Final ID: Mo3121
The Effect of Benzodiazepine Use in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Introduction: Sleep apnea is a common sleep disorder that can worsen atrial fibrillation(AF) prognosis. Benzodiazepines(BZD) are commonly prescribed for insomnia, which often accompanies sleep apnea. However, BZDs have been associated with worsening of sleep apnea due to respiratory depression, pharyngeal muscle relaxation, and increase of arousal threshold, which all may lead to prolonged hypoxia. There is little research on the effect of BZD use in AF patients with sleep apnea. Therefore, the objective of this study is to investigate the effects of BZD usage on outcomes in the AF population with sleep apnea.
Methods: Data from patients with AF and sleep apnea seen at Tulane Medical Center between 2010 and 2019 was obtained from Research Action for Health Network(REACHnet), a Clinical Research Network in PCORnet®. Patients with AF and sleep apnea were divided between those with a prescription of BZD and those without BZD. These two groups were compared using the Kaplan-Meier method for time-to outcome for all-cause mortality, ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction(MI), and hospitalizations in the five years following their AF diagnosis. Cox regression analysis was used to investigate proportional hazards and control for demographics, comorbidities, and medication use.
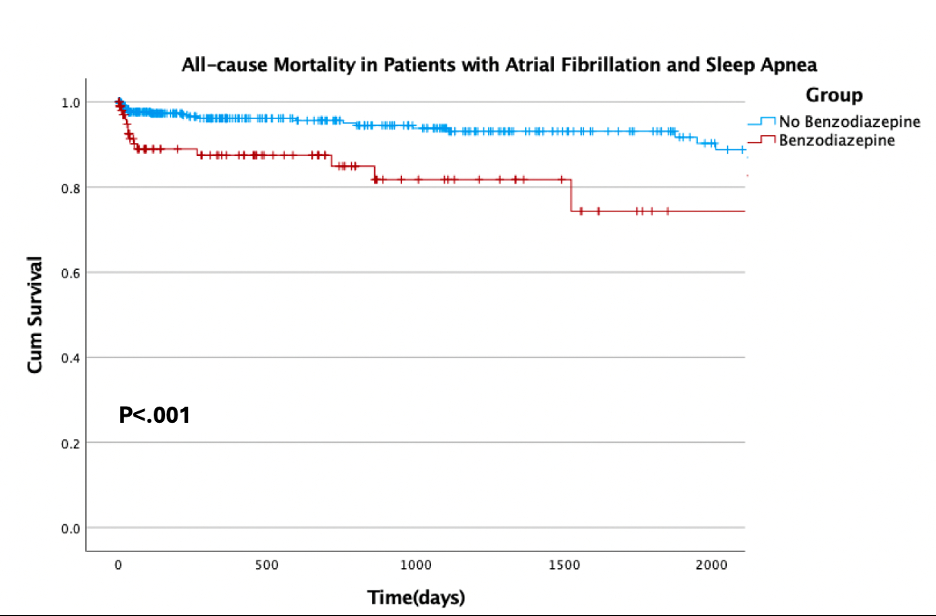
Results: There were 524 total patients included with AF and sleep apnea. Of these, 413(78.8%) were not prescribed BZDs, while 111(21.1%) were taking BZDs. Use of BZDs was associated with worse outcomes. In the no BZD and the BZD group over the 5 years following AF diagnosis, the rate of mortality was 6.1% and 12.6%(p<.001), the rate of ischemic stroke was 16% and 23.4%(p=.008), the rate of MI was 11.9% and 22.5%(p<.001), and the rate of hospitalization was 51.8% and 59.5%(p<.001), respectively. In multivariate Cox regression, use of BZD was associated with higher mortality(HR: 2.65; CI: 2.26-3.05; p=.013) and hospitalization(HR: 2.15; CI: 1.99-2.31;p<.001).
Conclusion: BZD use was associated with an over 2-fold increase in all-cause mortality and hospitalizations in patients with AF and sleep apnea. This suggests that BZDs should be used with caution in this patient population, and other treatment modalities for insomnia should be considered.
- Abi-rached, Joe ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Jia, Yishi ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Lim, Chanho ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Gu, Yuxuan ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Pandey, Amitabh ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Rao, Swati ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Donnellan, Eoin ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Kreidieh, Omar ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Marrouche, Nassir ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Bidaoui, Ghassan ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Tsakiris, Eli ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Feng, Han ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Liu, Yingshuo ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Younes, Hadi ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Assaf, Ala' ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Bsoul, Mayana ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
- Tirado Polo, Francisco ( Tulane University School of Medicine , New Orleans , Louisiana , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Substance Use and Cardiovascular Risk 2
Monday, 11/18/2024 , 01:30PM - 02:30PM
Abstract Poster Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Zafar Amna, Umar Muhammad, Ali Syed Awab, Habib Huzefa, Shamim Laiba, Hidayat Ayesha, Bareeqa Syeda Beenish, Noori Muhammad Atif Masood, Vasudev Rahul
A novel deep learning framework identified associated genes and Interpretable deep learning translation of GWAS findings for drug repurposing in Atrial FibrillationTonegawa-kuji Reina, Xu Jielin, Guntupalli Suman, Barnard John, Chung Mina, Cheng Feixiong
More abstracts from these authors:
Bsoul Mayana, Feng Han, Lim Chanho, Hui Yanpei, Hassan Abboud, Rao Swati, Kreidieh Omar, Pandey Amitabh, Donnellan Eoin, Marrouche Nassir, Assaf Ala', Bidaoui Ghassan, Tirado Polo Francisco, Gu Yuxuan, Mekhael Mario, Younes Hadi, Jia Yishi, Liu Yingshuo
Differential Impact of Left Atrial Volume on Post-Ablation Recurrence Rates in Patients with Normal and Reduced Left Atrial Ejection Fraction: A DECAAF II SubanalysisBsoul Mayana, Lim Chanho, Hui Yanpei, Hassan Abboud, Rao Swati, Pandey Amitabh, Kreidieh Omar, Donnellan Eoin, Marrouche Nassir, Liu Yingshuo, Assaf Ala', Bidaoui Ghassan, Jia Yishi, Younes Hadi, Feng Han, Mekhael Mario, Tirado Polo Francisco