Final ID: Mo2047
Exercise Capacity in Patients with Fontan Physiology
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction/Background
In the absence of a sub-pulmonary ventricle in the Fontan circulation, augmentation of pulmonary blood flow and filling of the systemic ventricle during exercise are limited. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) is a reliable method for evaluation of aerobic capacity, gas exchange, and other physiologic parameters used for risk stratification in this population. Despite the ubiquitous use of CPET, reference ranges for patients with Fontan physiology are limited. The purpose of this study is to describe exercise characteristics and their relationship with different characteristics of Fontan physiology, imaging, and hemodynamics.
Methods/Approach
In this retrospective cohort study, CPET results were reviewed for adult Fontan patients at the University of Washington between May 2021 and February 2024. Demographics, comorbidities, medications, type of Fontan conduit, imaging characteristics, hemodynamics, and exercise characteristics were included. Results were compared to a large previously published cohort of Fontan patients. Univariate linear regression was used to identify associations between demographics, cardiac anatomy, and exercise parameters. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results/Data
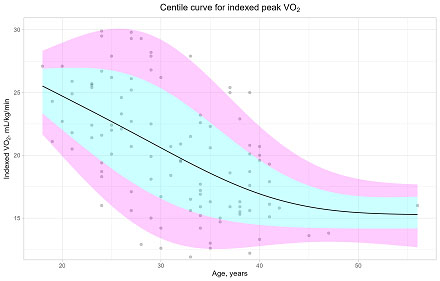
Baseline demographics were notable for an older patient population (31±7 years) with lower indexed peak VO2 (20.5±5.6 mL/kg/min) and greater VE/VCO2 slope (37±7) compared to the historic cohort. Indexed peak VO2 was associated with age, BMI, type of Fontan conduit, FEV1, FVC, resting oxygen saturation, peak systolic blood pressure, and peak heart rate. Indexed peak VO2 was notably not significantly associated with sex, systemic ventricular morphology, ventricular systolic function, Fontan pressure, or the presence of conventional heart failure medical therapy.
Conclusions
In the growing population of older patients with Fontan physiology, development of age-specific population normative data may increase the clinical utility of CPET. Further investigation of the relationship between imaging characteristics, hemodynamics, and exercise parameters is needed in the Fontan population.
In the absence of a sub-pulmonary ventricle in the Fontan circulation, augmentation of pulmonary blood flow and filling of the systemic ventricle during exercise are limited. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) is a reliable method for evaluation of aerobic capacity, gas exchange, and other physiologic parameters used for risk stratification in this population. Despite the ubiquitous use of CPET, reference ranges for patients with Fontan physiology are limited. The purpose of this study is to describe exercise characteristics and their relationship with different characteristics of Fontan physiology, imaging, and hemodynamics.
Methods/Approach
In this retrospective cohort study, CPET results were reviewed for adult Fontan patients at the University of Washington between May 2021 and February 2024. Demographics, comorbidities, medications, type of Fontan conduit, imaging characteristics, hemodynamics, and exercise characteristics were included. Results were compared to a large previously published cohort of Fontan patients. Univariate linear regression was used to identify associations between demographics, cardiac anatomy, and exercise parameters. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results/Data
Baseline demographics were notable for an older patient population (31±7 years) with lower indexed peak VO2 (20.5±5.6 mL/kg/min) and greater VE/VCO2 slope (37±7) compared to the historic cohort. Indexed peak VO2 was associated with age, BMI, type of Fontan conduit, FEV1, FVC, resting oxygen saturation, peak systolic blood pressure, and peak heart rate. Indexed peak VO2 was notably not significantly associated with sex, systemic ventricular morphology, ventricular systolic function, Fontan pressure, or the presence of conventional heart failure medical therapy.
Conclusions
In the growing population of older patients with Fontan physiology, development of age-specific population normative data may increase the clinical utility of CPET. Further investigation of the relationship between imaging characteristics, hemodynamics, and exercise parameters is needed in the Fontan population.
More abstracts on this topic:
Fontan-specific morbidities impact on heart transplant outcomes: a multicenter study
Ybarra Aecha, Joong Anna, Ploutz Michelle, Feingold Brian, Mao Chad, Lorts Angela, Simpson Kathleen, Richmond Marc, Amdani Shahnawaz, Conway Jennifer, Bearl David, Cousino Melissa, Friedland-little Joshua, Batazzi Adriana, Reichle Garrett, Yu Sunkyung, Rosenthal David, Schumacher Kurt, Blume Elizabeth, Bano Maria, Deshpande Shriprasad, O'connor Matthew, Chen Sharon, Wright Lydia, Kindel Steven
Application of Principal Component Analysis to Heterogenous Fontan Registry Data to Identify Independent Contributing Factors to DeclineFerrari Margaret, Schafer Michal, Hunter Kendall, Dimaria Michael