Final ID: MDP59
Machine Learning Uncovers the Contribution of Rare Genetic Variants and Enhances Risk Prediction for Coronary Artery Disease in the Japanese Population
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have enhanced our understanding of the genetic basis of coronary artery disease (CAD), and polygenic risk scores (PRSs) have facilitated the assessment of genetic risk. However, these methods predominantly focus on common variants due to statistical power, potentially leaving rare variants insufficiently analyzed and thus limiting the predictive performance of PRS.
Methods
We conducted whole genome sequencing (WGS) of 1,752 Japanese early-onset myocardial infarction (MI) patients and 3,019 controls from Biobank Japan (BBJ). We performed case-control association studies including GWAS and gene-based tests, as well as a novel machine learning-based framework. In this framework, we developed a penalized regression model to predict the CAD status from genome-wide rare nonsynonymous variants. The model identified the minimal set of most distinguishing features (genes) and generated a rare variant-based risk score (RVS). The RVS was evaluated on an independent validation WGS cohort of 200 cases and 824 controls. We also derived a PRS based on CAD-GWAS (25,668 CAD cases vs 141,667 controls from BBJ) to compare the properties and performance between the RVS and PRS.
Results
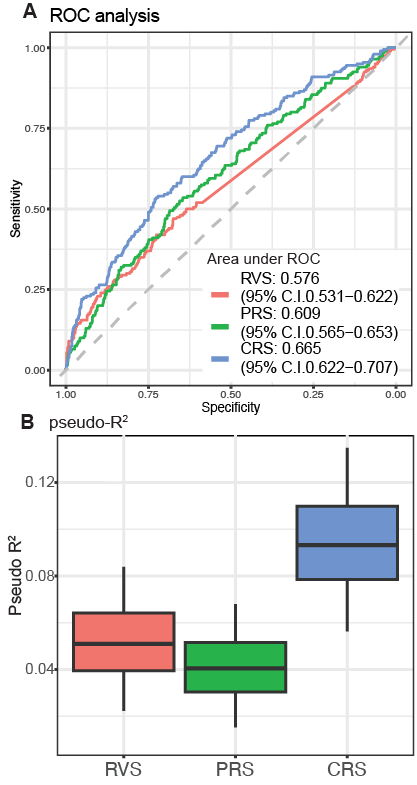
In the case-control studies, only two common variants in chromosome 12 were identified in GWAS, with no genes in gene-based analysis (SKAT-O), suggesting the challenges in rare variant analysis. On the other hand, our machine-learning framework identified 59 CAD-related genes, including LDLR, a causal gene of familial hypercholesteremia. Functional analyses revealed that various biological pathways, including lipid metabolism, immune system, and vessel development, are involved in CAD. For the genetic risk prediction, RVS significantly predicted CAD (area under the curve [AUC], 0.58; p=0.001, pseudo-R2, 0.051; p=7.92*10-9). RVS was significantly associated with LDL cholesterol levels and coagulation function (Pearson’s r, 0.21; p=4.5*10-5 and 0.10; p=0.03, respectively) and MI patients with high RVS (top 5%) showed higher cardiovascular mortality rate (p=0.03, log-rank test), highlighting the clinical importance of RVS. Finally, the combined risk score (CRS) of RVS and PRS significantly improved CAD prediction compared to PRS (AUC, 0.66 (CRS) vs 0.61 (PRS); p=0.007, pseudo-R2, 0.093 (CRS) vs 0.040 (PRS); p=0.0018, Figure).
Conclusions
Our machine learning framework successfully characterized rare variants and enhanced genetic risk prediction in CAD.
Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have enhanced our understanding of the genetic basis of coronary artery disease (CAD), and polygenic risk scores (PRSs) have facilitated the assessment of genetic risk. However, these methods predominantly focus on common variants due to statistical power, potentially leaving rare variants insufficiently analyzed and thus limiting the predictive performance of PRS.
Methods
We conducted whole genome sequencing (WGS) of 1,752 Japanese early-onset myocardial infarction (MI) patients and 3,019 controls from Biobank Japan (BBJ). We performed case-control association studies including GWAS and gene-based tests, as well as a novel machine learning-based framework. In this framework, we developed a penalized regression model to predict the CAD status from genome-wide rare nonsynonymous variants. The model identified the minimal set of most distinguishing features (genes) and generated a rare variant-based risk score (RVS). The RVS was evaluated on an independent validation WGS cohort of 200 cases and 824 controls. We also derived a PRS based on CAD-GWAS (25,668 CAD cases vs 141,667 controls from BBJ) to compare the properties and performance between the RVS and PRS.
Results
In the case-control studies, only two common variants in chromosome 12 were identified in GWAS, with no genes in gene-based analysis (SKAT-O), suggesting the challenges in rare variant analysis. On the other hand, our machine-learning framework identified 59 CAD-related genes, including LDLR, a causal gene of familial hypercholesteremia. Functional analyses revealed that various biological pathways, including lipid metabolism, immune system, and vessel development, are involved in CAD. For the genetic risk prediction, RVS significantly predicted CAD (area under the curve [AUC], 0.58; p=0.001, pseudo-R2, 0.051; p=7.92*10-9). RVS was significantly associated with LDL cholesterol levels and coagulation function (Pearson’s r, 0.21; p=4.5*10-5 and 0.10; p=0.03, respectively) and MI patients with high RVS (top 5%) showed higher cardiovascular mortality rate (p=0.03, log-rank test), highlighting the clinical importance of RVS. Finally, the combined risk score (CRS) of RVS and PRS significantly improved CAD prediction compared to PRS (AUC, 0.66 (CRS) vs 0.61 (PRS); p=0.007, pseudo-R2, 0.093 (CRS) vs 0.040 (PRS); p=0.0018, Figure).
Conclusions
Our machine learning framework successfully characterized rare variants and enhanced genetic risk prediction in CAD.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Variant in GNB2 as a Cause of Sick Sinus Syndrome
Bulut Aybike, Karacan Mehmet, Saygili E. Alper, Pirli Dogukan, Aydin Eylul, Ozdemir Ozkan, Balci Nermin, Alanay Yasemin, Bilguvar Kaya, Akgun Dogan Ozlem
A Genome-wide CRISPRi Screen Implicates Coronary Artery Disease GWAS Genes as Key Regulators of Adventitial Fibroblast ProliferationJackson William, Zhu Ashley, Gu Wenduo, Berezowitz Alexa, Iyer Meghana, Cheng Paul