Final ID: Sa4122
eQTL Analysis of the PAH Biomarker CCN2 Identifies a Novel SNP that Associates with Survival
Research Question: We sought to identify genetic variants associated with circulating levels of CCN2 and to determine those variants’ relationship with clinical severity and survival.
Methods: Serum CCN2 was measured by ELISA in subjects from a national sample repository, the PAH Biobank. A genome wide association study (GWAS) for CCN2 (natural log transformed) was performed in White idiopathic PAH (IPAH) PAH Biobank participants (n = 768) using Illumina OMNI5 genotypes in plink after standard quality control. Subsequent exploration of the SNP of interest was conducted in a separate dataset of 687 White PAH participants (n=360 IPAH, n=313 APAH) linked to genetic and clinical data, including REVEAL 2.0 risk score assessment (divided into low, medium, and high-risk levels) and outcomes (the STRIDE (Sitaxsentan To Relieve Impaired Exercise) trials cohort).
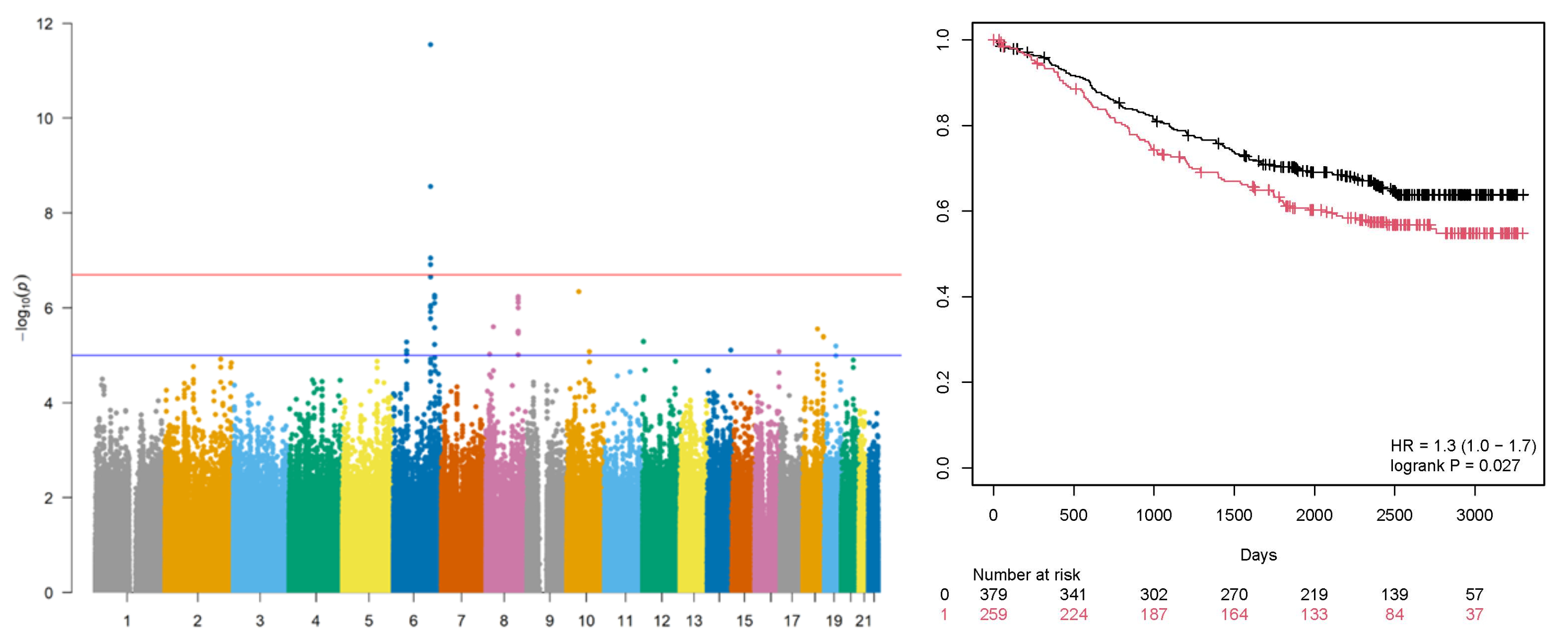
Results: In the PAH Biobank, using GWAS, we found CCN2 levels were significantly associated with rs9493157 (p = 2.8 x10-12) (Figure A). rs9493157 is reported in the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) portal to be an eQTL for CCN2 expression in the left ventricle. In the STRIDE cohort, the hazard ratio (HR) for death was 1.33 (99% CI 1.03 to 1.72) for participants with one or more T alleles (p=0.027; (Figure B)). On multivariate analysis, the HR for death was 1.28 (95% CI 0.99 to 1.66; p=0.060). Among subjects with the highest REVEAL2.0 risk, those with a T allele had worse survival than those no T allele, with best survival among those with low a REVEAL2.0 score and no T allele.
Conclusions: In White PAH subjects, rs9493157 associates with human levels of serum CCN2, a known biomarker for PAH. While additional studies are warranted, the T allele associates with worse survival and may enhance the prognostic value of the REVEAL2.0 risk score.
- Byrd, Carly ( Johns Hopkins University , Baltimore , Tennessee , United States )
- Simpson, Catherine ( Johns Hopkins University , Baltimore , Maryland , United States )
- Kolb, Todd ( JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY , Baltimore , Maryland , United States )
- Pauciulo, Michael ( CINCINNATI CHILDRENS HOSPITAL , Cincinnati , Ohio , United States )
- Nichols, William ( CINCINNATI CHILDRENS HOSPITAL , Cincinnati , Ohio , United States )
- Ivy, Dunbar ( UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO , Aurora , Colorado , United States )
- Hassoun, Paul ( Johns Hopkins University , Baltimore , Maryland , United States )
- Everett, Allen ( Johns Hopkins University , Glenwood , Maryland , United States )
- Austin, Eric ( VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CTR , Nashville , Tennessee , United States )
- Martin, Lisa ( CINCINNATI CHILDRENS HOSPITAL , Cincinnati , Ohio , United States )
- Benza, Raymond ( Mount Sinai Heart , New York , New York , United States )
- Webb, Amy ( CINCINNATI CHILDRENS HOSPITAL , Cincinnati , Ohio , United States )
- Schramm, Jennifer ( Johns Hopkins University , Baltimore , Maryland , United States )
- Yang, Jun ( JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY , Baltimore , Maryland , United States )
- Griffiths, Megan ( University of Texas Southwestern , Dallas , Texas , United States )
- Brandal, Stephanie ( Johns Hopkins University , Baltimore , Maryland , United States )
- Damico, Rachel ( JOHNS HOPKINS , Baltimore , Maryland , United States )
- Vaidya, Dhananjay ( JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY , Baltimore , Maryland , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Going Solo: Insights From Single Cell, Single Molecule and Novel Molecular Analyses
Saturday, 11/16/2024 , 10:30AM - 11:30AM
Abstract Poster Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Yuan Shuai, Khodursky Samuel, Geng Jiawei, Sharma Pranav, Spin Joshua, Tsao Philip, Levin Michael, Damrauer Scott
A Heart-pounding Case of Cardiomyopathy in PregnancyTran Linh, Everitt Ian, Vaught Arthur, Barth Andreas, Minhas Anum
More abstracts from these authors:
Ruan Peifeng, Manlhiot Cedric, Austin Eric, Nichols Bill, Everett Allen, Griffiths Megan
Role of Cellular Communication Network Protein Family in Pulmonary Arterial HypertensionByrd Carly, Austin Eric, Hassoun Paul, Everett Allen, Schramm Jennifer, Yang Jun, Griffiths Megan, Damico Rachel, Simpson Catherine, Kolb Todd, Nichols Bill, Ivy Dunbar