Final ID: Mo2055
Identification and Immunological Characterization of Arrhythmia-Related Molecular Clusters in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Ischemic cardiomyopathy, a severe cardiac condition resulting from prolonged myocardial ischemia, is characterized by ventricular dilation, dysfunction, and an increased risk of life-threatening arrhythmias. Arrhythmia, a common complication in ischemic cardiomyopathy, is associated with poor clinical outcomes. Recent studies have indicated that the molecular heterogeneity of ischemic cardiomyopathy may contribute to the development of arrhythmias. Therefore, our study aimed to explore arrhythmia-related molecular clusters in ischemic cardiomyopathy and establish a prediction model for risk stratification.
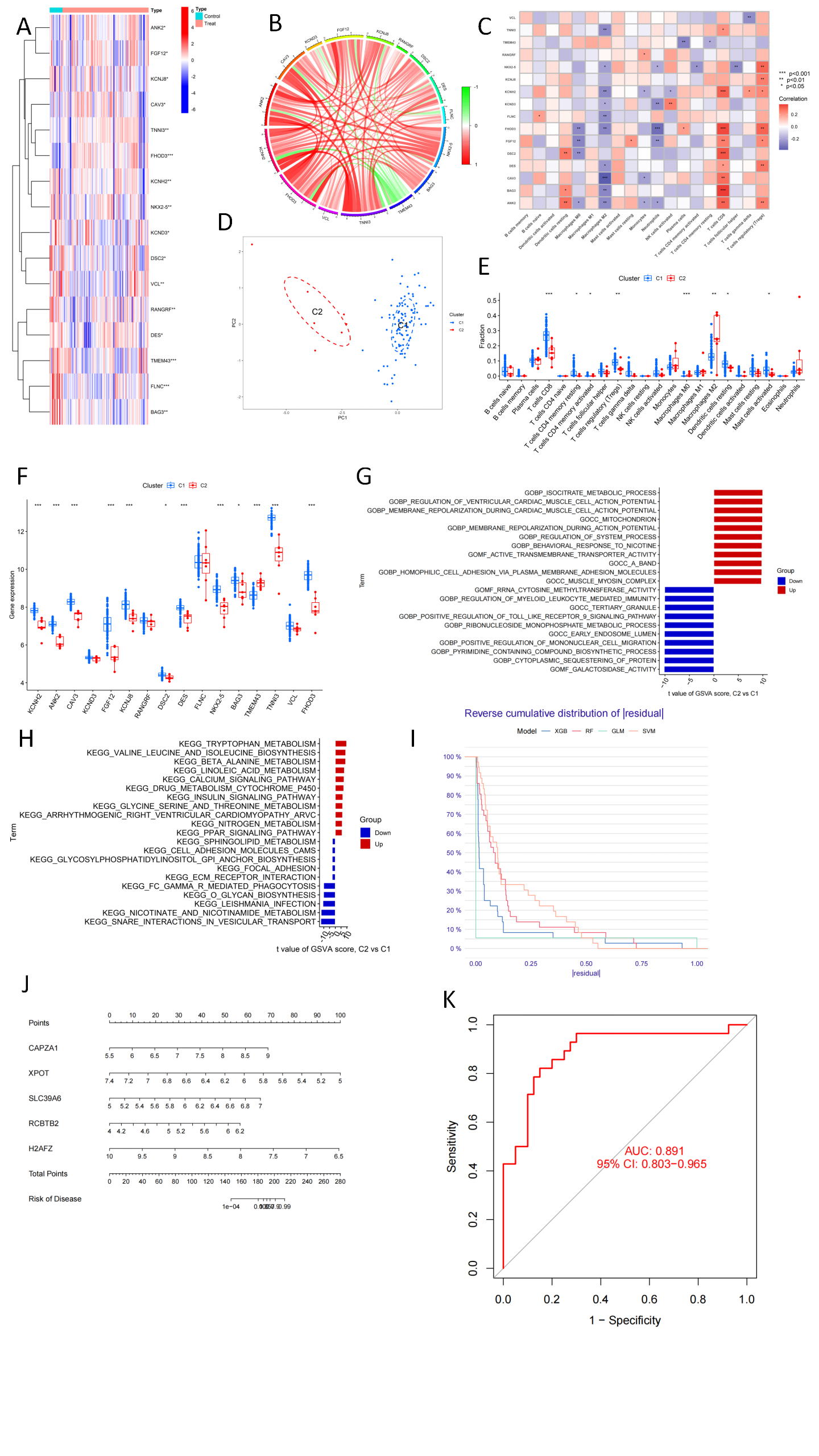
Based on gene expression profiles of ischemic cardiomyopathy patients, we analyzed the dysregulation of arrhythmia-associated genes and the associated immune characteristics (Figure 1A-C). Using unsupervised clustering analysis, we identified distinct arrhythmia-related molecular clusters in ischemic cardiomyopathy patients (Figure 1D-F). Cluster-specific differentially expressed genes were further identified using weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). Functional enrichment analysis revealed significant differences in biological processes and pathways between the clusters (Figure 1G-H). Subsequently, we developed a prediction model using a random forest algorithm, which showed superior performance in distinguishing patients with different arrhythmia risks (Figure 1I-J). This forest model demonstrated excellent performance in one external validation datasets with AUC values of 0.891.
In conclusion, our study provides novel insights into the molecular basis of arrhythmias in ischemic cardiomyopathy and establishes a prediction model with potential clinical utility for risk stratification and targeted therapies. Further investigation into the specific mechanisms underlying the identified molecular clusters may reveal new therapeutic targets for the management of arrhythmias in ischemic cardiomyopathy patients.
Based on gene expression profiles of ischemic cardiomyopathy patients, we analyzed the dysregulation of arrhythmia-associated genes and the associated immune characteristics (Figure 1A-C). Using unsupervised clustering analysis, we identified distinct arrhythmia-related molecular clusters in ischemic cardiomyopathy patients (Figure 1D-F). Cluster-specific differentially expressed genes were further identified using weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). Functional enrichment analysis revealed significant differences in biological processes and pathways between the clusters (Figure 1G-H). Subsequently, we developed a prediction model using a random forest algorithm, which showed superior performance in distinguishing patients with different arrhythmia risks (Figure 1I-J). This forest model demonstrated excellent performance in one external validation datasets with AUC values of 0.891.
In conclusion, our study provides novel insights into the molecular basis of arrhythmias in ischemic cardiomyopathy and establishes a prediction model with potential clinical utility for risk stratification and targeted therapies. Further investigation into the specific mechanisms underlying the identified molecular clusters may reveal new therapeutic targets for the management of arrhythmias in ischemic cardiomyopathy patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
9p21.3 variants drive coronary calcification by suppressing statherin expression
Soheili Fariborz, Almontashiri Naif, Heydarikhorneh Niloufar, Vilmundarson Ragnar, Chen Hsiao-huei, Stewart Alexandre
A Rare Case of Idiopathic Ventricular Fibrillation Triggered by Short-Coupled PVCs from the Apical Free Wall of the Right VentriclePatel Palak, Patel Gaurav, Oza Jaykumar, Correia Joaquim