Final ID: Su3055
Neighborhood Level Social Determinants of Health and Loss of Blood Pressure Control
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Uncontrolled hypertension is a potent cardiovascular risk factor, with a higher prevalence in adults with disadvantaged social determinants of health (SDoH). While prior work has shown an association with uncontrolled blood pressure (BP) and adverse SDoH in general, less is known about specific SDoH domain drivers of this association, knowledge of which may inform interventions to improve health and reduce disparities.
Methods
We examined health records in all adults with ≥2 outpatient visits/year in at least 2 consecutive years from 2017-2023. BP level was determined by the first 2 visits in the first year and last 2 readings in the second year; BP control was based on contemporary thresholds (<130/80 mmHg). Loss of BP control (controlled in first year and uncontrolled in second year) was determined year over year. Neighborhood SDoH was assessed by linking patients’ zip codes to the Healthy Places Index (HPI), including 8 domains (economic, education, transportation, social, housing, health insurance, clean environment, and neighborhood). Multivariable regression analyses were used to examine associations of demographics, clinical, and SDoH characteristics.
Results
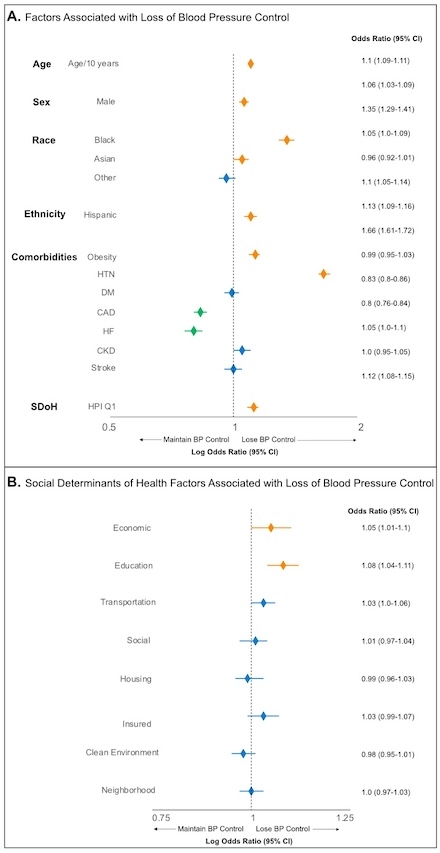
A total of 145,318 patients were identified, of whom 94,276 (64.9%) lost BP control at some point during the study period. In analyses adjusting for demographic, clinical, and SDoH factors (Figure 1A), risk of losing BP control was associated with living in a neighborhood with a HPI score in the worst quartile (OR 1.12, 95% CI 1.08-1.15). Evaluation of SDoH domain identified the economic (1.15 [1.12-1.18], P = 0.012) and education (1.15 [1.12-1.18], P < 0.001) as the only SDoH domains associated with loss of BP control, though positive association trends were also appreciated for transportation (1.09 [1.06-1.12], P = 0.079) and health insurance (1.1 [1.07-1.13], P = 0.097) domains (Figure 1B).
Conclusions
In over 140,000 adults with controlled BP, almost two-thirds lost BP control in the subsequent year. This loss of BP control was associated with many neighborhood level SDoH factors, specifically economic and educational domains. These results inform potential targets to help reduce disparities and improve BP related health outcomes.
Uncontrolled hypertension is a potent cardiovascular risk factor, with a higher prevalence in adults with disadvantaged social determinants of health (SDoH). While prior work has shown an association with uncontrolled blood pressure (BP) and adverse SDoH in general, less is known about specific SDoH domain drivers of this association, knowledge of which may inform interventions to improve health and reduce disparities.
Methods
We examined health records in all adults with ≥2 outpatient visits/year in at least 2 consecutive years from 2017-2023. BP level was determined by the first 2 visits in the first year and last 2 readings in the second year; BP control was based on contemporary thresholds (<130/80 mmHg). Loss of BP control (controlled in first year and uncontrolled in second year) was determined year over year. Neighborhood SDoH was assessed by linking patients’ zip codes to the Healthy Places Index (HPI), including 8 domains (economic, education, transportation, social, housing, health insurance, clean environment, and neighborhood). Multivariable regression analyses were used to examine associations of demographics, clinical, and SDoH characteristics.
Results
A total of 145,318 patients were identified, of whom 94,276 (64.9%) lost BP control at some point during the study period. In analyses adjusting for demographic, clinical, and SDoH factors (Figure 1A), risk of losing BP control was associated with living in a neighborhood with a HPI score in the worst quartile (OR 1.12, 95% CI 1.08-1.15). Evaluation of SDoH domain identified the economic (1.15 [1.12-1.18], P = 0.012) and education (1.15 [1.12-1.18], P < 0.001) as the only SDoH domains associated with loss of BP control, though positive association trends were also appreciated for transportation (1.09 [1.06-1.12], P = 0.079) and health insurance (1.1 [1.07-1.13], P = 0.097) domains (Figure 1B).
Conclusions
In over 140,000 adults with controlled BP, almost two-thirds lost BP control in the subsequent year. This loss of BP control was associated with many neighborhood level SDoH factors, specifically economic and educational domains. These results inform potential targets to help reduce disparities and improve BP related health outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association between Polysocial Risk Score and Cardiovascular Health among Women of Reproductive Age in the American Heart Association’s Research Goes Red
Metlock Faith, Kwapong Yaa, Vaidya Dhananjay, Evans Crystal, Ouyang Pamela, Commodore-mensah Yvonne, Sharma Garima
Artificial Intelligence Driven Subphenotyping of In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Patients Identifies Subgroups with Different Outcomes and Risk Factors: A Nation-Wide AnalysisJiang Joy, Zebrowski Alexis, Bhatt Deepak, Nadkarni Girish, Abbott Ethan, Oh Wonsuk, Buckler David, Kittrell Hannah, Jayaraman Pushkala, Chan Lili, Vaid Akhil, Gulamali Faris, Redlener Michael