Final ID: MDP740
Checkpoint Kinase 1 Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Maintaining SIRT1-Dependent Mitochondrial Homeostasis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Mitochondrial dysfunction is linked to myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. Checkpoint kinase 1 (CHK1) could facilitate cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac repair post myocardial infarction, however, its role on mitochondrial function in I/R injury remains unknown.
Research Questions: The purpose of this study is to explore the potential effects and mechanisms of CHK1 on mitochondrial homeostasis during myocardial I/R injury.
Methods: To investigate the role of CHK1 on mitochondrial function following I/R injury, cardiomyocyte-specific knockout/knock-in mouse models were generated. Mass spectrometry-proteomics analysis and protein co-immunoprecipitation assays were conducted to dissect the molecular mechanism of CHK1. The interaction between CHK1 and SIRT1 was explored using truncated plasmids.
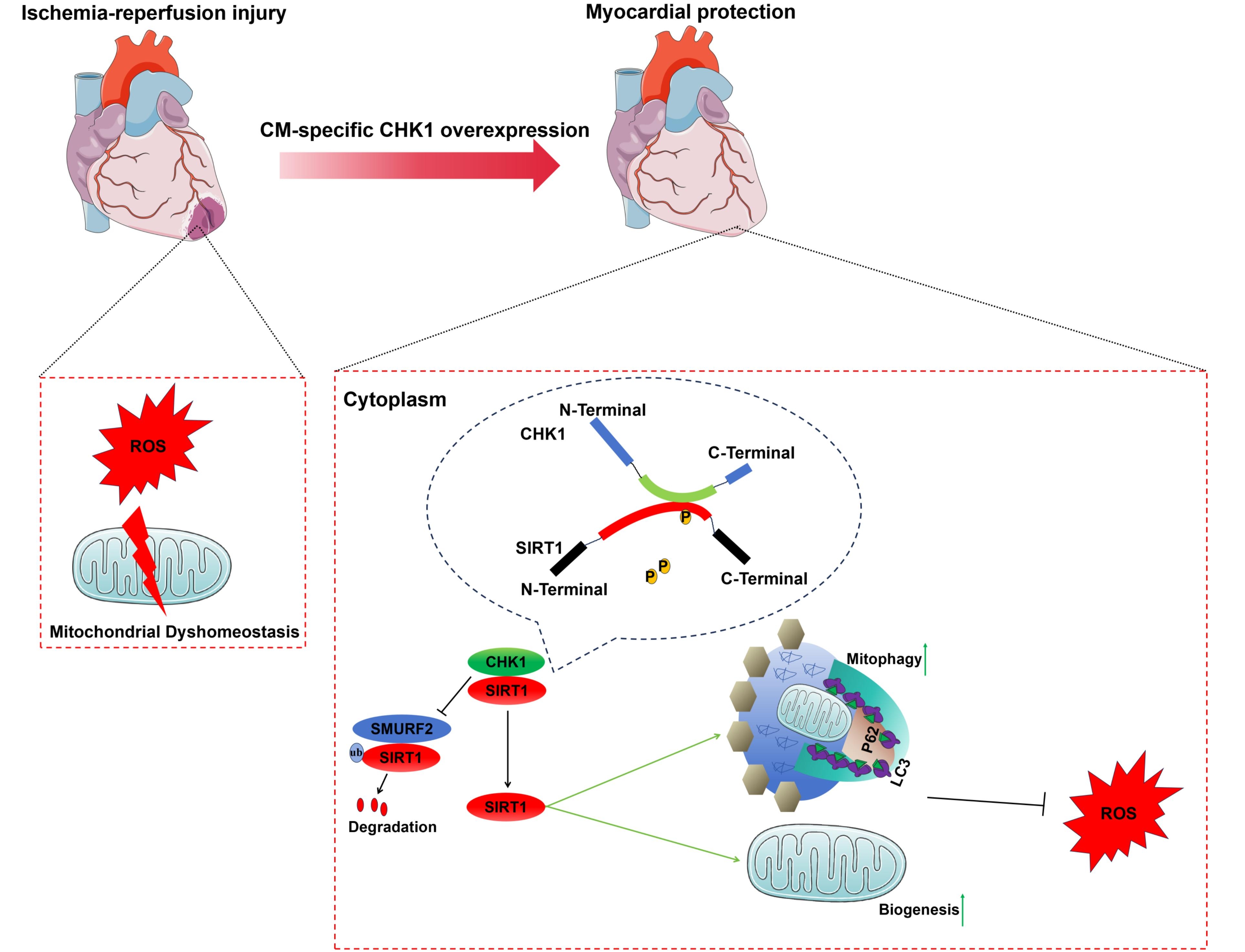
Results: CHK1 was downregulated in myocardium post I/R and neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes (NMCMs) post oxygen-glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation (OGD/R). In vivo, CHK1 overexpression protected against myocardial I/R injury, while heterogenous CHK1 knockout exacerbated cardiomyopathy. In vitro, CHK1 inhibited OGD/R-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and bolstered cardiomyocyte survival. Mechanistically, CHK1 attenuated oxidative stress and preserved mitochondrial metabolism in cardiomyocytes under I/R. Moreover, disrupted mitochondrial homeostasis in I/R myocardium was restored by CHK1 through the promotion of mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy. Through mass spectrometry analysis following co-immunoprecipitation, SIRT1 was identified as a direct target of CHK1. The 266-390 domain of CHK1 interacted with the 160-583 domain of SIRT1. Importantly, CHK1 phosphorylated SIRT1 at Thr530 residue, thereby inhibiting SMURF2-mediated degradation of SIRT1. CHK1 Δ390 amino acids (aa) mutant functioned similarly to full-length CHK1 in scavenging ROS and maintaining mitochondrial dynamics. Consistently, cardiac-specific SIRT1 knockdown partially attenuated the protective role of CHK1 in I/R injury.
Conclusions: Our findings revealed that CHK1 mitigates I/R injury and restores mitochondrial dynamics in cardiomyocytes through a SIRT1-dependent mechanism.
Research Questions: The purpose of this study is to explore the potential effects and mechanisms of CHK1 on mitochondrial homeostasis during myocardial I/R injury.
Methods: To investigate the role of CHK1 on mitochondrial function following I/R injury, cardiomyocyte-specific knockout/knock-in mouse models were generated. Mass spectrometry-proteomics analysis and protein co-immunoprecipitation assays were conducted to dissect the molecular mechanism of CHK1. The interaction between CHK1 and SIRT1 was explored using truncated plasmids.
Results: CHK1 was downregulated in myocardium post I/R and neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes (NMCMs) post oxygen-glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation (OGD/R). In vivo, CHK1 overexpression protected against myocardial I/R injury, while heterogenous CHK1 knockout exacerbated cardiomyopathy. In vitro, CHK1 inhibited OGD/R-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and bolstered cardiomyocyte survival. Mechanistically, CHK1 attenuated oxidative stress and preserved mitochondrial metabolism in cardiomyocytes under I/R. Moreover, disrupted mitochondrial homeostasis in I/R myocardium was restored by CHK1 through the promotion of mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy. Through mass spectrometry analysis following co-immunoprecipitation, SIRT1 was identified as a direct target of CHK1. The 266-390 domain of CHK1 interacted with the 160-583 domain of SIRT1. Importantly, CHK1 phosphorylated SIRT1 at Thr530 residue, thereby inhibiting SMURF2-mediated degradation of SIRT1. CHK1 Δ390 amino acids (aa) mutant functioned similarly to full-length CHK1 in scavenging ROS and maintaining mitochondrial dynamics. Consistently, cardiac-specific SIRT1 knockdown partially attenuated the protective role of CHK1 in I/R injury.
Conclusions: Our findings revealed that CHK1 mitigates I/R injury and restores mitochondrial dynamics in cardiomyocytes through a SIRT1-dependent mechanism.
More abstracts on this topic:
Alterations in Heart Rate Variability After Ischemic Stroke in Rats: Heart-Brain Connectivity
Alavi Rashid, Dai Wangde, Li Jiajun, Carreno Juan, Pahlevan Niema, Arakaki Xianghong, Gharib Morteza, Kloner Robert
Photobiomodulation Protects the Cardiorenal Axis in Diabetic NephropathyVattimo Maria De Fatima, Garcia Villalba Jessica, Goncalves Maikol Lucas, Oliveira Silva Eloiza, Gomes Alves Mikelly, Victoria Carla, Veloso Juliana