Final ID: MDP985
Association of smoking status with incident heart failure among patients with chronic kidney disease: Insights from CRIC
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Smoking is a well-known risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and kidney failure among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). However, the association of former and current smoking status (vs. never) with incident heart failure (HF) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) among patients with CKD warrants further exploration.
Methods
Using data from participants of the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort, without a history of HF, we used Cox regression models to estimate the association of smoking status (never, former, current) with incident HF. We also fit linear regression models to explore the association of smoking status with log-transformed NT-proBNP. Models were adjusted for demographics, comorbid disease, medications, systolic blood pressure, and socioeconomic variables (including income, education, marital status, illicit drug use, and alcohol use).
Results
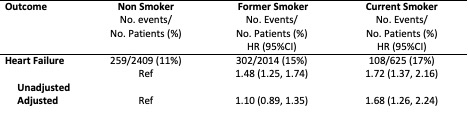
Of the 5,083 included participants, 2,423 (48%) were never smokers, 2,030 (40%) were former smokers, and 630 (12%) were current smokers. Over a median follow-up of 6.7 years, there were 664 HF events. In adjusted analyses, compared with never smokers, the risk for future HF events was non-significantly higher for former smokers (HR 1.10; 0.89, 1.35), but significantly higher for current smokers (HR 1.68; 95%CI 1.26, 2.24; Table 1). Similarly, compared with never smoking, former smoking was non-significantly associated with NT-proBNP (-3%; 95%CI -12, +6%), while current smoking was associated with higher NT-proBNP (+24%; 95%CI +9%, +42%).
Conclusion
Current smoking status, but not former smoking, is associated with higher NT-proBNP and a higher risk of incident heart failure among patients with CKD. Enhanced public health efforts to promote smoking cessation among patients with CKD may be relevant to prevention of HF.
Smoking is a well-known risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and kidney failure among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). However, the association of former and current smoking status (vs. never) with incident heart failure (HF) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) among patients with CKD warrants further exploration.
Methods
Using data from participants of the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort, without a history of HF, we used Cox regression models to estimate the association of smoking status (never, former, current) with incident HF. We also fit linear regression models to explore the association of smoking status with log-transformed NT-proBNP. Models were adjusted for demographics, comorbid disease, medications, systolic blood pressure, and socioeconomic variables (including income, education, marital status, illicit drug use, and alcohol use).
Results
Of the 5,083 included participants, 2,423 (48%) were never smokers, 2,030 (40%) were former smokers, and 630 (12%) were current smokers. Over a median follow-up of 6.7 years, there were 664 HF events. In adjusted analyses, compared with never smokers, the risk for future HF events was non-significantly higher for former smokers (HR 1.10; 0.89, 1.35), but significantly higher for current smokers (HR 1.68; 95%CI 1.26, 2.24; Table 1). Similarly, compared with never smoking, former smoking was non-significantly associated with NT-proBNP (-3%; 95%CI -12, +6%), while current smoking was associated with higher NT-proBNP (+24%; 95%CI +9%, +42%).
Conclusion
Current smoking status, but not former smoking, is associated with higher NT-proBNP and a higher risk of incident heart failure among patients with CKD. Enhanced public health efforts to promote smoking cessation among patients with CKD may be relevant to prevention of HF.
More abstracts on this topic:
Associations Between Smoking Status and Sleep Health among South Korean Adolescents
__PRESENT
Cho Nagyeong, Cho Sung-il
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and Cardiovascular Health: Future of Families and Child Wellbeing Study (FFCWS)__PRESENT
Pedamallu Havisha, Van Horn Linda, Stein James, Korcarz Claudia, Hansen Kristin, Mitchell Colter, Heard-garris Nia, Lloyd-jones Donald, Allen Norrina, Gauen Abigail, Ning Hongyan, Wilkins John, Goldman Noreen, Notterman Daniel, Hou Lifang, Zheng Yinan, Marma Amanda