Final ID: Sa1046
The Lack of Sphingosine Kinase 1 in Smooth Muscle Cells Protects Mice Against Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: The function of the cardiovascular system is regulated by sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) signaling. Vascular sphingosine kinase 1 (Sphk1), an S1P-producing enzyme, is upregulated in hypertension (HTN), and mice lacking Sphk1 globally exhibit alleviated AngII-induced HTN. Identifying cellular mechanisms providing this protection remains challenging due to the pleiotropic action of S1P.
Aim: To identify the contributions of Sphk1 within endothelial cells (ECs) or vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) to the blood pressure-lowering effect of global Sphk1 deletion in mice.
Methods: Mice lacking Sphk1 either in SMCs or ECs were generated using the Cre-loxP system. Male mice were infused with AngII (490 ng/min/kg for 14 days), using osmotic minipumps, to induce HTN. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) was monitored, and vascular structure and function were examined ex vivo using wire/pressure myography and histological analysis. To identify key mechanistic pathways, RNA Sequencing was performed in mouse aortas and mesenteric arteries, followed by Gene set enrichment analysis. The expression patterns of the identified genes were confirmed by RT-qPCR and Western Blotting in mouse arteries and human internal mammary arteries (IMAs).
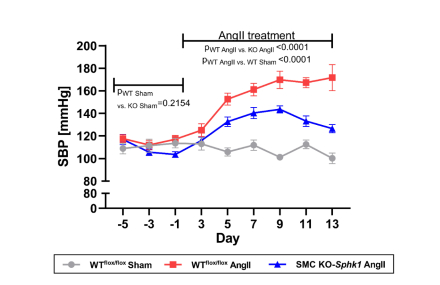
Results: The lack of Sphk1 in SMC conferred significant protection against HTN (mean SBP±SD 132±14.6 mmHg vs. 168±14.3 mmHg as compared to WTflox/flox control, p<0.05, Fig. 1), while EC KO-Sphk1 developed HTN to the same extent as WTflox/flox controls (mean SBP±SD: 166±22.8 mmHg vs. 171±27.7 mmHg respectively). Lower SBP in SMC KO-Sphk1 in HTN was associated with a significantly reduced myogenic tone of mesenteric arteries and lower expression of Rock1/2. In spite of impaired HTN development, mesenteric arteries of AngII-infused SMC KO-Sphk1 mice were significantly stiffer and showed impaired vasorelaxations compared to the control arteries of AngII-infused WT mice, which was associated with excessive fibronectin 1 deposition. Likewise, an inverse correlation between FN1 and SPHK1 protein expression was observed in human IMAs.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate a prevailing role of SMC-derived Sphk1 in the regulation of myogenic tone as an important molecular regulator of AngII-induced HTN.
Aim: To identify the contributions of Sphk1 within endothelial cells (ECs) or vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) to the blood pressure-lowering effect of global Sphk1 deletion in mice.
Methods: Mice lacking Sphk1 either in SMCs or ECs were generated using the Cre-loxP system. Male mice were infused with AngII (490 ng/min/kg for 14 days), using osmotic minipumps, to induce HTN. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) was monitored, and vascular structure and function were examined ex vivo using wire/pressure myography and histological analysis. To identify key mechanistic pathways, RNA Sequencing was performed in mouse aortas and mesenteric arteries, followed by Gene set enrichment analysis. The expression patterns of the identified genes were confirmed by RT-qPCR and Western Blotting in mouse arteries and human internal mammary arteries (IMAs).
Results: The lack of Sphk1 in SMC conferred significant protection against HTN (mean SBP±SD 132±14.6 mmHg vs. 168±14.3 mmHg as compared to WTflox/flox control, p<0.05, Fig. 1), while EC KO-Sphk1 developed HTN to the same extent as WTflox/flox controls (mean SBP±SD: 166±22.8 mmHg vs. 171±27.7 mmHg respectively). Lower SBP in SMC KO-Sphk1 in HTN was associated with a significantly reduced myogenic tone of mesenteric arteries and lower expression of Rock1/2. In spite of impaired HTN development, mesenteric arteries of AngII-infused SMC KO-Sphk1 mice were significantly stiffer and showed impaired vasorelaxations compared to the control arteries of AngII-infused WT mice, which was associated with excessive fibronectin 1 deposition. Likewise, an inverse correlation between FN1 and SPHK1 protein expression was observed in human IMAs.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate a prevailing role of SMC-derived Sphk1 in the regulation of myogenic tone as an important molecular regulator of AngII-induced HTN.
More abstracts on this topic:
Follistatin Improves Vascular Function by Regulating Perivascular Adipose Tissue in Essential Hypertension
Kuganathan Ann, Lu Vincent, Gao Bo, Macdonald Melissa, Dickhout Jeffrey, Krepinsky Joan
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 Mediates TGF-β-induced Smooth Muscle Cell DifferentiationGuo Xia, Olajuyin Ayobami, Mandlem Venkata Kiran Kumar, Sunil Christudas, Hou Yunzhuan, Adeyanju Oluwaseun, Petkar Sana, Qian Guoqing