Final ID: Su4138
Late Gadolinium Enhancement CMR Tissue Characterization for Central Venous Catheter Associated Right Atrial Thrombus – Structural Risk Factors and Stratification of Embolic Outcomes among Systemic Cancer Patients
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Central venous catheters (CVC) are common in cancer pts but provide a nidus for right atrial thrombus (RA-Th). CMR can identify presence and risk factors for RA-Th.
Objectives: To evaluate predisposing factors and embolic risk conferred by RA-Th.
Methods: The population comprised adult (≥18yo) cancer pts with CVC who underwent CMR at two sites; RA-Th was defined by avascularity on LGE-CMR. Registry data included clinical and CVC indices and chart review for pulmonary embolism (PE) 1 month pre- or 6 months post-CMR.
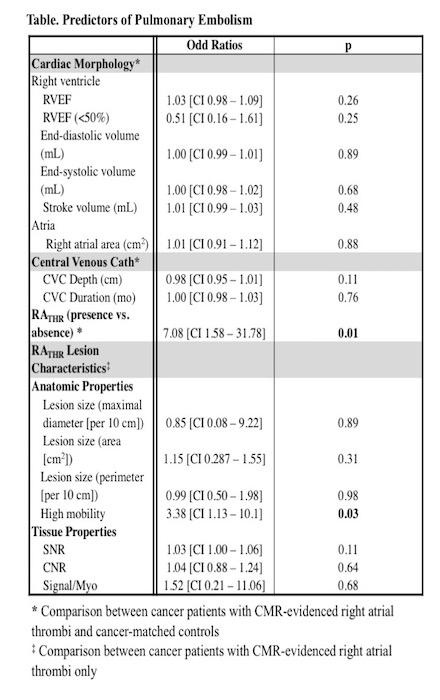
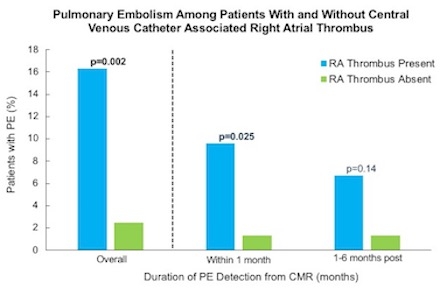
Results: 211 pts with CVC (52±17yo; 45% M) were studied, inclusive of RA-Th and controls matched for cancer etiology/stage (heme 28%| GI 27%| sarcoma 22%). CVC type varied (Mediport 81% |PICC 9%| pheresis 6%| HD 4%), as did time between RA-Th and catheter insertion (6.5[2.4-15.8] mo). Pts with and w/o RA-Th were of similar age, sex, CVC type/duration, and cardiac function on CMR (p=NS). CVC depth was greater in pts with RA-Th (2.8±1.6cm vs. 1.5±1.6cm, p<0.001). Prevalence of RA-Th increased in proportion to CVC depth (<1|1-3|>3cm from SVC-RA: 31%|57%|75%; p<0.001 without influencing RA-Th size (p=NS). Anticoagulation (LMWH 42%| NOAC 25%| warfarin 3.4%| combination 26%) was more common in pts with RA-Th (99% vs. 43%; p<0.001). Despite this, RA-Th was strongly associated with embolic risk, as shown by >5-fold higher incidence of PE vs. controls (16% vs 2.5%, p=0.002; OR=7.08 [CI 1.58–31.78], p=0.01; Table 1). In pts with RA-Th and PE (n=17), majority of PE (59%) occurred within 1mo of CMR, and the remaining occurred within 1-6mo after CMR (Fig 1). Among pts with RA-Th, the likelihood of PE increased with high lesion mobility (27% vs 10%, p=0.02; OR=3.38 [CI 1.13–10.1], p=0.03).
Conclusions: Increased catheter depth increases risk for RA-Th implicating mechanical factors as a key thrombogenic driver. Despite anticoagulation, patients with RA-Th are at markedly higher risk for embolic events, particularly within the first month of detection on CMR.
Objectives: To evaluate predisposing factors and embolic risk conferred by RA-Th.
Methods: The population comprised adult (≥18yo) cancer pts with CVC who underwent CMR at two sites; RA-Th was defined by avascularity on LGE-CMR. Registry data included clinical and CVC indices and chart review for pulmonary embolism (PE) 1 month pre- or 6 months post-CMR.
Results: 211 pts with CVC (52±17yo; 45% M) were studied, inclusive of RA-Th and controls matched for cancer etiology/stage (heme 28%| GI 27%| sarcoma 22%). CVC type varied (Mediport 81% |PICC 9%| pheresis 6%| HD 4%), as did time between RA-Th and catheter insertion (6.5[2.4-15.8] mo). Pts with and w/o RA-Th were of similar age, sex, CVC type/duration, and cardiac function on CMR (p=NS). CVC depth was greater in pts with RA-Th (2.8±1.6cm vs. 1.5±1.6cm, p<0.001). Prevalence of RA-Th increased in proportion to CVC depth (<1|1-3|>3cm from SVC-RA: 31%|57%|75%; p<0.001 without influencing RA-Th size (p=NS). Anticoagulation (LMWH 42%| NOAC 25%| warfarin 3.4%| combination 26%) was more common in pts with RA-Th (99% vs. 43%; p<0.001). Despite this, RA-Th was strongly associated with embolic risk, as shown by >5-fold higher incidence of PE vs. controls (16% vs 2.5%, p=0.002; OR=7.08 [CI 1.58–31.78], p=0.01; Table 1). In pts with RA-Th and PE (n=17), majority of PE (59%) occurred within 1mo of CMR, and the remaining occurred within 1-6mo after CMR (Fig 1). Among pts with RA-Th, the likelihood of PE increased with high lesion mobility (27% vs 10%, p=0.02; OR=3.38 [CI 1.13–10.1], p=0.03).
Conclusions: Increased catheter depth increases risk for RA-Th implicating mechanical factors as a key thrombogenic driver. Despite anticoagulation, patients with RA-Th are at markedly higher risk for embolic events, particularly within the first month of detection on CMR.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Curious Complete Heart Block with Carfilzomib
Shah Mohammed, Rahman Naveed, Al-mohamad Talal, Batra Sejal, Vyas Apurva
90-Day Readmission Rates, Predictors, and Causes of Readmission After Placement of Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Device in Patients With history of different malignancies: National Readmission Database analysisQuevedo Ramirez Andres, Teaima Taha, Jha Vivek, Ibarra Joshua, Soon-shiong Raquel, Gomez Valencia Javier