Final ID: Mo3127
Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Inhibitors and Lipid Reduction: A Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors offer additional lipid reduction beyond that achieved with statins. However, the optimal PCSK9 therapy for lowering lipid levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia and/or hyperlipidemia on background statin therapy remains unclear.
Methods: PubMed and EMBASE databases were searched for RCTs assessing tafolecimab, evolocumab or alirocumab vs. placebo (administrated Q2W or Q4W, 12-week treatment) in patients with hypercholesterolemia and/or hyperlipidemia on medium-intensity statin up to March 28, 2024. The outcomes of interest were the percentage change in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) or lipoprotein(a) from baseline to the 12th week. A frequentist random-effect network meta-analysis was applied to calculate MD and 95% CI using Stata 16.0 software.
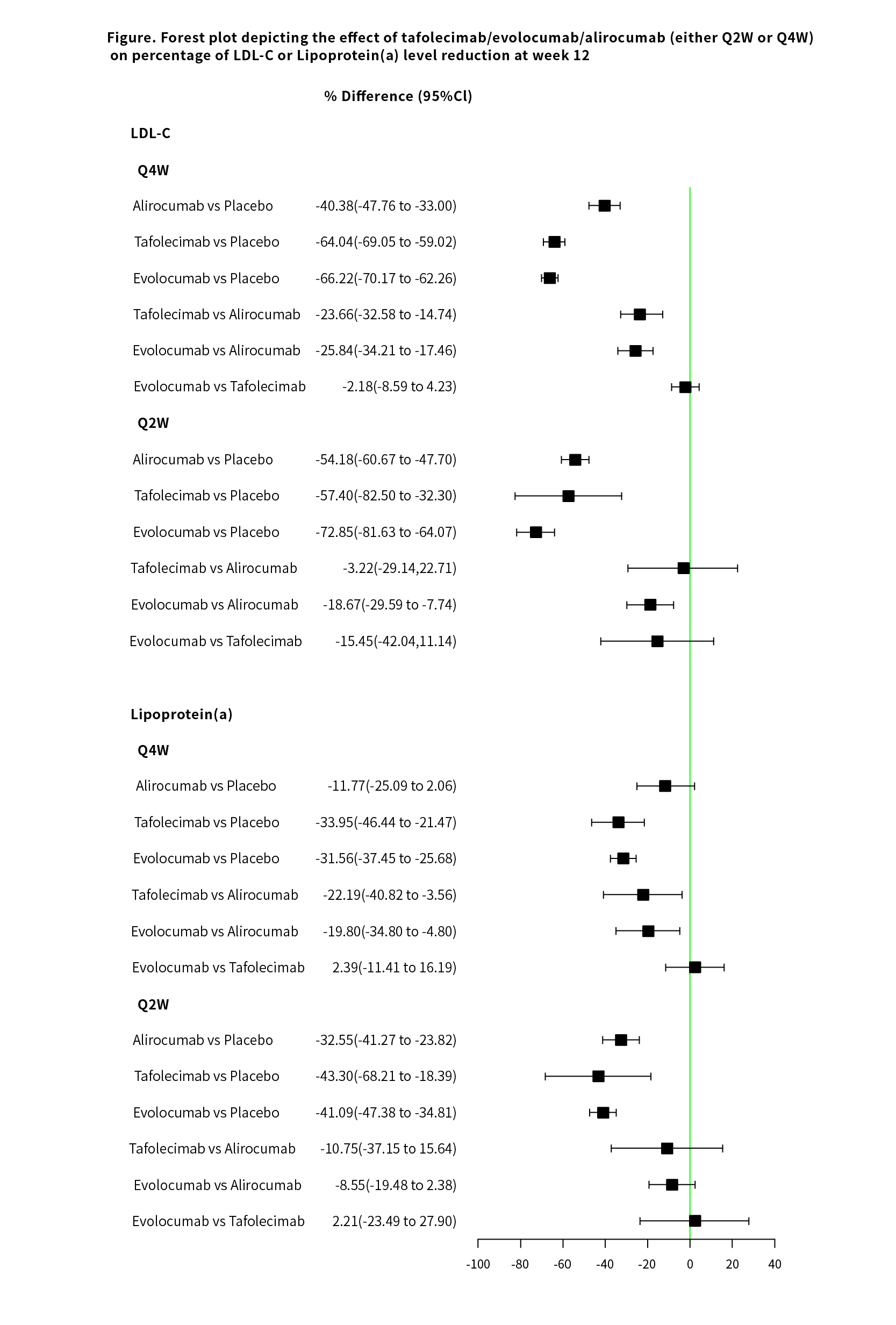
Results: A total of 4960 patients [PCSK9 inhibitors (n=3230), placebo (n=1730)] across 13 RCTs were included. At week 12, tafolecimab, evolocumab and alirocumab (either Q2W or Q4W) all induced significant reductions in LDL-C levels compared to placebo (Figure). The efficacy of evolocumab Q2W was significantly higher compared with alirocumab Q2W (MD=-18.67%, 95% Cl [-29.59%, -7.74%]), while similar LDL-C reduction was observed in tafolecimab Q2W vs. alirocumab Q2W and evolocumab Q2W vs. tafolecimab Q2W. Furthermore, tafolecimab Q4W and evolocumab Q4W were more effective in lowering LDL-C levels compared to alirocumab Q4W (tafolecimab vs. alirocumab: MD=-23.66%, 95% Cl [-32.58%, -14.74%]; evolocumab vs. alirocumab: MD=-25.84%, 95% Cl [-34.21%, -17.46%]), while there was no difference between evolocumab Q4W and tafolecimab Q4W. Lastly, the ranking of the effects for reducing lipoprotein(a) levels was as follows: tafolecimab > evolocumab> alirocumab (either Q2W or Q4W).
Conclusions: In patients with hypercholesterolemia and/or hyperlipidemia treated with medium-intensity statins, tafolecimab and evolocumab (either Q2W or Q4W) might be preferred choices for lowering LDL-C. Additionally, tafolecimab (either Q2W or Q4W) appears to be the most effective agent for reducing lipoprotein(a) levels.
Methods: PubMed and EMBASE databases were searched for RCTs assessing tafolecimab, evolocumab or alirocumab vs. placebo (administrated Q2W or Q4W, 12-week treatment) in patients with hypercholesterolemia and/or hyperlipidemia on medium-intensity statin up to March 28, 2024. The outcomes of interest were the percentage change in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) or lipoprotein(a) from baseline to the 12th week. A frequentist random-effect network meta-analysis was applied to calculate MD and 95% CI using Stata 16.0 software.
Results: A total of 4960 patients [PCSK9 inhibitors (n=3230), placebo (n=1730)] across 13 RCTs were included. At week 12, tafolecimab, evolocumab and alirocumab (either Q2W or Q4W) all induced significant reductions in LDL-C levels compared to placebo (Figure). The efficacy of evolocumab Q2W was significantly higher compared with alirocumab Q2W (MD=-18.67%, 95% Cl [-29.59%, -7.74%]), while similar LDL-C reduction was observed in tafolecimab Q2W vs. alirocumab Q2W and evolocumab Q2W vs. tafolecimab Q2W. Furthermore, tafolecimab Q4W and evolocumab Q4W were more effective in lowering LDL-C levels compared to alirocumab Q4W (tafolecimab vs. alirocumab: MD=-23.66%, 95% Cl [-32.58%, -14.74%]; evolocumab vs. alirocumab: MD=-25.84%, 95% Cl [-34.21%, -17.46%]), while there was no difference between evolocumab Q4W and tafolecimab Q4W. Lastly, the ranking of the effects for reducing lipoprotein(a) levels was as follows: tafolecimab > evolocumab> alirocumab (either Q2W or Q4W).
Conclusions: In patients with hypercholesterolemia and/or hyperlipidemia treated with medium-intensity statins, tafolecimab and evolocumab (either Q2W or Q4W) might be preferred choices for lowering LDL-C. Additionally, tafolecimab (either Q2W or Q4W) appears to be the most effective agent for reducing lipoprotein(a) levels.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association Between Lipoprotein(a) Levels and Incident Complex Coronary Revascularization Procedures in the FOURIER Trial
Gaba Prakriti, Sabatine Marc, Bergmark Brian, O'donoghue Michelle, Giugliano Robert, Bellavia Andrea, Monsalvo Maria Laura, Flores-arredondo Jose, Kuder Julia, Atar Dan, Keech Anthony
Adiponectin and Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio Associate with Cardiometabolic Risk in South Asian Americans: Updates from the MASALA StudyUttarwar Salil, Shah Nilay, Kanaya Alka, Gadgil Meghana