Final ID: MDP1244
Racial And Ethnic Disparities In Outcomes Of St Segment Elevated Myocardial Infarction With Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Racial disparities in healthcare are a persistent and troubling issue, with profound implications for patient outcomes and societal well-being. Despite advances in medical science, studies consistently show that minority patients, particularly African Americans and Hispanics, face higher rates of STEMI incidence, delayed treatment, and poorer outcomes compared to their white counterparts.
Methods
we examined the national inpatient sample 2017-2020 for adult admitted with st segment myocardial infarction,we compared the clincal outcome of patients admitted with stemi with pci based on racial distribution.STATA 18th edition was used for analyses. Age, gender, race, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, and Elixhauser comorbidity index were identified as confounders by univariate analyses and tested further with multivariate logistic regression models. The primary outcome was mortality. Secondary outcomes were the need for intubation, cardiac arrest, length of stay (LOS), and total hospital charges.
Results
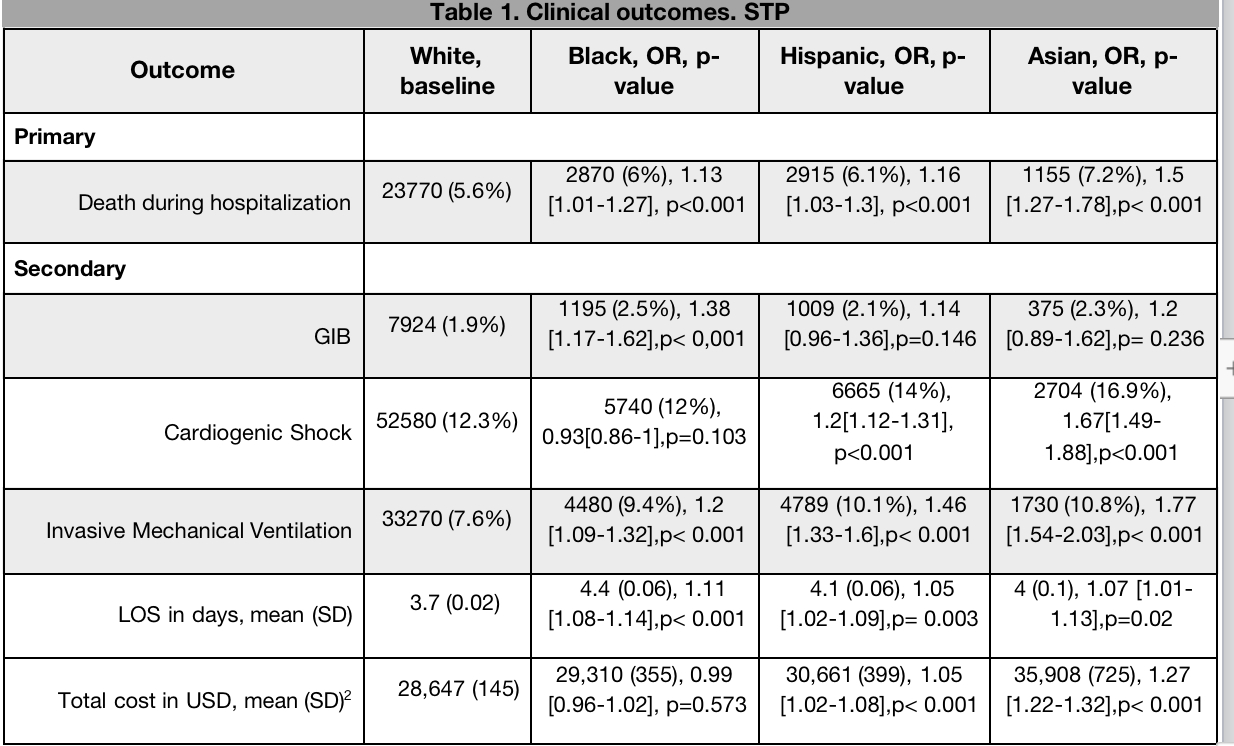
There were 582420 hospitalizations with STEMI with PCI. Mean age was 62 yrs and 71% were male. Among the admitted patients, Caucasians were 425064 (66.1%), Blacks were 47635(8.2%),Hispanics were 47555(8.2%), Asians were 16004(2.8%). . All-cause mortality in patients admitted with STEMI with PCI were 34090 where subgroup Analysis with Caucasians, Blacks ,Hispanics and Asians had 23700 (5.6%) vs 32870 (6%) vs 2915(6.1%) and 1155(7.2%) respectively.
Further subgroups analysis revealed that Asians (10.8%, aOR 1.77 CI 1.54-2.03,P value<0.001) were more likely to require intubation,followed by Hispanics(10.1% aOR 1.46 CI 1.33-1.6, p value <0.001) ,then Blacks (9.4% aOR 1.2,CI 1.09-1.32 P vale <0.001)and caucasians were least likely to require intubation(7.6% )
Finally, racial subgroup showed significant primary andsecondary outcomes that are presented in Table 1.
Conclusion
All obtained results revealed statistical significance and we considered Caucasian population as baseline. Mortality, intensive care services and resource utilization proportion was highest among Asian race followed by Hispanic race then by Black race. Understanding these disparities is essential for improving healthcare equity and ensuring that all patients receive appropriate and equitable care regardless of their racial or ethnic background.
Racial disparities in healthcare are a persistent and troubling issue, with profound implications for patient outcomes and societal well-being. Despite advances in medical science, studies consistently show that minority patients, particularly African Americans and Hispanics, face higher rates of STEMI incidence, delayed treatment, and poorer outcomes compared to their white counterparts.
Methods
we examined the national inpatient sample 2017-2020 for adult admitted with st segment myocardial infarction,we compared the clincal outcome of patients admitted with stemi with pci based on racial distribution.STATA 18th edition was used for analyses. Age, gender, race, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, and Elixhauser comorbidity index were identified as confounders by univariate analyses and tested further with multivariate logistic regression models. The primary outcome was mortality. Secondary outcomes were the need for intubation, cardiac arrest, length of stay (LOS), and total hospital charges.
Results
There were 582420 hospitalizations with STEMI with PCI. Mean age was 62 yrs and 71% were male. Among the admitted patients, Caucasians were 425064 (66.1%), Blacks were 47635(8.2%),Hispanics were 47555(8.2%), Asians were 16004(2.8%). . All-cause mortality in patients admitted with STEMI with PCI were 34090 where subgroup Analysis with Caucasians, Blacks ,Hispanics and Asians had 23700 (5.6%) vs 32870 (6%) vs 2915(6.1%) and 1155(7.2%) respectively.
Further subgroups analysis revealed that Asians (10.8%, aOR 1.77 CI 1.54-2.03,P value<0.001) were more likely to require intubation,followed by Hispanics(10.1% aOR 1.46 CI 1.33-1.6, p value <0.001) ,then Blacks (9.4% aOR 1.2,CI 1.09-1.32 P vale <0.001)and caucasians were least likely to require intubation(7.6% )
Finally, racial subgroup showed significant primary andsecondary outcomes that are presented in Table 1.
Conclusion
All obtained results revealed statistical significance and we considered Caucasian population as baseline. Mortality, intensive care services and resource utilization proportion was highest among Asian race followed by Hispanic race then by Black race. Understanding these disparities is essential for improving healthcare equity and ensuring that all patients receive appropriate and equitable care regardless of their racial or ethnic background.
More abstracts on this topic:
30-Day Outcomes of Dual vs Triple Antithrombotic Therapy After PCI
Meeks William, Slone Sarah, Barringhaus Kurt
Abbreviated Ticagrelor-Based Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisHarmouch Wissam, Elbadawi Ayman, Thakker Ravi, Khalid Umair, Khalife Wissam, Kleiman Neal, Rangasetty Umamahesh, Kayani Waleed, Jneid Hani, Al Hemyari Bashar