Final ID: MDP700
Explainable Machine Learning to Predict Heart Failure Outcomes Using Exercise and Clinical Data
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Heart failure (HF) hospitalizations are associated with disease burden and cardiovascular mortality. International guidelines highlight cardiopulmonary testing (CPET) for risk stratification and prognosis in HF. Identifying individuals at risk could direct interventions to prevent admissions. This study uses explainable machine learning (XML) tools to identify CPET and clinical variables predictive of HF hospitalizations.
Hypothesis
XML analysis of CPET parameters and clinical factors can yield accurate, patient-specific prediction of HF admission within one year.
Methods
A retrospective single center review of 178 CPETs in patients referred for HF was completed. Clinical data within one year of CPET trained a boosted machine learning model (XGBoost). SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations) explainability analysis emphasized key features for model predictions.
Results
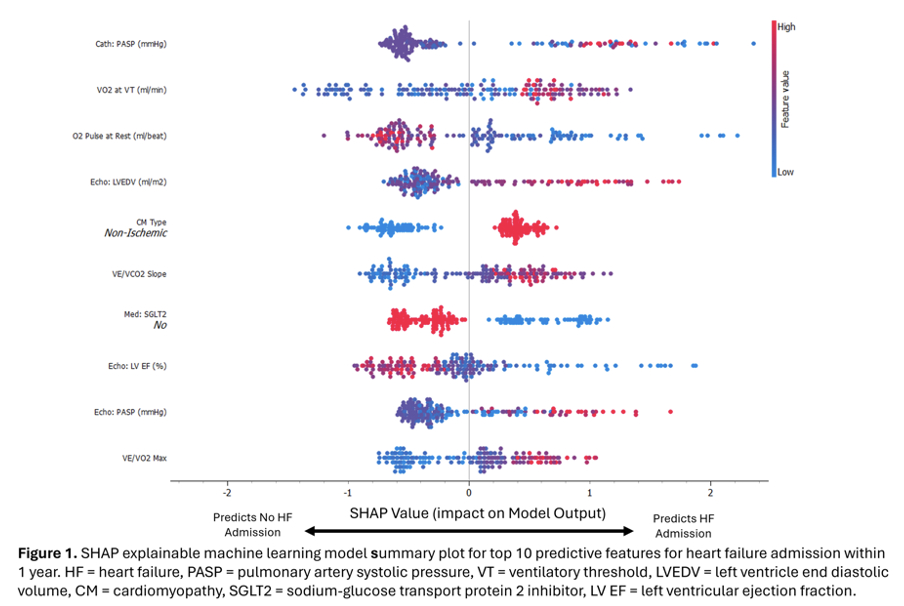
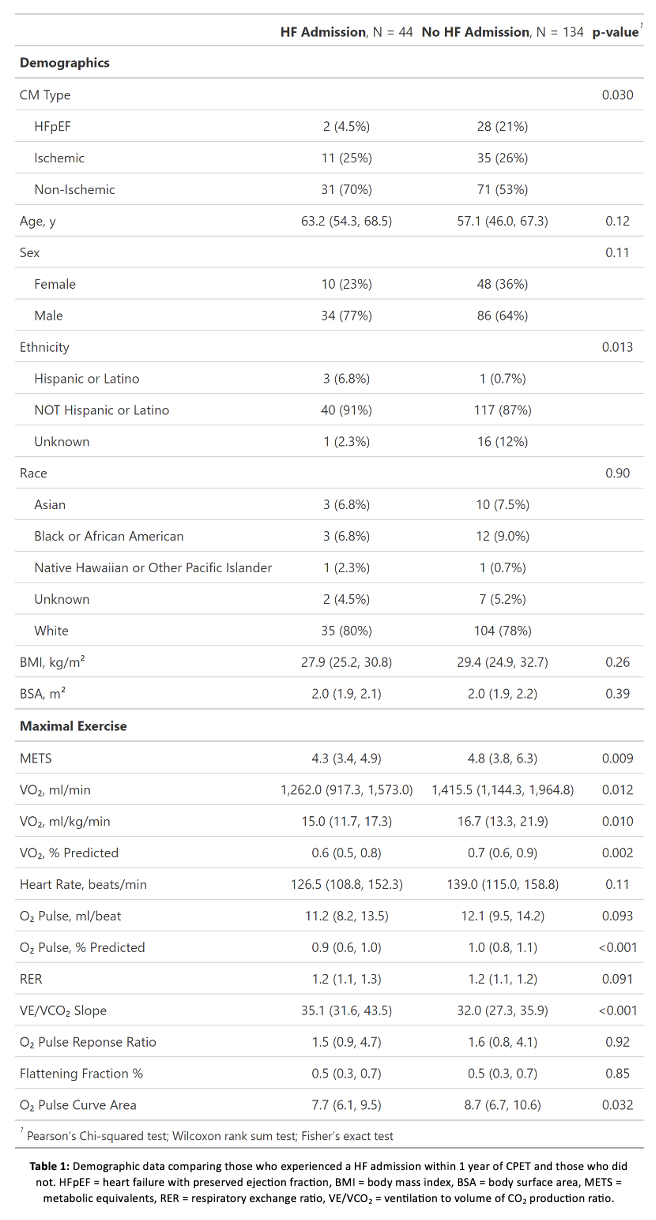
44 (24.7%) patients with CPET were admitted for HF within one year. The model predicted this outcome with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.772. SHAP analysis (Figure 1) selected factors for decision making: pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP) via cardiac catheterization or echocardiogram; oxygen consumption at the ventilatory threshold (VO2 at VT); O2 pulse at rest; ventilatory efficiency (VE/VCO2 slope); minute ventilation per oxygen consumption at maximal exercise (VE/VO2 max) during CPET; left ventricle end diastolic volume by echocardiogram; and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor usage. Peak VO2, predicted VO2, predicted O2 pulse, and VE/VCO2 slope were significant, consistent with past studies (Table 1).
Conclusion
Our XML analysis emphasizes PASP (partially related to high left ventricular filling pressures) and VO2 (at ventilatory threshold) as predictive for HF hospitalization within one year of CPET testing. Studies to prospectively evaluate these highlighted factors are needed to continue exploring predictive capabilities to tailor interventions.
Heart failure (HF) hospitalizations are associated with disease burden and cardiovascular mortality. International guidelines highlight cardiopulmonary testing (CPET) for risk stratification and prognosis in HF. Identifying individuals at risk could direct interventions to prevent admissions. This study uses explainable machine learning (XML) tools to identify CPET and clinical variables predictive of HF hospitalizations.
Hypothesis
XML analysis of CPET parameters and clinical factors can yield accurate, patient-specific prediction of HF admission within one year.
Methods
A retrospective single center review of 178 CPETs in patients referred for HF was completed. Clinical data within one year of CPET trained a boosted machine learning model (XGBoost). SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations) explainability analysis emphasized key features for model predictions.
Results
44 (24.7%) patients with CPET were admitted for HF within one year. The model predicted this outcome with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.772. SHAP analysis (Figure 1) selected factors for decision making: pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP) via cardiac catheterization or echocardiogram; oxygen consumption at the ventilatory threshold (VO2 at VT); O2 pulse at rest; ventilatory efficiency (VE/VCO2 slope); minute ventilation per oxygen consumption at maximal exercise (VE/VO2 max) during CPET; left ventricle end diastolic volume by echocardiogram; and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor usage. Peak VO2, predicted VO2, predicted O2 pulse, and VE/VCO2 slope were significant, consistent with past studies (Table 1).
Conclusion
Our XML analysis emphasizes PASP (partially related to high left ventricular filling pressures) and VO2 (at ventilatory threshold) as predictive for HF hospitalization within one year of CPET testing. Studies to prospectively evaluate these highlighted factors are needed to continue exploring predictive capabilities to tailor interventions.
More abstracts on this topic:
9-Year Longitudinal Assessment of the 12-lead Electrocardiogram of Volunteer Firefighters
Bae Alexander, Dzikowicz Dillon, Lai Chi-ju, Brunner Wendy, Krupa Nicole, Carey Mary, Tam Wai Cheong, Yu Yichen
A Simple One-Item Nursing Falls Assessment Predicts Outcomes For Patients With Stage D Heart Failure Undergoing Surgical Advanced TherapiesSalvador Vincent, Perez Jaime Abraham, Hudec Paige, Gorodeski Eiran, Oneill Thomas