Final ID: MDP1124
The impact of the stress hyperglycemia ratio on adverse prognosis in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background Risk assessment for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) remain challenging. Stress hyperglycemia represents the regulation of glucose metabolism in response to stress. Meanwhile, stress hyperglycemia ratio (SHR) is recently found to reflect true acute hyperglycemic status. However, the relationship between SHR and adverse prognosis is uncertain. This study aimed to investigate the prognostic value of SHR in CTEPH patients.
Methods A total of 451 CTEPH patients with available baseline SHR measurement were enrolled between February 2014 to July 2023 at Fuwai hospital. The predictive values of SHR for adverse events were assessed.
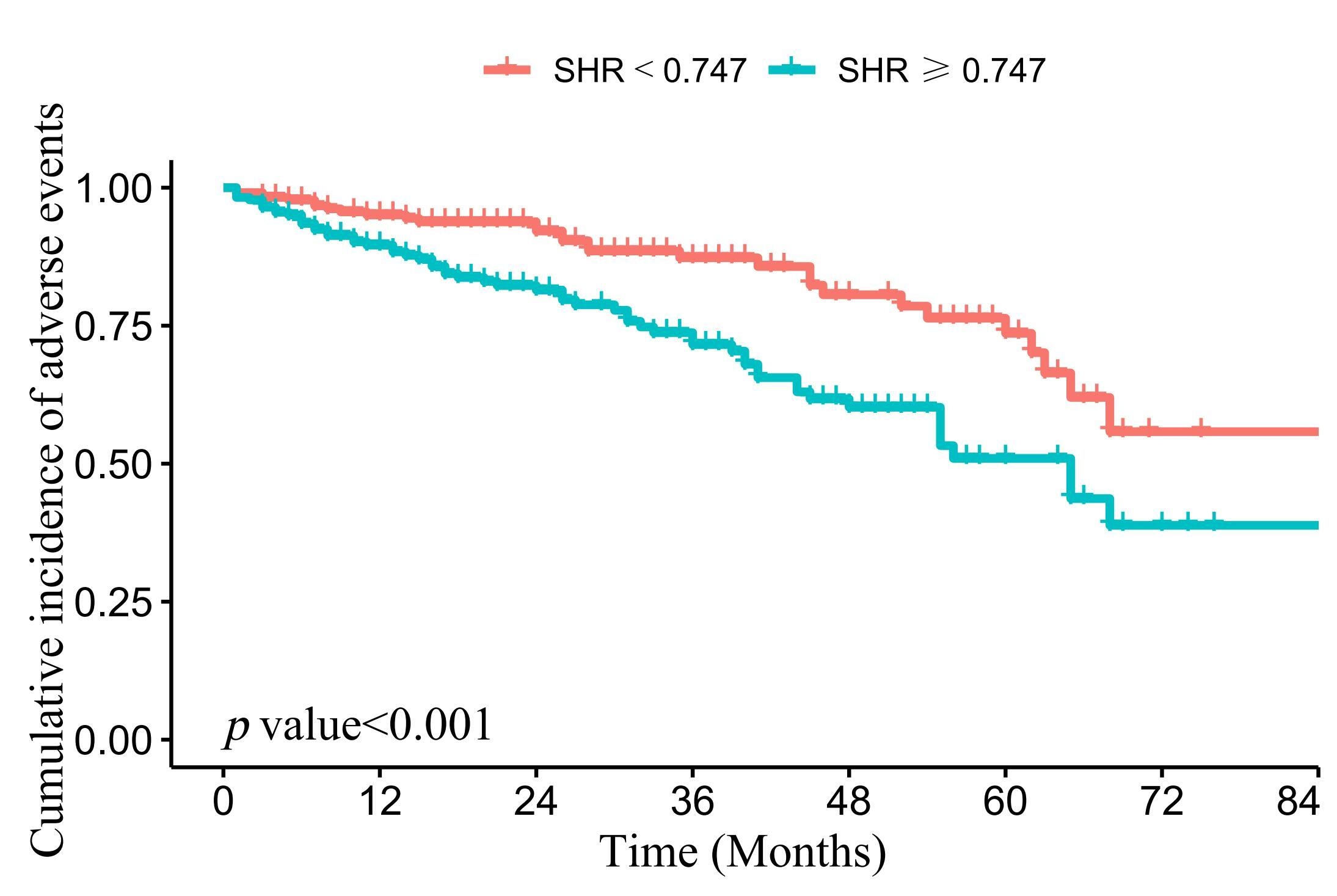
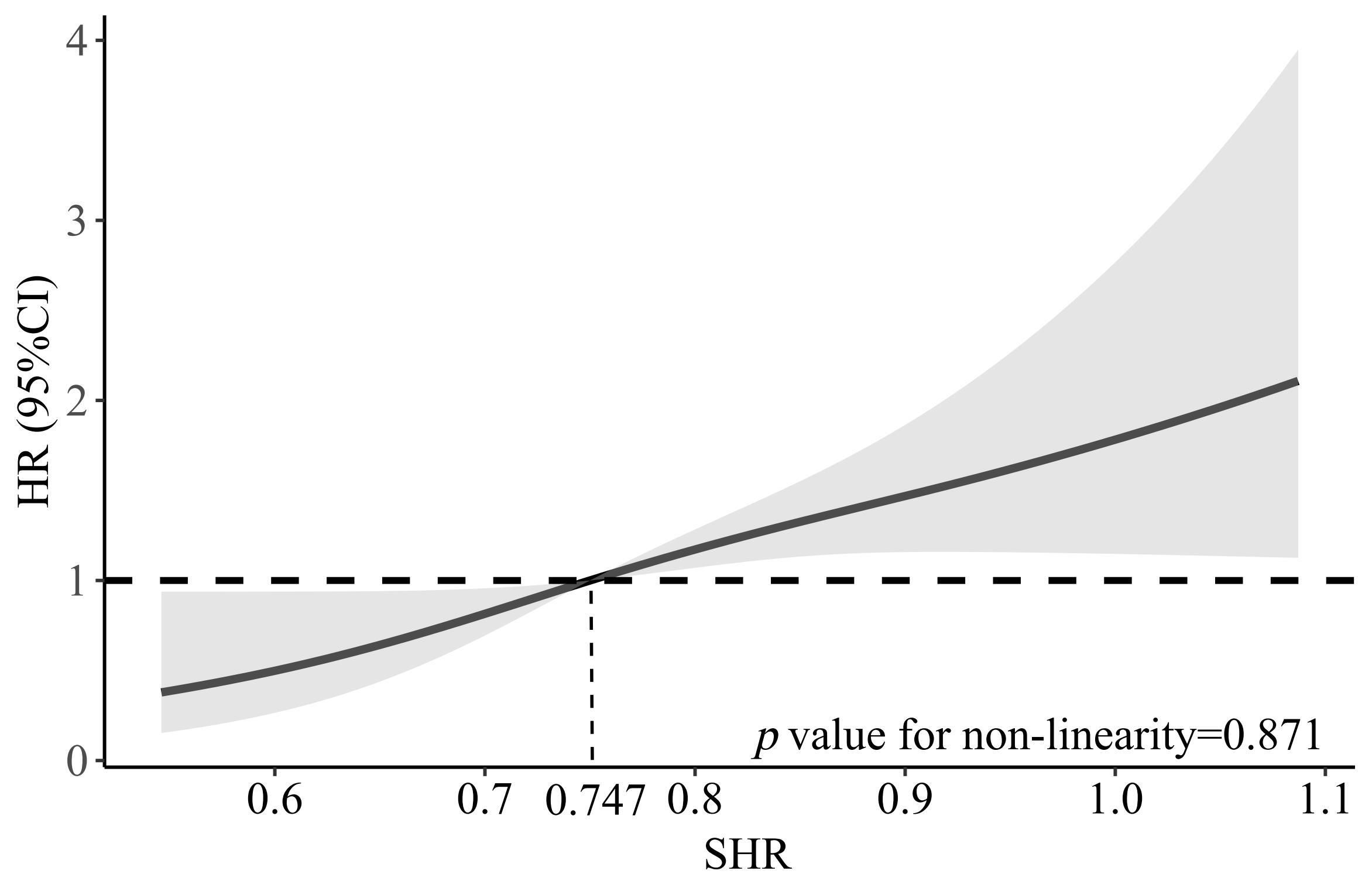
Results During a median follow-up of 21 months, 89 (19.7%) CTEPH patients experienced adverse clinical outcomes. Kaplan-Meier curve analysis revealed that the cumulative adverse event rates were significant higher in the SHR≥0.747 with CTEPH patients, compared with patients in the SHR<0.747. The multivariable analysis revealed that high level of SHR, whether as a continuous variable or categorical variable, were independent risk factor for adverse events after adjusting various confounding factors. Restricted cubic spline also revealed a correlation between SHR and the risk of adverse events after adjusted clinical risk factors (p value for non-linearity=0.871). Furthermore, when incorporating SHR into the baseline risk model, a significant improvement in the predictive ability for adverse prognosis was noted in CTEPH patients, as evidenced by the C-statistic rising from 0.690 to 0.711 (p value=0.037). Significant enhancements in continuous net reclassification improvement, and integrated discrimination improvement were also observed as a result of incorporating the SHR into the baseline risk model (p value <0.05).
Conclusions The high level of SHR was independently associated with long-term adverse prognosis risk in CTEPH patients. The integration of SHR into the baseline risk model may have improved the accuracy in predicting the risk of adverse prognosis. Our findings support the utility of SHR as a reliable indicator for clinical outcome risk stratification of CTEPH patients in the real world. Further research is needed to explore whether interventions targeting SHR can improve the clinical outcomes for patients with CTEPH.
Methods A total of 451 CTEPH patients with available baseline SHR measurement were enrolled between February 2014 to July 2023 at Fuwai hospital. The predictive values of SHR for adverse events were assessed.
Results During a median follow-up of 21 months, 89 (19.7%) CTEPH patients experienced adverse clinical outcomes. Kaplan-Meier curve analysis revealed that the cumulative adverse event rates were significant higher in the SHR≥0.747 with CTEPH patients, compared with patients in the SHR<0.747. The multivariable analysis revealed that high level of SHR, whether as a continuous variable or categorical variable, were independent risk factor for adverse events after adjusting various confounding factors. Restricted cubic spline also revealed a correlation between SHR and the risk of adverse events after adjusted clinical risk factors (p value for non-linearity=0.871). Furthermore, when incorporating SHR into the baseline risk model, a significant improvement in the predictive ability for adverse prognosis was noted in CTEPH patients, as evidenced by the C-statistic rising from 0.690 to 0.711 (p value=0.037). Significant enhancements in continuous net reclassification improvement, and integrated discrimination improvement were also observed as a result of incorporating the SHR into the baseline risk model (p value <0.05).
Conclusions The high level of SHR was independently associated with long-term adverse prognosis risk in CTEPH patients. The integration of SHR into the baseline risk model may have improved the accuracy in predicting the risk of adverse prognosis. Our findings support the utility of SHR as a reliable indicator for clinical outcome risk stratification of CTEPH patients in the real world. Further research is needed to explore whether interventions targeting SHR can improve the clinical outcomes for patients with CTEPH.
More abstracts on this topic:
A single-cell atlas of the human PAH lung identifies ITGA9 as a candidate regulator of fibroblast activation and vascular remodeling
Brownstein Adam, Wong Brenda, Graves Tammy, Aldred Micheala, Dai Zhiyu, Yang Xia, Eghbali Mansoureh, Hong Jason
Age-stratified Monogenic and Polygenic Contributions for Atrial Fibrillation in the All of Us Research ProgramChen Zhanlin, Gordon Adam, Webster Gregory