Final ID: Mo4115
Adaptation of Prompt-enabled Segment-Anything-Model Enhance the Accuracy and Generalizability of Cine Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Segmentation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Accurate segmentation of cine cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) throughout the cardiac cycle is essential for comprehensive cardiac functional analysis. However, current deep-learning (DL) approaches often suffer from reduced accuracy on unseen datasets due to generalizability issues. The Segment-Anything Model (SAM) is a new prompt-enabled segmentation foundation model trained on one billion natural images, known for its generalizability and user-defined prompts.
Hypothesis:
Adapting SAM for cine CMR segmentation can improve accuracy and generalizability on previously unseen CMR data.
Methods:
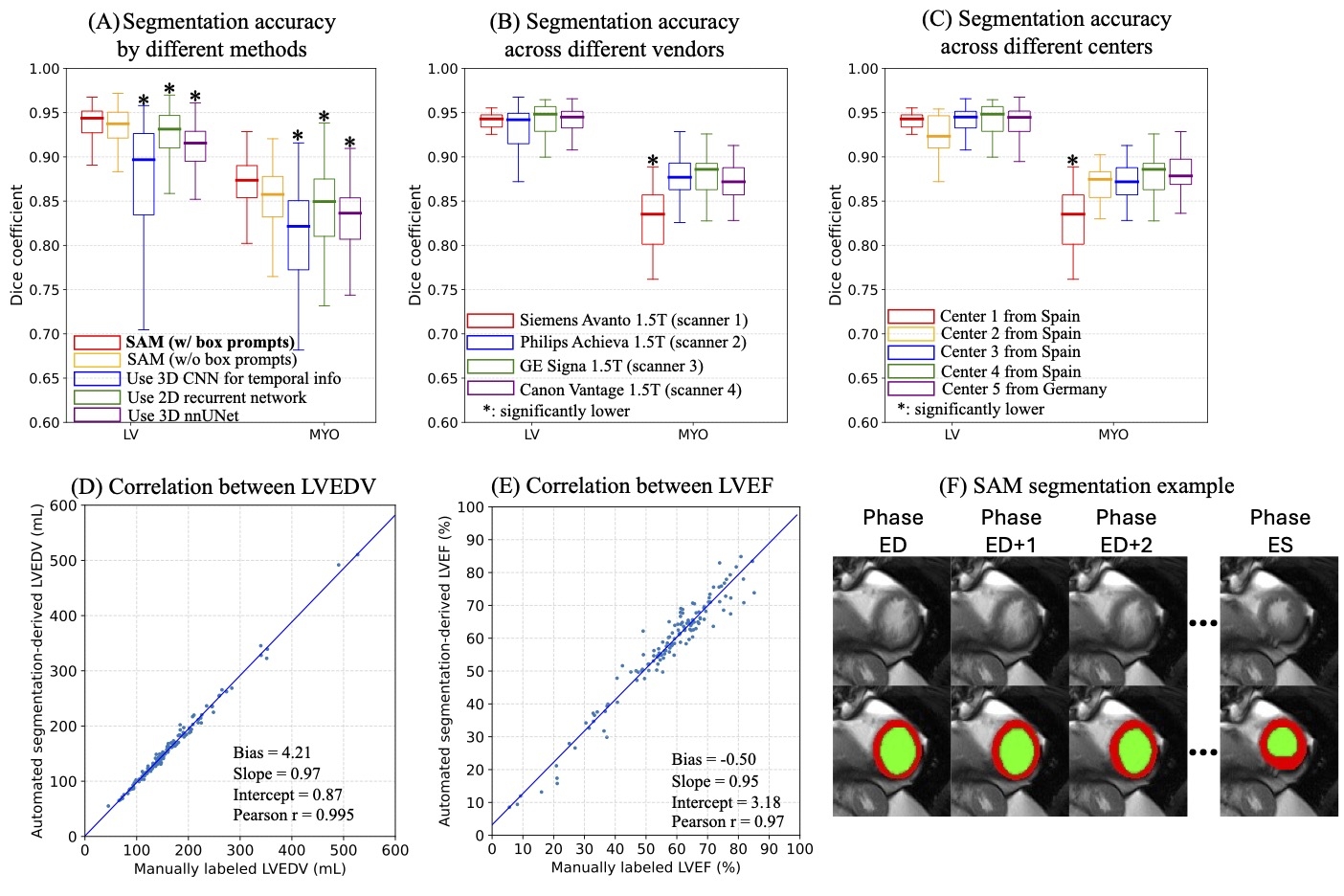
We adapted SAM for cine CMR segmentation by incorporating a temporal attention mechanism to maintain temporal consistency across the cardiac cycle and parameter-efficient transfer learning to segment the left ventricle (LV) and myocardium (MYO). User-defined bounding box prompts were used around MYO at end-diastole and end-systole phases to guide the segmentation region. The model can output segmentations for all phases throughout one cardiac cycle at once. We evaluated the model using a multi-center, multi-vendor (M&M) international dataset of 136 cine CMR cases, which was unseen during model training.The trained model was applied to this dataset without fine-tuning to assess generalizability. We compared SAM with three state-of-the-art (SOTA) cine CMR DL segmenters. Segmentation accuracy was evaluated using the Dice coefficient. Clinical parameters, including LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), were compared between manual and automatic measurements.
Results:
The adapted SAM with box prompts demonstrated superior generalization compared to SOTA methods (p<0.01 by one-sided Wilcoxon test). The Dice coefficient was 0.937±0.024 for LV and 0.870±0.029 for MYO, with no significant differences across different centers and vendors, except for one center. The agreement for LVEDV and EF was high, with r = 0.995 and bias = 4.21±6.75 ml for LVEDV and r = 0.97 and bias = -0.50±3.75% for EF. Using bounding box prompts around the MYO region enhanced its segmentation accuracy from 0.853±0.032 to 0.870±0.029 (p<0.05) compared to no prompts.
Conclusion:
Adapting SAM with box prompts enhances accuracy and generalizability in cine CMR segmentation..
Accurate segmentation of cine cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) throughout the cardiac cycle is essential for comprehensive cardiac functional analysis. However, current deep-learning (DL) approaches often suffer from reduced accuracy on unseen datasets due to generalizability issues. The Segment-Anything Model (SAM) is a new prompt-enabled segmentation foundation model trained on one billion natural images, known for its generalizability and user-defined prompts.
Hypothesis:
Adapting SAM for cine CMR segmentation can improve accuracy and generalizability on previously unseen CMR data.
Methods:
We adapted SAM for cine CMR segmentation by incorporating a temporal attention mechanism to maintain temporal consistency across the cardiac cycle and parameter-efficient transfer learning to segment the left ventricle (LV) and myocardium (MYO). User-defined bounding box prompts were used around MYO at end-diastole and end-systole phases to guide the segmentation region. The model can output segmentations for all phases throughout one cardiac cycle at once. We evaluated the model using a multi-center, multi-vendor (M&M) international dataset of 136 cine CMR cases, which was unseen during model training.The trained model was applied to this dataset without fine-tuning to assess generalizability. We compared SAM with three state-of-the-art (SOTA) cine CMR DL segmenters. Segmentation accuracy was evaluated using the Dice coefficient. Clinical parameters, including LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), were compared between manual and automatic measurements.
Results:
The adapted SAM with box prompts demonstrated superior generalization compared to SOTA methods (p<0.01 by one-sided Wilcoxon test). The Dice coefficient was 0.937±0.024 for LV and 0.870±0.029 for MYO, with no significant differences across different centers and vendors, except for one center. The agreement for LVEDV and EF was high, with r = 0.995 and bias = 4.21±6.75 ml for LVEDV and r = 0.97 and bias = -0.50±3.75% for EF. Using bounding box prompts around the MYO region enhanced its segmentation accuracy from 0.853±0.032 to 0.870±0.029 (p<0.05) compared to no prompts.
Conclusion:
Adapting SAM with box prompts enhances accuracy and generalizability in cine CMR segmentation..
More abstracts on this topic:
A Silent Storm: Incidental Discovery of IVC and Right Atrium Thrombus in a Patient with Uterine Stromal Sarcoma
Wasef Natale, Fatima Tehreem, Stys Adam
A Silent Murmur: Incidental Finding of a Cardiac ParagangliomaMin Kyung, Srikanth Kishan, Lien Tann, Hernandez Salvador, Colicci Steven, Wheeler Amber, Ting Jennifer