Final ID: MDP320
Cardiac imaging-pathology correlation in 283 pediatric heart transplant biopsy specimens: Cardiac MRI detects clinically important fibrosis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) derived T1 parametric mapping offers quantitative, regional assessments of myocardial edema and fibrosis. Pediatric cardiac allografts are subject to fibrosis due to rejection inflammation, coronary vasculopathy, cardiopulmonary bypass and graft failure. The role of CMR parametric mapping in identifying clinically important myocardial fibrosis in this population remains unknown. Thus, the aim of this study was to correlate endomyocardial biopsy (EMB)-derived fibrosis measurements with local T1 values in PHTx patients.
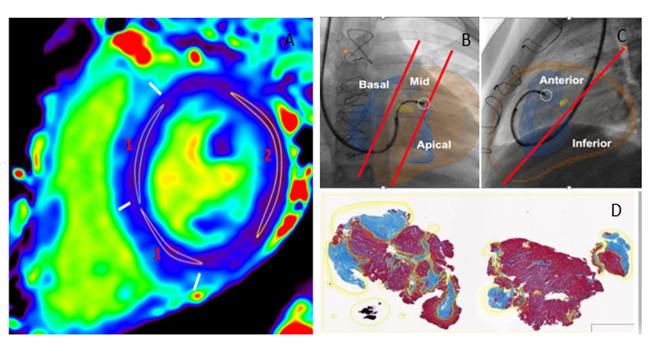
Methods: PHTx pts undergoing EMB also underwent simultaneous cardiac MRI including T1 parametric mapping in 6 short axis slices at 1.5 T. Segmental T1 values were measured and the segments corresponding to EMB sites were noted from overlay registration. Trichrome-stained EMBs were digitally scanned and analyzed for fibrosis content. Encounters were divided into low and high fibrosis groups, and clinical variables from echocardiography, clinical treatment, and cardiac catheterization were compared using student’s t-test and linear regression.
Results: Thirty-three PHTx pts (age of 12.8 + 4.9 years) underwent 94 surveillance encounters, for a total of 283 EMB samples. 75 encounters had no active rejection and 19 encounters had active rejection requiring treatment. Average T1 was significantly higher in active rejection group (1056 vs 1018 ms, p<0.01), and there was no difference in fibrosis score between the 2 groups, thus identifying rejection as the main driver of T1 elevation. In the group with no active rejection, the T1 value from the EMB site was elevated in the high fibrosis score group (1023 vs 1011 ms, p=0.01). Of these patients without rejection, the higher fibrosis group had higher BNP (626 vs 145, p=0.04), higher lateral mitral E/e’ (8 vs 6.6, p=0.03) and higher RVEDP (11 vs 9 mmHg, p=0.05), all suggestive of more significant diastolic dysfunction.
Conclusions: CMR derived segmental T1 value can detect clinically significant graft rejection. In the absence of rejection, elevated T1 correlates with clinically significant fibrosis on EMB, which correlates with markers of diastolic dysfunction.
Methods: PHTx pts undergoing EMB also underwent simultaneous cardiac MRI including T1 parametric mapping in 6 short axis slices at 1.5 T. Segmental T1 values were measured and the segments corresponding to EMB sites were noted from overlay registration. Trichrome-stained EMBs were digitally scanned and analyzed for fibrosis content. Encounters were divided into low and high fibrosis groups, and clinical variables from echocardiography, clinical treatment, and cardiac catheterization were compared using student’s t-test and linear regression.
Results: Thirty-three PHTx pts (age of 12.8 + 4.9 years) underwent 94 surveillance encounters, for a total of 283 EMB samples. 75 encounters had no active rejection and 19 encounters had active rejection requiring treatment. Average T1 was significantly higher in active rejection group (1056 vs 1018 ms, p<0.01), and there was no difference in fibrosis score between the 2 groups, thus identifying rejection as the main driver of T1 elevation. In the group with no active rejection, the T1 value from the EMB site was elevated in the high fibrosis score group (1023 vs 1011 ms, p=0.01). Of these patients without rejection, the higher fibrosis group had higher BNP (626 vs 145, p=0.04), higher lateral mitral E/e’ (8 vs 6.6, p=0.03) and higher RVEDP (11 vs 9 mmHg, p=0.05), all suggestive of more significant diastolic dysfunction.
Conclusions: CMR derived segmental T1 value can detect clinically significant graft rejection. In the absence of rejection, elevated T1 correlates with clinically significant fibrosis on EMB, which correlates with markers of diastolic dysfunction.
More abstracts on this topic:
Application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Predictive Modelling and Imaging in Cardiac Transplantation - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Iyer Vardhini Ganesh, Chandra Mohan Trisha, Gupta Aryan, Gupta Era, Prasad Kushal, Kalra Shekhar, Chandramouli Bellur Vinay, Prasad Ananya, Oudit Omar, Magaji Rishikesh R
Activation of the Histamine-3 Receptor Prevents Cardiac Fibrosis and Diastolic Dysfunction by Opposing a Profibrotic Cardiac Fibroblast Phenotype through Inhibition of cAMP SignalingConnery Heather, Herrnreiter Anja, Campbell William, Widiapradja Alexander, Levick Scott