Final ID: Sa3021
SGLT2i And Cardio-Renal Outcomes In Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Diabetes Mellitus (DM) significantly impacts global health through cardiovascular and renal complications. SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) have emerged as beneficial for cardiovascular outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). However, only few studies report outcomes related to renal function.
Aim: This study aims to analyse the efficacy of SGLT2i on cardiorenal outcomes in adults with T2DM.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis, following PRISMA-2020 guidelines was conducted. We evaluated the efficacy of SGLT2i on cardiorenal outcomes in adults with T2DM. We included randomized controlled trials(RCT) and post hoc analyses that compared SGLT2i with placebo, focusing on cardiovascular mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, heart failure hospitalizations, and renal outcomes such as the progression of albuminuria and the decline of eGFR. Dichotomous outcomes were calculated using relative risk (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI).
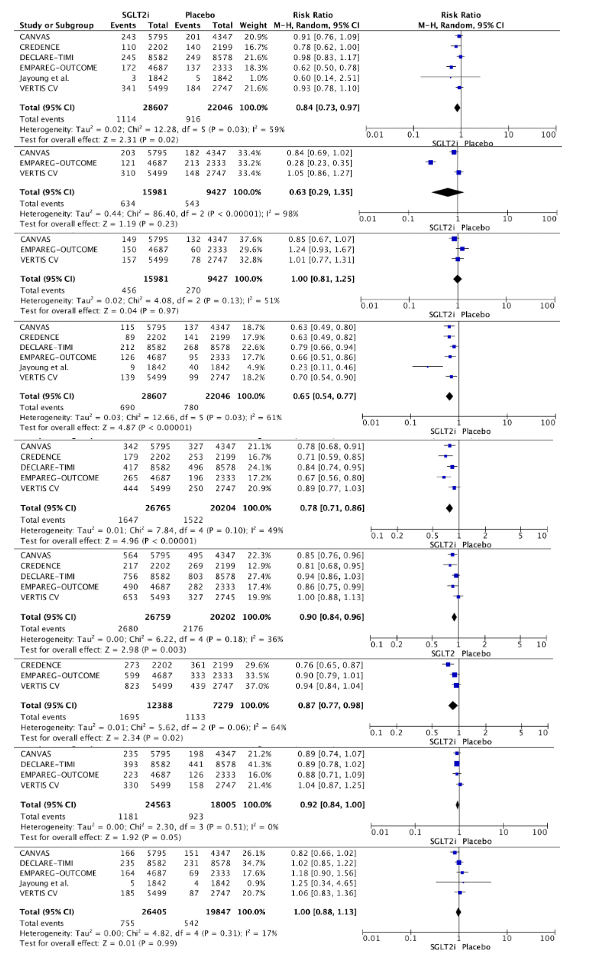
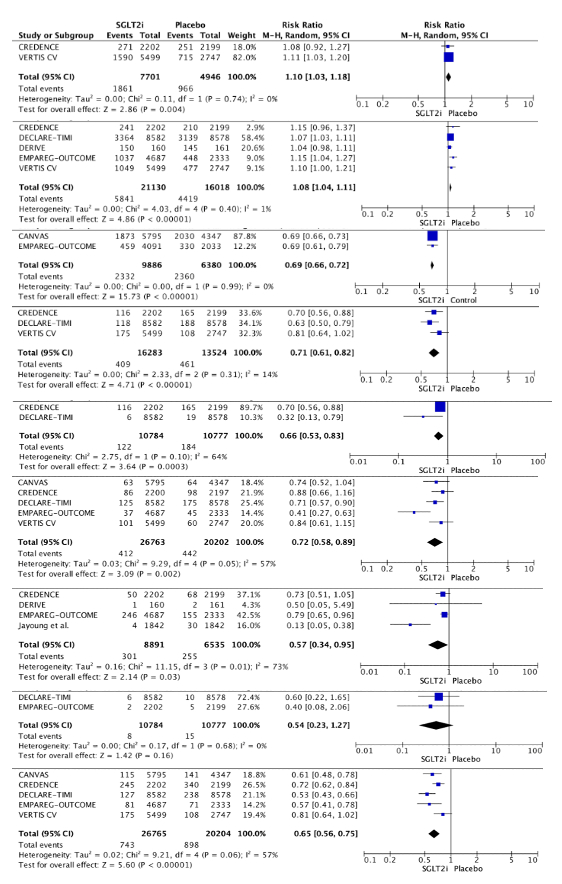
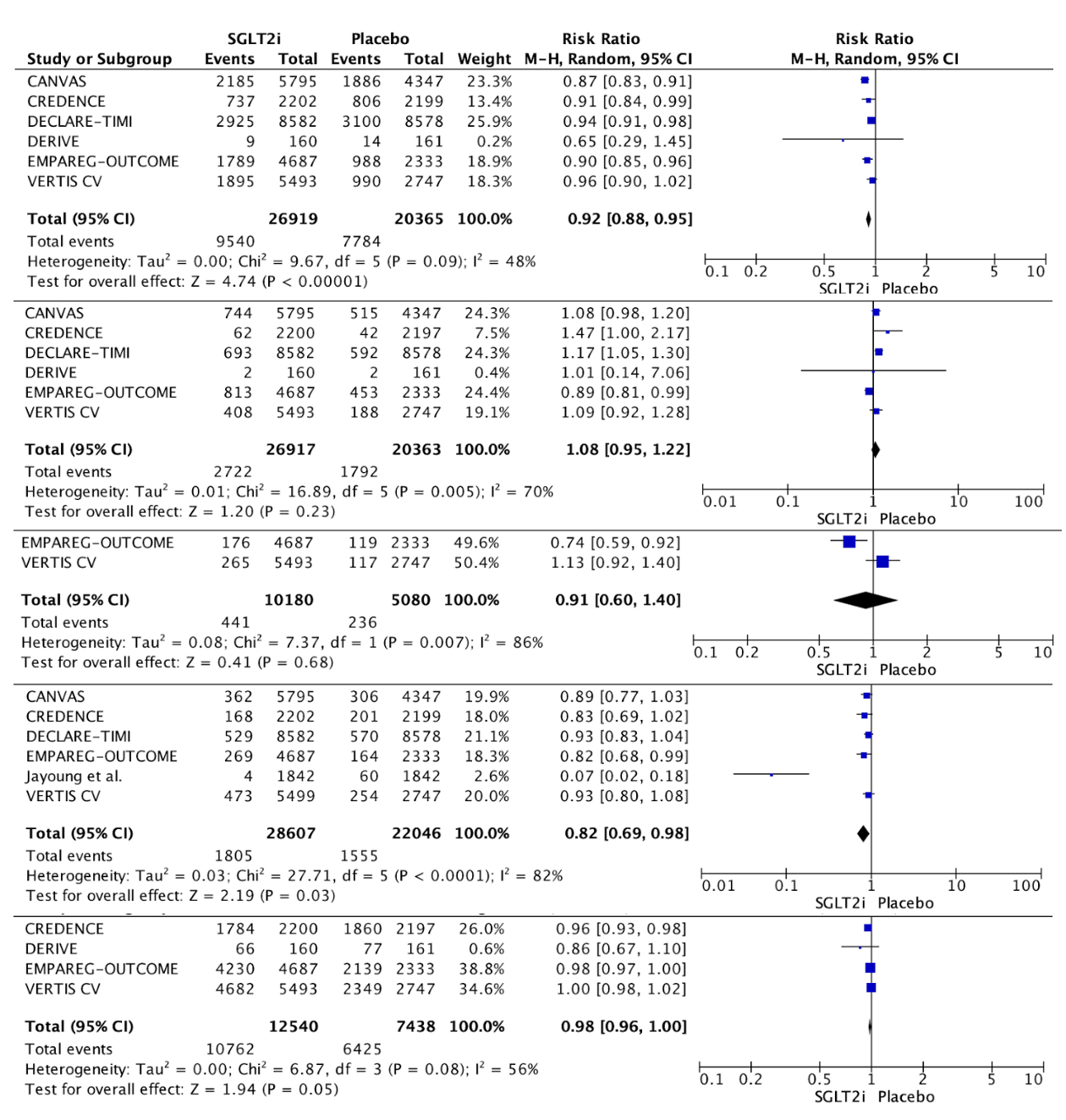
Results: We identified 2753 studies, registered in PubMed(=788), Embase(n=538), WoS(n=369), Scopus(n=908), and Cochrane(n=150). We included 11 studies 6 RCT and 7 Post Hoc Analysis, sample size of 50.653 patients. Meta-analysis showed that SGLT2i improve cardiovascular outcomes such as reduced cardiovascular mortality (RR 0.84 [95% CI 0.73–0.97] p=0.02), heart failure hospitalizations (RR 0.65 [95%CI 0.54–0.77]p<0.00001), and their composites outcomes. Furthermore, renal outcomes with SGLT2i significantly improve Urinary Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (RR1.10 [95%CI 1.03–1.18]p=0.004), Improvement of the decline of the eGFR (RR1.08 [95%CI 1.04–1.11] p<0.00001) and progression of albuminuria (RR 0.69[95%CI 0.66–0.72]p<0.00001). Slower Doubling of serum creatinine (RR 0.71 [95% CI 0.61–0.82] p<0.00001), end-stage kidney disease (RR 0.66 [95% CI 0.53–0.83] p=0.0003). Reduced Acute Kidney Injury (RR 0.72 [95% CI 0.58–0.89] p=0.002) and renal impairment (RR 0.57 [95% CI 0.34–0.95] p=0.03). Regarding death from renal causes, we identified a 46% relative reduction in the risk in SGLT2i group, although was not statistically significant (RR 0.54 [95% CI: 0.23, 1.27] p=0.16). The observed heterogeneity across studies calls for careful application of these results to individual patients.
Conclusion: SGLT2i confers notable advantages in managing cardiorenal complications in T2DM, demonstrating a reduction in cardiovascular mortality and heart failure hospitalizations and offering a nephroprotective effect.
Aim: This study aims to analyse the efficacy of SGLT2i on cardiorenal outcomes in adults with T2DM.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis, following PRISMA-2020 guidelines was conducted. We evaluated the efficacy of SGLT2i on cardiorenal outcomes in adults with T2DM. We included randomized controlled trials(RCT) and post hoc analyses that compared SGLT2i with placebo, focusing on cardiovascular mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, heart failure hospitalizations, and renal outcomes such as the progression of albuminuria and the decline of eGFR. Dichotomous outcomes were calculated using relative risk (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI).
Results: We identified 2753 studies, registered in PubMed(=788), Embase(n=538), WoS(n=369), Scopus(n=908), and Cochrane(n=150). We included 11 studies 6 RCT and 7 Post Hoc Analysis, sample size of 50.653 patients. Meta-analysis showed that SGLT2i improve cardiovascular outcomes such as reduced cardiovascular mortality (RR 0.84 [95% CI 0.73–0.97] p=0.02), heart failure hospitalizations (RR 0.65 [95%CI 0.54–0.77]p<0.00001), and their composites outcomes. Furthermore, renal outcomes with SGLT2i significantly improve Urinary Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (RR1.10 [95%CI 1.03–1.18]p=0.004), Improvement of the decline of the eGFR (RR1.08 [95%CI 1.04–1.11] p<0.00001) and progression of albuminuria (RR 0.69[95%CI 0.66–0.72]p<0.00001). Slower Doubling of serum creatinine (RR 0.71 [95% CI 0.61–0.82] p<0.00001), end-stage kidney disease (RR 0.66 [95% CI 0.53–0.83] p=0.0003). Reduced Acute Kidney Injury (RR 0.72 [95% CI 0.58–0.89] p=0.002) and renal impairment (RR 0.57 [95% CI 0.34–0.95] p=0.03). Regarding death from renal causes, we identified a 46% relative reduction in the risk in SGLT2i group, although was not statistically significant (RR 0.54 [95% CI: 0.23, 1.27] p=0.16). The observed heterogeneity across studies calls for careful application of these results to individual patients.
Conclusion: SGLT2i confers notable advantages in managing cardiorenal complications in T2DM, demonstrating a reduction in cardiovascular mortality and heart failure hospitalizations and offering a nephroprotective effect.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Model-Sharing Approach for Quality Improvement of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
Elligers Kyle, Pollner Meghan, Overton Katherine, Congdon Michelle, Greenway Stacey, Lambro Patricia, Sadiku Steven, Schechter Rona, Whelan John, Pressley Bianca, Sednew Renee, Duckett Sara
Characterization and Translational Potential of a Nonhuman Primate Model of Heart Failure with Renal Disease: Insights into Cardio-Renal Syndrome ProgressionDe Villa Flordeliza, Zhu Zhenghua, Zhang Jie, Yang Lichuan, Perez Rosario