Final ID: MDP471
Clinical Hepatic Scores as Predictors of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in a SMuRFless Population
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Recent evidence suggests that a significant proportion of individuals presenting with myocardial infarction lack standard modifiable cardiovascular disease risk factors (SMuRFs). This SMuRFless population has an elevated risk of mortality, highlighting the need for identifying novel risk markers. Liver steatosis and fibrosis are potential non-traditional markers that have not been evaluated in this population. Therefore, this study investigates clinical hepatic scores as proxies for metabolic liver disease and their association with major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in a SMuRFless population within the UK Biobank.
Methods
We analyzed data from the UK Biobank, a population-based cohort study with a median follow-up of 11 years. The Fatty Liver Index (FLI), Hepatic Steatosis Index (HSI), and Fibrosis Index Based on 4 Factors (FIB-4) were used as non-invasive measures to predict metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, hepatic steatosis, and hepatic fibrosis, respectively. Participants with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, or cigarette smoking (SMuRFs) were excluded. Cox proportional hazards models were used to assess the association between FLI, HSI, and FIB-4 scores and MACE, defined as fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
Results
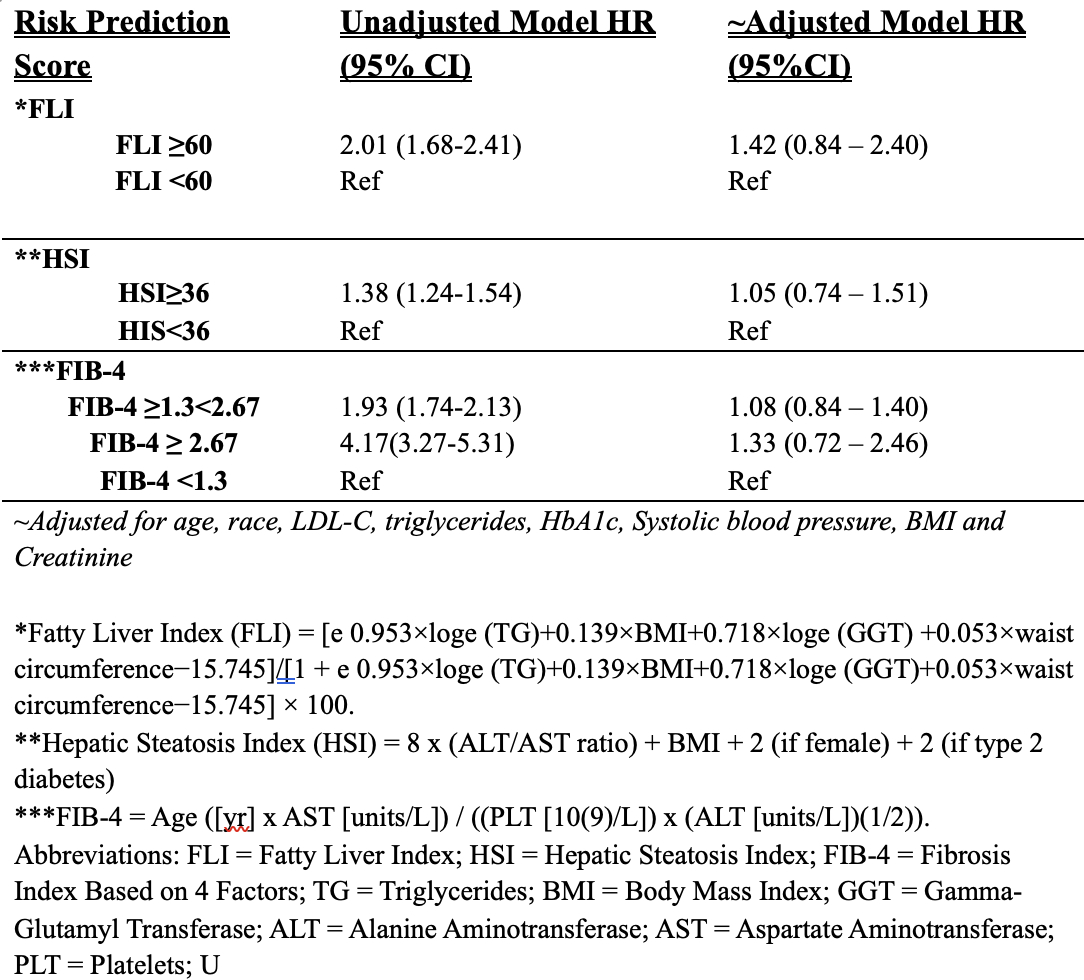
Among 81,339 SMuRFless participants, the mean age was 51.5 years (SD 7.9), and 50,347 (62%) were women. In unadjusted models, higher liver scores (FLI, HSI, and FIB-4) were significantly associated with MACE. Participants with FLI > 60 had a hazard ratio (HR) of 2.01 (95% CI: 1.68-2.41) compared to those with FLI < 60. Those with HSI > 36 had HR of 1.38 (95% CI: 1.14-1.54) compared to HSI < 36, and participants with FIB-4 > 2.67 had an HR of 4.17 (95% CI: 3.27-5.31) compared to FIB-4 < 1.3. However, after adjusting for age, race, hemoglobin A1C, triglycerides, LDL-cholesterol, total cholesterol, body mass index (BMI), and creatinine, these associations were attenuated, and HRs were not statistically significant (Table).
Conclusion
FLI, HSI, and FIB-4 scores are not significant predictors of MACE in a SMuRFless asymptomatic population after adjusting for confounders.
Recent evidence suggests that a significant proportion of individuals presenting with myocardial infarction lack standard modifiable cardiovascular disease risk factors (SMuRFs). This SMuRFless population has an elevated risk of mortality, highlighting the need for identifying novel risk markers. Liver steatosis and fibrosis are potential non-traditional markers that have not been evaluated in this population. Therefore, this study investigates clinical hepatic scores as proxies for metabolic liver disease and their association with major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in a SMuRFless population within the UK Biobank.
Methods
We analyzed data from the UK Biobank, a population-based cohort study with a median follow-up of 11 years. The Fatty Liver Index (FLI), Hepatic Steatosis Index (HSI), and Fibrosis Index Based on 4 Factors (FIB-4) were used as non-invasive measures to predict metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, hepatic steatosis, and hepatic fibrosis, respectively. Participants with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, or cigarette smoking (SMuRFs) were excluded. Cox proportional hazards models were used to assess the association between FLI, HSI, and FIB-4 scores and MACE, defined as fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
Results
Among 81,339 SMuRFless participants, the mean age was 51.5 years (SD 7.9), and 50,347 (62%) were women. In unadjusted models, higher liver scores (FLI, HSI, and FIB-4) were significantly associated with MACE. Participants with FLI > 60 had a hazard ratio (HR) of 2.01 (95% CI: 1.68-2.41) compared to those with FLI < 60. Those with HSI > 36 had HR of 1.38 (95% CI: 1.14-1.54) compared to HSI < 36, and participants with FIB-4 > 2.67 had an HR of 4.17 (95% CI: 3.27-5.31) compared to FIB-4 < 1.3. However, after adjusting for age, race, hemoglobin A1C, triglycerides, LDL-cholesterol, total cholesterol, body mass index (BMI), and creatinine, these associations were attenuated, and HRs were not statistically significant (Table).
Conclusion
FLI, HSI, and FIB-4 scores are not significant predictors of MACE in a SMuRFless asymptomatic population after adjusting for confounders.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Measure of Residential Segregation and Thrombo-inflammation in Black and White Americans
Manogaran Erin, Cushman Mary, Kamin Mukaz Debora, Sparks Andrew, Packer Ryan, Brochu Paige, Judd Suzanne, Howard Virginia, Plante Timothy, Long Leann, Cheung Katherine
Age and White Matter Injury due to Cerebral Small Vessel Disease are Synergistically Associated with Impaired Neurovascular Coupling.Yang Sheng, Webb Alastair