Final ID: TP198
Alpha-Delta Ratio as an Acute Marker of Intracerebral Hemorrhage on Sub-galeal EEG
Abstract Body: Background
Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) remains one of the most devastating forms of stroke, leaving many patients unresponsive with disorders of consciousness. However, there remain few options for continuous brain monitoring for ICH. While EEG markers such as decreased alpha-delta power ratio may indicate ischemic stroke, similar EEG markers of ICH have yet to be explored. Sub-galeal EEG is a promising method for robust continuous brain monitoring, which may have relevance for detecting new ischemic or hemorrhagic events in ICH patients. We therefore aimed to evaluate electrophysiologic features of ICH on sub-galeal EEG.
Methods
Consecutive patients at one center with ICH who underwent minimally-invasive surgical ICH evacuation received bilateral sub-galeal EEG for continuous brain monitoring. To explore markers of ICH, electrophysiologic features on sub-galeal EEG were compared between hemorrhagic and non-hemorrhagic hemispheres.
Results
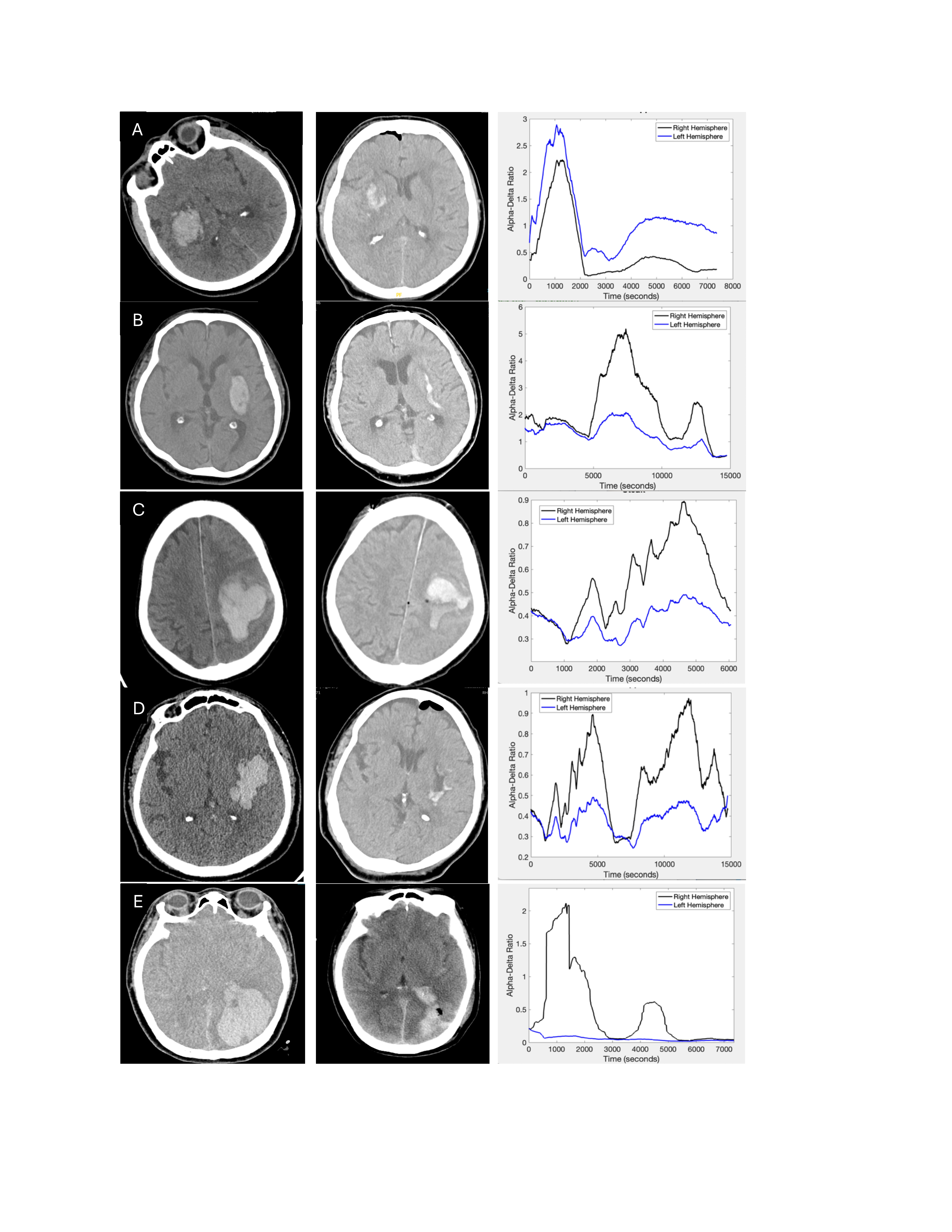
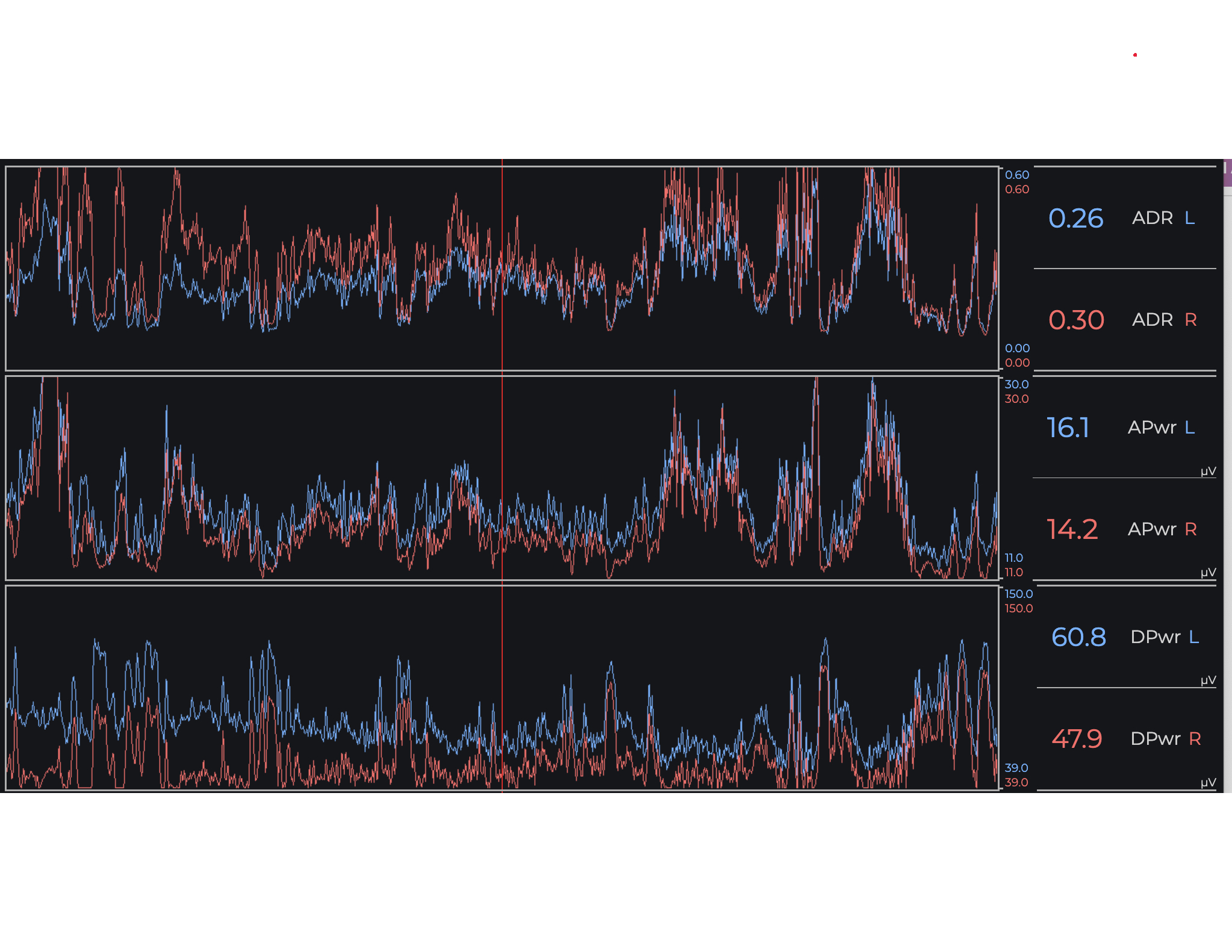
Six patients with ICH who underwent minimally-invasive surgical evacuation were implanted with sub-galeal EEG intraoperatively. Patient age was on average 66.0±7.5 years, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale at presentation was 19.6±4.0, and ICH volume was 54.0±42.4mL. In five patients, significant reductions in alpha-delta power ratio (power between 8-13Hz relative to power from 2-4Hz) were seen in the hemorrhagic hemisphere compared to the non-hemorrhagic hemisphere. Decreased alpha-delta ratio was seen both with lobar cortical ICH and with basal ganglia ICH. In one of the six patients, higher alpha-delta ratio was seen on the side of left-sided hemorrhage in the context of bilateral epileptiform Lateralized Rhythmic Delta Activity (LRDA) unique to this patient.
Conclusions
In patients at elevated risk of ICH or with ICH, sub-galeal EEG may be an effective method of continuous brain monitoring. In addition to ischemic stroke, decreased alpha-delta ratio on EEG may be seen in hemorrhagic stroke.
Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) remains one of the most devastating forms of stroke, leaving many patients unresponsive with disorders of consciousness. However, there remain few options for continuous brain monitoring for ICH. While EEG markers such as decreased alpha-delta power ratio may indicate ischemic stroke, similar EEG markers of ICH have yet to be explored. Sub-galeal EEG is a promising method for robust continuous brain monitoring, which may have relevance for detecting new ischemic or hemorrhagic events in ICH patients. We therefore aimed to evaluate electrophysiologic features of ICH on sub-galeal EEG.
Methods
Consecutive patients at one center with ICH who underwent minimally-invasive surgical ICH evacuation received bilateral sub-galeal EEG for continuous brain monitoring. To explore markers of ICH, electrophysiologic features on sub-galeal EEG were compared between hemorrhagic and non-hemorrhagic hemispheres.
Results
Six patients with ICH who underwent minimally-invasive surgical evacuation were implanted with sub-galeal EEG intraoperatively. Patient age was on average 66.0±7.5 years, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale at presentation was 19.6±4.0, and ICH volume was 54.0±42.4mL. In five patients, significant reductions in alpha-delta power ratio (power between 8-13Hz relative to power from 2-4Hz) were seen in the hemorrhagic hemisphere compared to the non-hemorrhagic hemisphere. Decreased alpha-delta ratio was seen both with lobar cortical ICH and with basal ganglia ICH. In one of the six patients, higher alpha-delta ratio was seen on the side of left-sided hemorrhage in the context of bilateral epileptiform Lateralized Rhythmic Delta Activity (LRDA) unique to this patient.
Conclusions
In patients at elevated risk of ICH or with ICH, sub-galeal EEG may be an effective method of continuous brain monitoring. In addition to ischemic stroke, decreased alpha-delta ratio on EEG may be seen in hemorrhagic stroke.
More abstracts on this topic:
A rare case of ventriculobronchial fistula caused by an epicardial defibrillator patch
Alampoondi Venkataramanan Sai Vikram, Windle John
Anisotropic conductive hydrogel reduces the incidence of major adverse cardiac events in a beagle model of myocardial infarctionWang Xiaofei, Zhang Zizhuo, Wang Jiale, Yu Lilei
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)