Final ID: 4142708
DIgital REgistry for CardiomeTabolic conditions – Diabetes Mellitus (DIRECT-DM): A Large, Pragmatic, Multisite, Diverse Longitudinal Registry of Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Despite the rising prevalence of T2DM, contemporary information on its longitudinal care and outcomes is limited and largely derived from small, self-selected cohorts. We describe the development and patterns of care of a digital pragmatic cohort of all T2DM patients seeking care in the multisite network of an integrated health system.
Methods: DIRECT-DM is a digital registry of T2DM patients seeking care across multiple hospitals and community practices in CT and RI from 2013 to 2023. From 223,932 individuals with T2DM, those with regular care (≥1 visit every 2 years) were included in the longitudinal cohort. Mortality was derived from the CT Death Index, healthcare resource utilization (HRU) was tracked across all care settings, and exposomic drivers of outcomes were linked via zip-code-based community and environmental characteristics, including data drawn from census, surveys, and air quality metrics. In this report, we describe the cohort’s characteristics, patterns of HRU, particularly in those with CV disease and factors associated with HRU using multivariate Poisson regression.
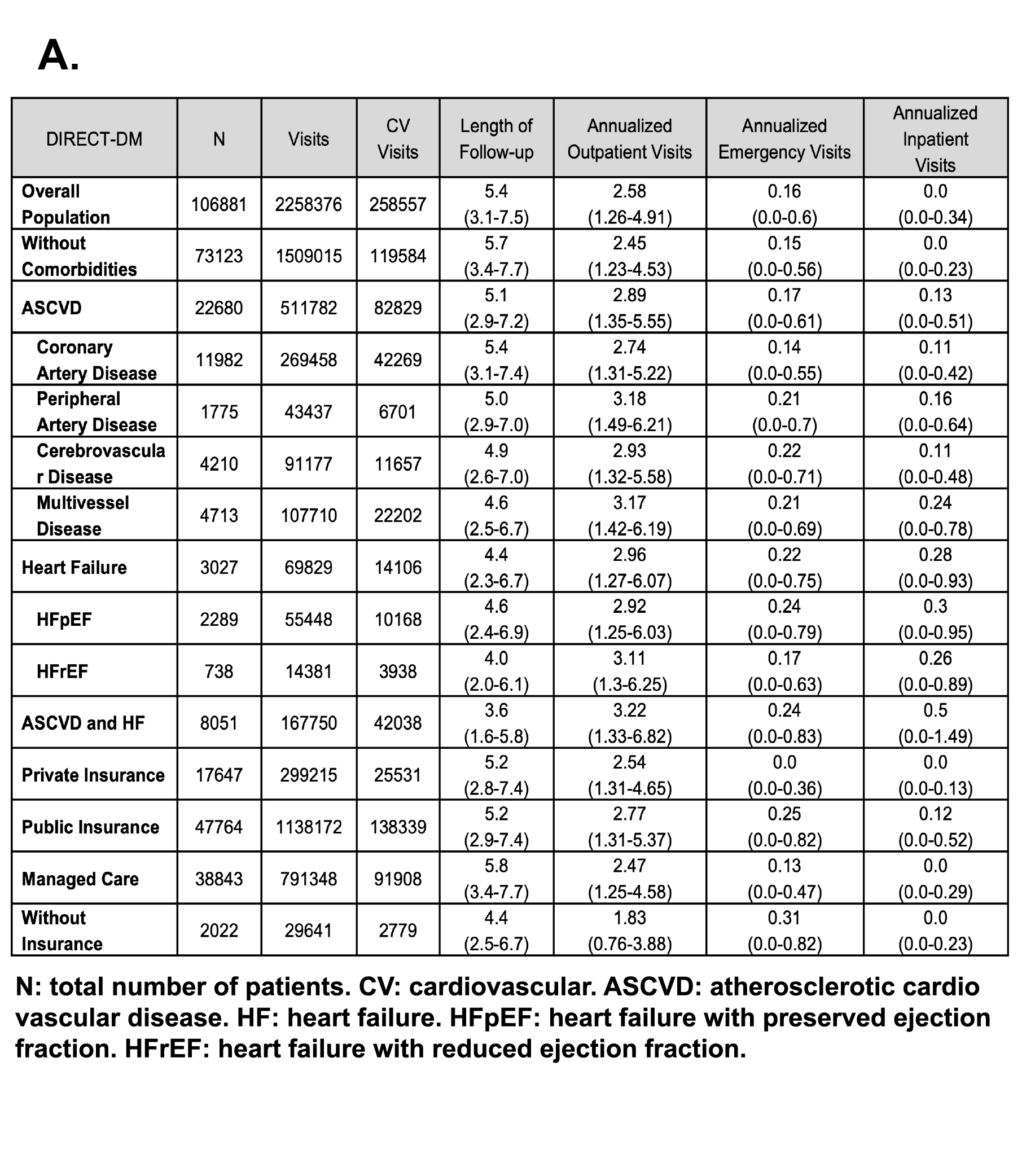
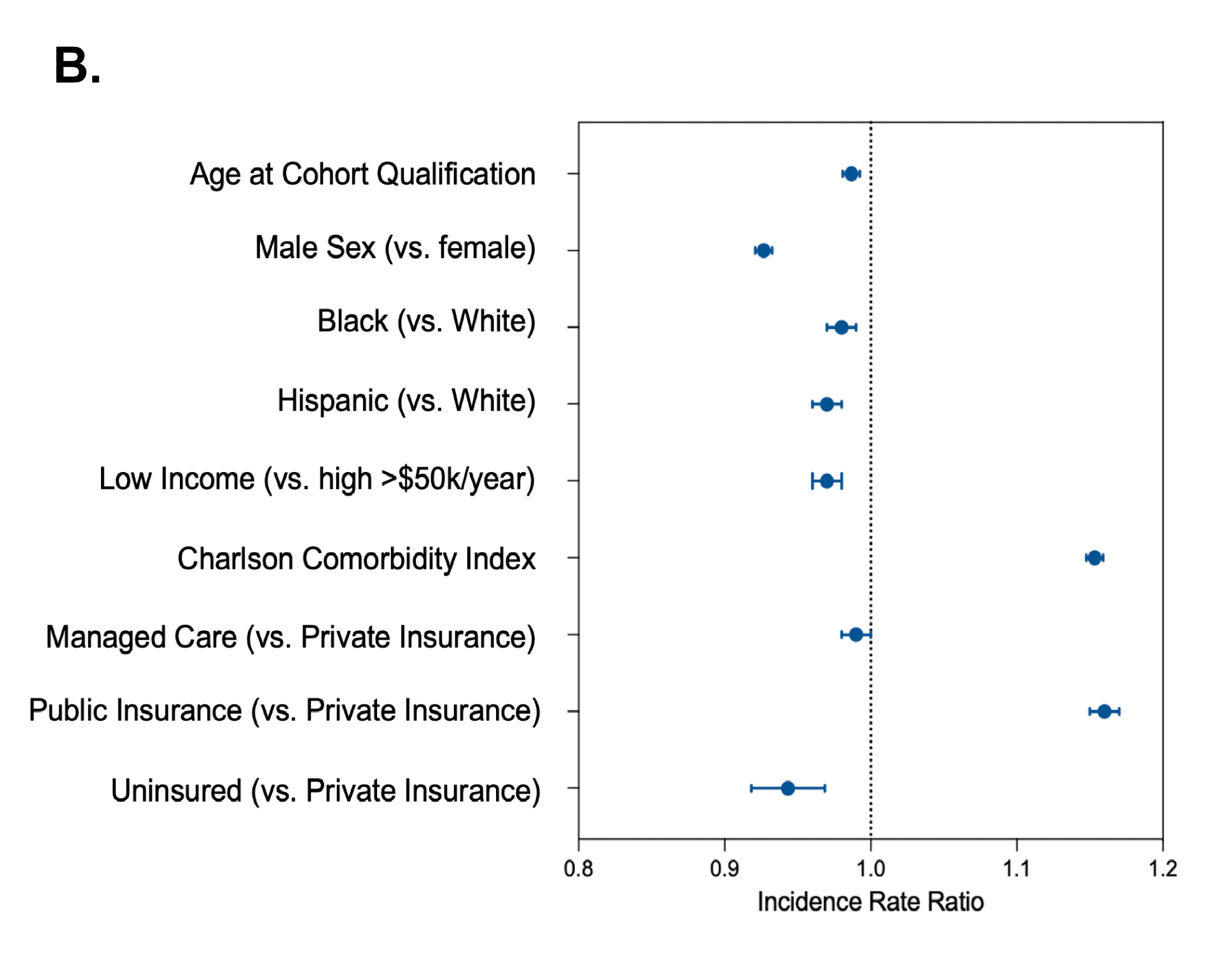
Results: DIRECT-DM included 106,881 T2DM individuals with a median age of 63 years (IQR 52-73), 50% women and 16% Black, who were followed for a median of 5.4 years (3.1-7.5), and 9% died. There were 2.3M healthcare visits, including 1.5M hospitalizations, 250K emergency department visits, and 1.9M outpatient visits with 11.4% of CV-related principal diagnoses. In the DIRECT-DM cohort, where 31.5% had established CV disease, the burden of HRU increased with the comorbidities burden, with those having CV disease experiencing the highest HRU (3.7 median visits/year for ASCVD [1.9-6.8] and 4.4 [2.2-8.0] for HF). However, for the same age, sex, and comorbidity profile, lack of health insurance (IRR 0.94; 0.92-0.97), low income (IRR 0.97; 0.96-0.98), and Black vs. White race (IRR 0.98; 0.98-0.99) were associated with lower HRU.
Conclusions: DIRECT-DM is a pragmatic T2DM registry in a diverse high-risk population, identifying key factors associated with HRU among T2DM patients. While there was an expected increased HRU in established CV disease, there was a lower-than-expected HRU among racially and socioeconomically disadvantaged populations.
Methods: DIRECT-DM is a digital registry of T2DM patients seeking care across multiple hospitals and community practices in CT and RI from 2013 to 2023. From 223,932 individuals with T2DM, those with regular care (≥1 visit every 2 years) were included in the longitudinal cohort. Mortality was derived from the CT Death Index, healthcare resource utilization (HRU) was tracked across all care settings, and exposomic drivers of outcomes were linked via zip-code-based community and environmental characteristics, including data drawn from census, surveys, and air quality metrics. In this report, we describe the cohort’s characteristics, patterns of HRU, particularly in those with CV disease and factors associated with HRU using multivariate Poisson regression.
Results: DIRECT-DM included 106,881 T2DM individuals with a median age of 63 years (IQR 52-73), 50% women and 16% Black, who were followed for a median of 5.4 years (3.1-7.5), and 9% died. There were 2.3M healthcare visits, including 1.5M hospitalizations, 250K emergency department visits, and 1.9M outpatient visits with 11.4% of CV-related principal diagnoses. In the DIRECT-DM cohort, where 31.5% had established CV disease, the burden of HRU increased with the comorbidities burden, with those having CV disease experiencing the highest HRU (3.7 median visits/year for ASCVD [1.9-6.8] and 4.4 [2.2-8.0] for HF). However, for the same age, sex, and comorbidity profile, lack of health insurance (IRR 0.94; 0.92-0.97), low income (IRR 0.97; 0.96-0.98), and Black vs. White race (IRR 0.98; 0.98-0.99) were associated with lower HRU.
Conclusions: DIRECT-DM is a pragmatic T2DM registry in a diverse high-risk population, identifying key factors associated with HRU among T2DM patients. While there was an expected increased HRU in established CV disease, there was a lower-than-expected HRU among racially and socioeconomically disadvantaged populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Hospital Shock Center Level with In-Hospital Outcomes in Cardiogenic Shock: An Analysis of the Nationwide Readmissions Database
Pawar Shubhadarshini, Bansal Kannu, Abbott J Dawn, Katz Jason, Dudzinski David, Van Diepen Sean, Solomon Michael, Ton Van-khue, Vallabhajosyula Saraschandra
A Contemporary Machine Learning-Based Risk Stratification for Mortality and Hospitalization in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Using Multimodal Real-World DataFudim Marat, Weerts Jerremy, Patel Manesh, Balu Suresh, Hintze Bradley, Torres Francisco, Micsinai Balan Mariann, Rigolli Marzia, Kessler Paul, Touzot Maxime, Lund Lars, Van Empel Vanessa, Pradhan Aruna, Butler Javed, Zehnder Tobias, Sauty Benoit, Esposito Christian, Balazard Félix, Mayer Imke, Hallal Mohammad, Loiseau Nicolas