Final ID: Sa2089
Pathophysiological evidence for abnormal P-wave terminal force reflects atrial myopathy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Although P-wave terminal force (PWTF), a marker of atrial myopathy, has been implicated in predicting incident atrial fibrillation (AF) and ischemic stroke, its pathophysiological mechanisms remain unclear. This study investigates the association between abnormal PWTF and atrial myopathy, diastolic function, epicardial adipose tissue (EAT), or AF recurrence following AF catheter ablation (AFCA).
Methods: We included 3,528 AF patients (59.7 (10.8) years, 28.8% female, 64.2% paroxysmal AF) who underwent AFCA with baseline and 1-year follow-up echocardiograms. We evaluated the characteristics of the patients with abnormal PWTF (≥4000 μV × ms) and its association with clinical, hemodynamical, and imaging parameters.
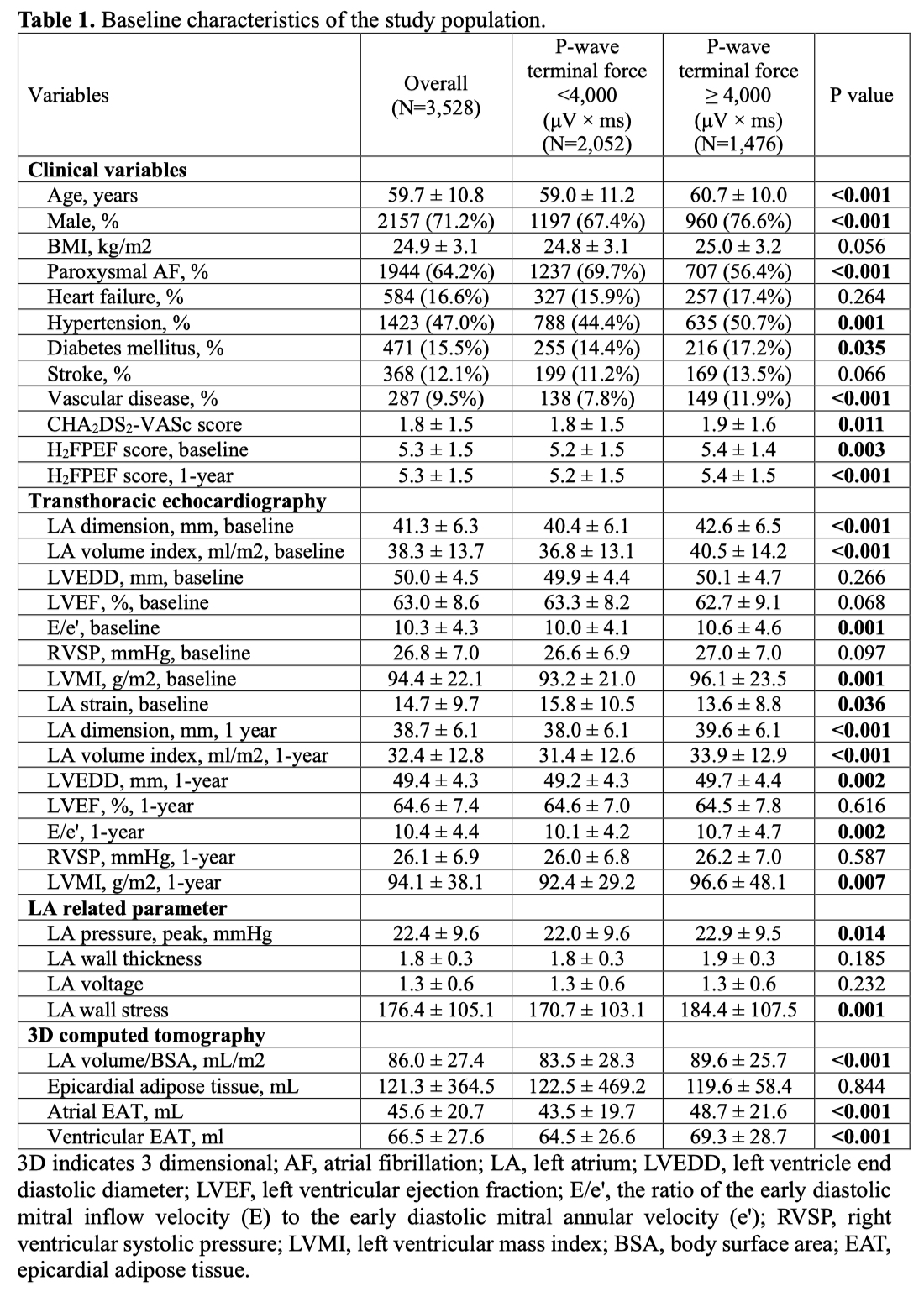
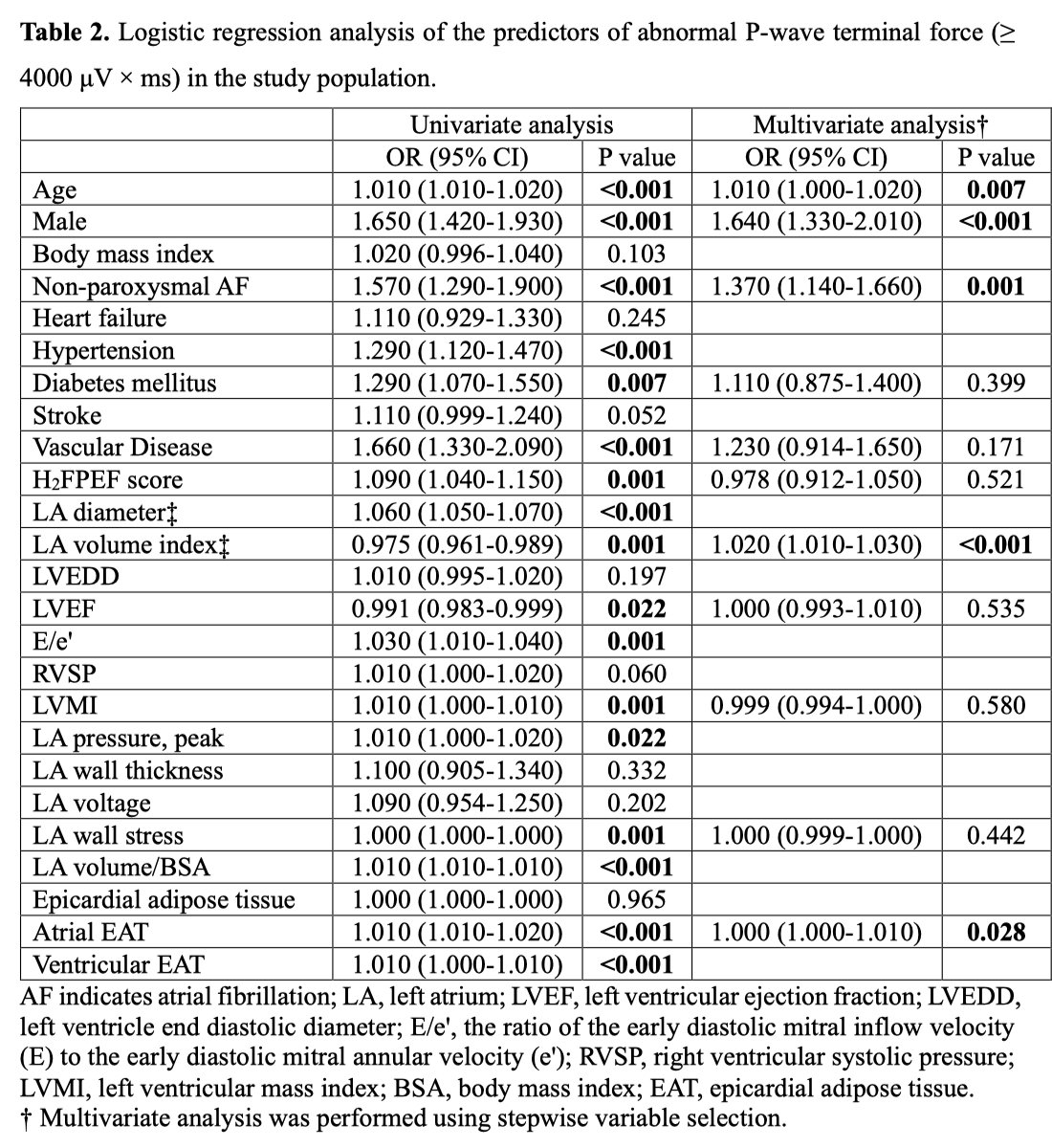
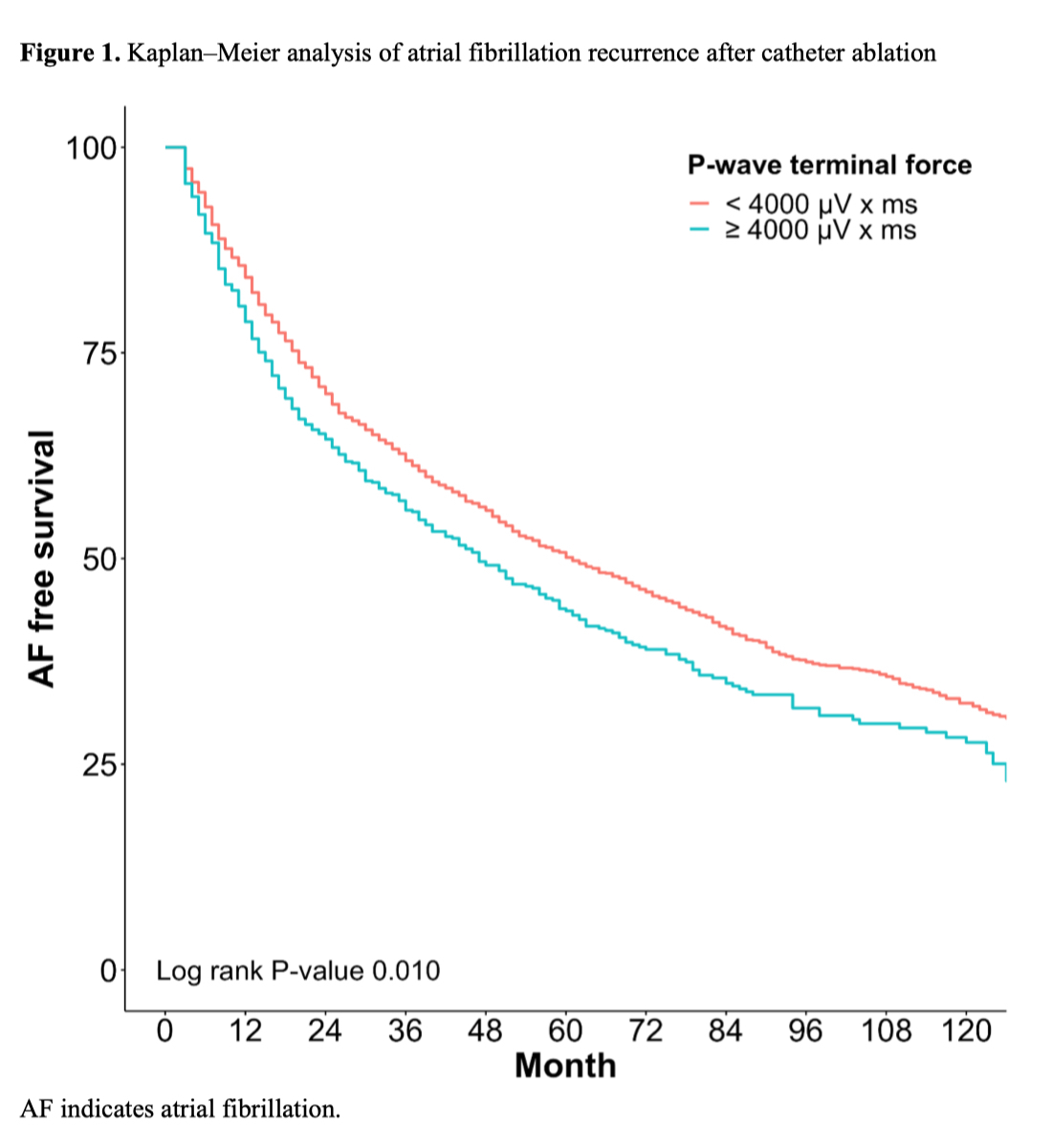
Result: Patients with AF and abnormal PWTF (≥4000 μV × ms) were older (p=0.001) and had higher proportions of male (p<0.001) and non-paroxysmal AF (p<0.001), higher CHA2DS2-VASc (p=0.011), H2FPEF scores (p=0.003), higher left atrial (LA) dimension (p<0.001), left ventricular mass index (p=0.001), LA pressure (n=3,067, p=0.014), and atrial EAT volume (p<0.001), and lower LA strain (n=368, p=0.036) than their counterpart. The patients with abnormal PWTF were independently associated with age (OR 1.01 [1.00-1.02], p=0.007), male gender (OR 1.64 [1.33-2.01], p<0.001), non-paroxysmal AF (OR 1.37 [1.14-1.66], p=0.001), LA volume index (OR 1.02 [1.01-1.03], p<0.001), or atrial EAT volume (OR 1.00 [1.00-1.01], p=0.028). Among 2,929 patients who did not recur within a year, PWTF was an independent predictor of blunted LA reverse remodeling a year after AFCA (OR 0.97 [0.94-0.99], p=0.029). During a median follow-up of 31 (interquartile range 15–61) month, patients with abnormal PWTF demonstrated a significantly higher AF recurrence (log-rank p=0.010; HR 1.14 [1.04-1.25], p=0.008).
Conclusion: Abnormal PWTF is associated with a blunted LA reverse remodeling, atrial EAT volume, and an increased risk of AF recurrence following catheter ablation and is indicative of LA myopathy.
Methods: We included 3,528 AF patients (59.7 (10.8) years, 28.8% female, 64.2% paroxysmal AF) who underwent AFCA with baseline and 1-year follow-up echocardiograms. We evaluated the characteristics of the patients with abnormal PWTF (≥4000 μV × ms) and its association with clinical, hemodynamical, and imaging parameters.
Result: Patients with AF and abnormal PWTF (≥4000 μV × ms) were older (p=0.001) and had higher proportions of male (p<0.001) and non-paroxysmal AF (p<0.001), higher CHA2DS2-VASc (p=0.011), H2FPEF scores (p=0.003), higher left atrial (LA) dimension (p<0.001), left ventricular mass index (p=0.001), LA pressure (n=3,067, p=0.014), and atrial EAT volume (p<0.001), and lower LA strain (n=368, p=0.036) than their counterpart. The patients with abnormal PWTF were independently associated with age (OR 1.01 [1.00-1.02], p=0.007), male gender (OR 1.64 [1.33-2.01], p<0.001), non-paroxysmal AF (OR 1.37 [1.14-1.66], p=0.001), LA volume index (OR 1.02 [1.01-1.03], p<0.001), or atrial EAT volume (OR 1.00 [1.00-1.01], p=0.028). Among 2,929 patients who did not recur within a year, PWTF was an independent predictor of blunted LA reverse remodeling a year after AFCA (OR 0.97 [0.94-0.99], p=0.029). During a median follow-up of 31 (interquartile range 15–61) month, patients with abnormal PWTF demonstrated a significantly higher AF recurrence (log-rank p=0.010; HR 1.14 [1.04-1.25], p=0.008).
Conclusion: Abnormal PWTF is associated with a blunted LA reverse remodeling, atrial EAT volume, and an increased risk of AF recurrence following catheter ablation and is indicative of LA myopathy.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case Report of Cardiac Tamponade due to Mycoplasma Pneumoniae-induced Pericarditis - A Rare Complication of a Commonly seen Bacterial Infection
Patel Vidhi, Maharjan Reeju, Okan Tetyana, Singh Bhupinder, Colasacco Joseph
A Chemogenetic Tool for In Vivo Control of Electromechanical Activity of hiPSC-Derived CardiomyocytesPatino Guerrero Alejandra, Zhu Wuqiang