Final ID: MDP75
Piezo2 channels expressed in cardiac ganglionated plexus modulate atrial fibrillation susceptibility
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:Pressure overload of the atria has been postulated to play a significant role in the development of atrial fibrillation. Piezo is a mechanosensitive channel protein and studies have revealed that piezo overexpressed in cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts can promote atrial fibrillation. However, whether pizeo is involved in cardiac ganglionated plexus and its role in atrial fibrillation remains unclear.
Hypothesis:The aim of this study is to investigate whether piezo is expressed in the cardiac ganglionated plexus and plays an important role in atrial fibrillation.
Methods:Cardiac ganglionated plexus were collected from 6 specimen with high left atrial pressure (high-LAP) or normal left atrial pressure (normal-LAP). Beagles were randomly allocated into sham group, AF group and piezo2-/- group. Atrial electrophysiological parameters, wov, left atrial pressure, neural function, neural activity and tissue of ganglionated plexus were detected.
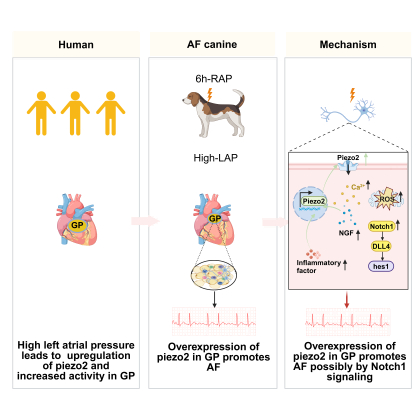
Results:Compared to the normal-LAP specimen, high-LAP resulted in an elevation of piezo2 in ganglionated plexus. RAP-induced increase in left atrial pressure promotes atrial fibrillation by overexpression of piezo2 increasing the function, activity, inflammation and oxidative stress levels of ganglionated plexus. Piezo2 -/- ameliorated atrial fibrillation susceptibility and showed a mild neuranagenesis. Moreover, notch signaling pathway maybe a significant mechanism.
Conclusions:Piezo2-mediated mechanical transduction promotes atrial fibrillation by increasing ganglionated plexus activity and facilitating nerve regeneration, possibly through notch signaling.
Hypothesis:The aim of this study is to investigate whether piezo is expressed in the cardiac ganglionated plexus and plays an important role in atrial fibrillation.
Methods:Cardiac ganglionated plexus were collected from 6 specimen with high left atrial pressure (high-LAP) or normal left atrial pressure (normal-LAP). Beagles were randomly allocated into sham group, AF group and piezo2-/- group. Atrial electrophysiological parameters, wov, left atrial pressure, neural function, neural activity and tissue of ganglionated plexus were detected.
Results:Compared to the normal-LAP specimen, high-LAP resulted in an elevation of piezo2 in ganglionated plexus. RAP-induced increase in left atrial pressure promotes atrial fibrillation by overexpression of piezo2 increasing the function, activity, inflammation and oxidative stress levels of ganglionated plexus. Piezo2 -/- ameliorated atrial fibrillation susceptibility and showed a mild neuranagenesis. Moreover, notch signaling pathway maybe a significant mechanism.
Conclusions:Piezo2-mediated mechanical transduction promotes atrial fibrillation by increasing ganglionated plexus activity and facilitating nerve regeneration, possibly through notch signaling.
More abstracts on this topic:
Beyond the Cuff: Diagnosing Baroreceptor Failure After Head and Neck Radiation
A Large Animal Model of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Khan Aarish Husain, Parekh Vinit, Safdar Nawaz, Khan Sabir, Norris Robert B, Kohut Andrew
A Large Animal Model of Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
Mostafizi Pouria, Goldman Steven, Moukabary Talal, Lefkowitz Eli, Ref Jacob, Daugherty Sherry, Grijalva Adrian, Cook Kyle Eric, Chinyere Ike, Lancaster Jordan, Koevary Jen