Final ID: MDP4
Lipoprotein Apheresis improves HDL Proteomics and reduces the risk of Aortic Stenosis in patients with elevated Lipoprotein(a) levels and Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The prevalence of calcific valve stenosis (CAVS) in familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is 30-40%. Eleveated Lp(a) levels independently promotes faster progression of CAVS. Low HDL particles (HDL-P), increase apoC3 and serum amyloid A (SAA)-bound HDL are associated with long-term incidence and progression of CAVS.
Aim: Dextran-sulfate-adsorption lipoprotein-apheresis (LA), the only LA device available in the United States, reduces LDL-C and Lp(a) by an average of 60%-80% via binding positive-charged apolipoprotein B to a negative-changed environment. Despite the negative charge of HDL-C, it is acutely reduced by 10%-20%. However, the total HDL-P number, as measured by nuclear magnetic resonance testing, is increased by an average of 16% following LA therapy. We hypothesized that regular LA may improve cardiovascular outcomes and slow the progression of CAVS via its effects on HDL functionality and Lp(a) levels.
Methods: This case series describes 39 Caucasian patients (mean age 61 years, 70% female, 80% statin intolerant) with FH and/or elevated Lp(a) (Liposorber LA-15, Kaneka) over a mean treatment period of 4.8 years, as compared to an average of 5.3 years pre-treatment. Pre-treatment LDL-C and Lp(a) levels were 144 mg/dL (range, 35-314) and 167 nmol/L (range 2-530). HDL proteomic analysis was performed to identify numerous proteins and lipids segregated into distinct subclasses. Major adverse cardiovascular events were defined as: MI=myocardial event, PCI=percutaneous cornary intervention, CABG=coronary artery bypass surgery, TIA=transient ischemic attack, CAVS=calcific artic stenosis.
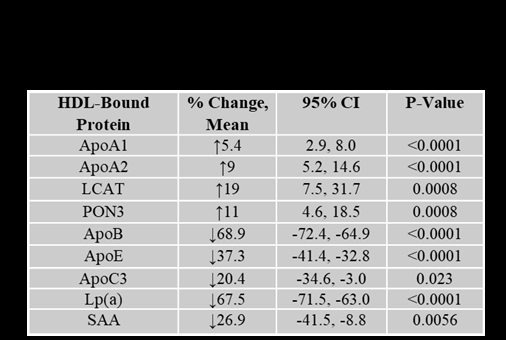
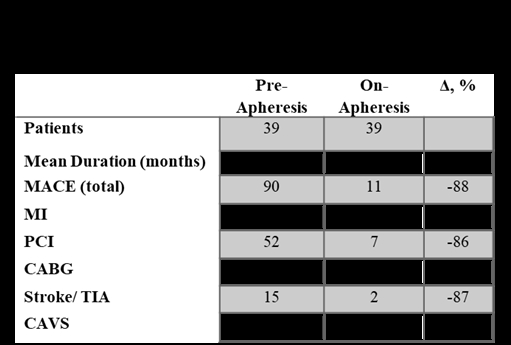
Results: LA therapy reduced mean LDL-C to an average of 40 mg/dL and Lp(a) to 24nmol/L, while total HDL-C was lowered by 14%. Extra small and small-sized HDL-P was reduced by 42% and 20%, respectively (P<0.001). Medium-sized HDL-P increased by 12% (P<0.001). We observed significant modifications in the HDL-bound proteins (Table 1). There was an 88% reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events, with no patient developing CAVS (Table 2).
Conclusions: In patients with FH and/or elevated Lp(a) with established ASCVD, LA effectively lowered the incidence rate of cardiovascular events. LA selectively reduced pro-inflammatory apoC3- and SAA-bound HDL and increased HDL-P, potentially explaining the lack of development and progression of CAVS in patients with elevated Lp(a). This observation merits further investigation with a dedicated controlled clinical study.
Aim: Dextran-sulfate-adsorption lipoprotein-apheresis (LA), the only LA device available in the United States, reduces LDL-C and Lp(a) by an average of 60%-80% via binding positive-charged apolipoprotein B to a negative-changed environment. Despite the negative charge of HDL-C, it is acutely reduced by 10%-20%. However, the total HDL-P number, as measured by nuclear magnetic resonance testing, is increased by an average of 16% following LA therapy. We hypothesized that regular LA may improve cardiovascular outcomes and slow the progression of CAVS via its effects on HDL functionality and Lp(a) levels.
Methods: This case series describes 39 Caucasian patients (mean age 61 years, 70% female, 80% statin intolerant) with FH and/or elevated Lp(a) (Liposorber LA-15, Kaneka) over a mean treatment period of 4.8 years, as compared to an average of 5.3 years pre-treatment. Pre-treatment LDL-C and Lp(a) levels were 144 mg/dL (range, 35-314) and 167 nmol/L (range 2-530). HDL proteomic analysis was performed to identify numerous proteins and lipids segregated into distinct subclasses. Major adverse cardiovascular events were defined as: MI=myocardial event, PCI=percutaneous cornary intervention, CABG=coronary artery bypass surgery, TIA=transient ischemic attack, CAVS=calcific artic stenosis.
Results: LA therapy reduced mean LDL-C to an average of 40 mg/dL and Lp(a) to 24nmol/L, while total HDL-C was lowered by 14%. Extra small and small-sized HDL-P was reduced by 42% and 20%, respectively (P<0.001). Medium-sized HDL-P increased by 12% (P<0.001). We observed significant modifications in the HDL-bound proteins (Table 1). There was an 88% reduction in major adverse cardiovascular events, with no patient developing CAVS (Table 2).
Conclusions: In patients with FH and/or elevated Lp(a) with established ASCVD, LA effectively lowered the incidence rate of cardiovascular events. LA selectively reduced pro-inflammatory apoC3- and SAA-bound HDL and increased HDL-P, potentially explaining the lack of development and progression of CAVS in patients with elevated Lp(a). This observation merits further investigation with a dedicated controlled clinical study.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Elevated Serum Lipoprotein(a) with New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Study of 108930 Patients
Kamel Moaz, Arsanjani Reza, Awad Kamal, Mahmoud Ahmed K., Farina Juan, Scalia Isabel, Pereyra Milagros, Abbas Mohammed Tiseer, Baba Nima, Ayoub Chadi
Association of Elevated Lipoprotein(a) Levels with Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Stable Angina Undergoing Stent-less PCI with Paclitaxel-coated BalloonTakahashi Tomonori, Yamaguchi Koji, Yagi Shusuke, Yamada Hirotsugu, Soeki Takeshi, Sata Masataka, Wakatsuki Tetsuzo, Saijo Yoshihiro, Kawabata Yutaka, Ueno Rie, Kadota Muneyuki, Hara Tomoya, Matsuura Tomomi, Ise Takayuki