Final ID: MDP196
Predicting 30-Day and 1-Year Mortality in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) using Electronic Health Record Data
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
INTRODUCTION
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) represents 50% of heart failure patients. Predictive models in HFpEF, specifically those derived from electronic health record (EHR) data, are less established.
HYPOTHESIS
EHR models can predict 30-day and 1-year mortality in HFpEF patients. Machine learning (ML) models compared with traditional may show superior performance.
AIM
Develop and compare prediction models for 30-day and 1-year mortality in HFpEF using EHR data, using traditional and ML techniques.
METHODS
Using MIMIC-IV data (EHR data from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston) from 2008-2019, we identified patients aged ≥ 18 years admitted with a primary diagnosis of HFpEF using ICD-9 and 10 codes. Demographics, vital signs, prior diagnoses, and lab data were extracted. After preprocessing, data was partitioned into 70% training and 30% test. Prediction models from seven model classes were developed using a variety of imputation and oversampling techniques using 5-fold cross validation - Support Vector Classifier (SVC), Logistic Regression, Lasso Regression, Elastic Net, Random Forest, HistGradient Boosting Classifier, and XGBoost. Model performance was compared using several metrics. SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) analysis was used to assess individual feature influence on model output.
RESULTS
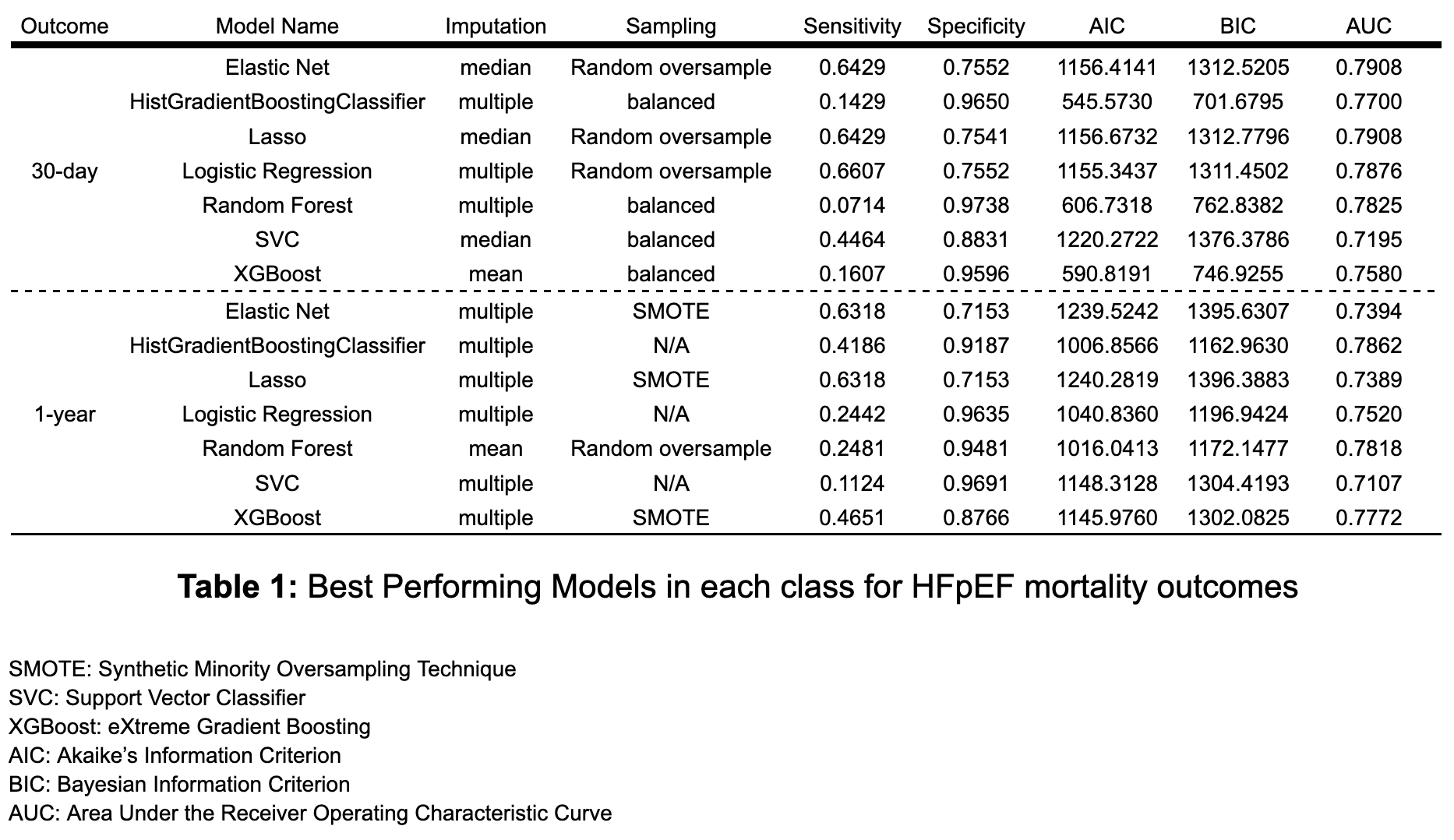
Among 3910 individual hospitalizations for HFpEF the 30-day mortality was 6.3% and 1-year mortality was 29.2%. Performance metrics of the best model in each class is shown in Table 1. By AUCs, Lasso and Elastic Net Regression models provided superior prediction for 30-day mortality (AUCs of 0.79, each), whereas Random Forest and HistGradient Boosting Classifier for 1-year mortality (AUCs of 0.78 each). Overall, considering all metrics, Elastic Net and Lasso regression models gave a good combination of sensitivity, specificity and AUC enhancing their clinical applicability. SHAP analyses showed age, NT-proBNP and sodium levels, WBC, and platelet counts as key drivers of these predictions.
CONCLUSION
Models derived from EHR data, which is important for implementability, predict mortality after HFpEF hospitalization with good performance comparable to models derived from registry or trial data.
INTRODUCTION
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) represents 50% of heart failure patients. Predictive models in HFpEF, specifically those derived from electronic health record (EHR) data, are less established.
HYPOTHESIS
EHR models can predict 30-day and 1-year mortality in HFpEF patients. Machine learning (ML) models compared with traditional may show superior performance.
AIM
Develop and compare prediction models for 30-day and 1-year mortality in HFpEF using EHR data, using traditional and ML techniques.
METHODS
Using MIMIC-IV data (EHR data from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston) from 2008-2019, we identified patients aged ≥ 18 years admitted with a primary diagnosis of HFpEF using ICD-9 and 10 codes. Demographics, vital signs, prior diagnoses, and lab data were extracted. After preprocessing, data was partitioned into 70% training and 30% test. Prediction models from seven model classes were developed using a variety of imputation and oversampling techniques using 5-fold cross validation - Support Vector Classifier (SVC), Logistic Regression, Lasso Regression, Elastic Net, Random Forest, HistGradient Boosting Classifier, and XGBoost. Model performance was compared using several metrics. SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) analysis was used to assess individual feature influence on model output.
RESULTS
Among 3910 individual hospitalizations for HFpEF the 30-day mortality was 6.3% and 1-year mortality was 29.2%. Performance metrics of the best model in each class is shown in Table 1. By AUCs, Lasso and Elastic Net Regression models provided superior prediction for 30-day mortality (AUCs of 0.79, each), whereas Random Forest and HistGradient Boosting Classifier for 1-year mortality (AUCs of 0.78 each). Overall, considering all metrics, Elastic Net and Lasso regression models gave a good combination of sensitivity, specificity and AUC enhancing their clinical applicability. SHAP analyses showed age, NT-proBNP and sodium levels, WBC, and platelet counts as key drivers of these predictions.
CONCLUSION
Models derived from EHR data, which is important for implementability, predict mortality after HFpEF hospitalization with good performance comparable to models derived from registry or trial data.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning-Derived Socio-Environmental Risk Score More Accurately Predicts Cardiovascular Events and Better Addresses Health Inequities than Social Deprivation Index
Chen Zhuo, Nasir Khurram, Al-kindi Sadeer, Rajagopalan Sanjay, Ponnana Sai Rahul, Dazard Jean-eudes, Zhang Tong, Dong Weichuan, Okyere Robert, Sirasapalli Santosh, Deo Salil, Khraishah Haitham
A Machine Learning Algorithm to Detect Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Risk from Baseline ECGsArezoumand Amirhossein, Danala Gopichandh, Masnadi Khiabani Parisa, Ebert David, Behere Shashank