.005). Additionally, catheter ablation was associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality (RR = 0.60, 95% CI: 0.45-0.80, P = 0.00006).
Conclusion
This meta-analysis demonstrates that catheter ablation is superior to medical therapy in managing persistent atrial fibrillation. Catheter ablation offers significant benefits in reducing atrial arrhythmia recurrence, lowering hospitalization rates, improving cardiac function and exercise capacity, and reducing mortality. These findings support the consideration of catheter ablation as a preferred treatment strategy for patients with persistent AF.
Persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) presents a significant management challenge, particularly in patients with concurrent heart failure. The effectiveness of catheter ablation compared to medical therapy for these patients remains under debate.
Aim
This meta-analysis aims to evaluate the outcomes of catheter ablation versus medical therapy for managing persistent AF.
Research Question
How does catheter ablation compare to medical therapy in managing persistent AF considering outcomes like arrhythmia recurrence, hospitalizations, cardiac function, exercise capacity, and mortality?
Methods
We performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing catheter ablation with medical therapy in patients with persistent AF. Data sources included PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Clinicaltrial.gov, Google Scholar, and CINAHL/EBSCOHOST, with studies selected based on predefined inclusion criteria. Primary outcomes assessed were recurrence of atrial arrhythmias, hospitalizations, changes in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), changes in 6-minute walk test (6MWT) distance, and all-cause mortality. The data extraction was done using a spreadsheet, and the data analysis was done using RevMan 5.4.1: for meta-analysis
Results
A total of 10 RCTs involving 1812 patients were included in the analysis. Compared to medical therapy, catheter ablation significantly reduced the recurrence of atrial arrhythmias (risk ratio [RR] = 0.43, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.29-0.63, P < 0.0001). Hospitalization rates due to heart failure were also lower in the ablation group (RR = 0.57, 95% CI: 0.44-0.73, P < 0.001). Improvements in LVEF were observed with a mean difference (MD) of 5.98% (95% CI: 3.81% to 8.15%, P < 0.00001). The performance on the 6MWT was better in the catheter ablation group, with an MD of 28.83 meters (95% CI: 8.61 to 49.05 meters, P = 0.005). Additionally, catheter ablation was associated with a reduction in all-cause mortality (RR = 0.60, 95% CI: 0.45-0.80, P = 0.00006).
Conclusion
This meta-analysis demonstrates that catheter ablation is superior to medical therapy in managing persistent atrial fibrillation. Catheter ablation offers significant benefits in reducing atrial arrhythmia recurrence, lowering hospitalization rates, improving cardiac function and exercise capacity, and reducing mortality. These findings support the consideration of catheter ablation as a preferred treatment strategy for patients with persistent AF.
More abstracts on this topic:
4-Phenylbutyric Acid Reduces Endoplasmic Reticulum Retention and Partially Restores Function of LDLR p.D622N Mutation In Vitro: A Potential Therapy for Hypercholesterolemia
Wang Yongxiang, Zhang Piyi, Bai Ming, Zhang Zheng
Catheter Ablation of Atrial Arrhythmias in Patients with Cardiac AmyloidosisDiep Brian, Kewcharoen Jakrin, Garg Jalaj