Final ID: Mo2120
Effect Of Renal Denervation In Combination With Cardiac Ablation On The Recurrence Of Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Atrial fibrillation(AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia, affecting millions globally. Despite various treatments, recurrence remains high, especially among those with drug-resistant hypertension.
Aim: To evaluate the efficacy of combining Renal Denervation and Cardiac Ablation compared to Cardiac Ablation Alone in reducing AF recurrence.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted following the PRISMA-2020 guidelines, A search for randomized controlled clinical trials was carried out in PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Scopus, and ScienceDirect until March 2024. Specifically, about adult patients aged 18 years and above diagnosed with AF and drug-resistant hypertension undergoing renal denervation and or cardiac ablation. The primary outcome was the recurrence of AF. The secondary outcomes were effects on systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, cardiovascular structural changes, glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). In addition, periprocedural events and major complication events. Dichotomous outcomes were calculated using relative risk (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). For continuous variables, the results were shown considering the mean difference (MD) and standard deviation with 95% CI.
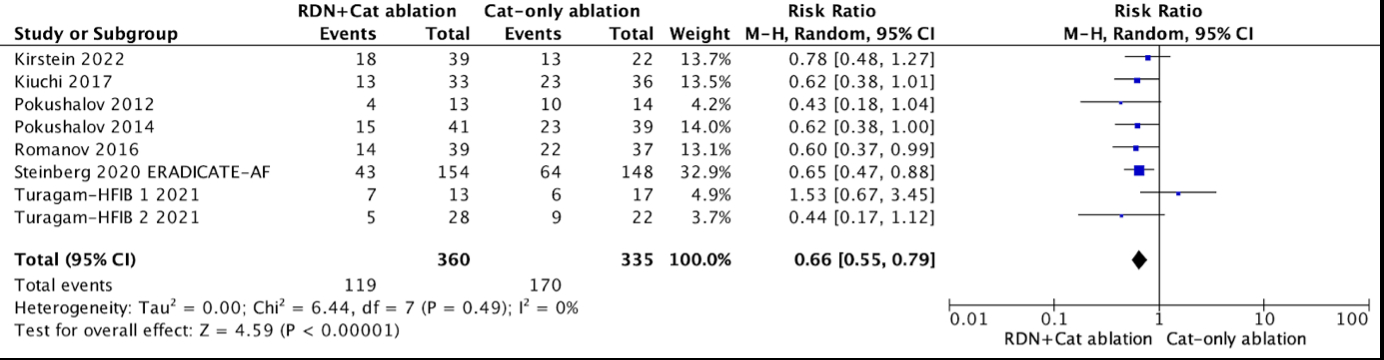
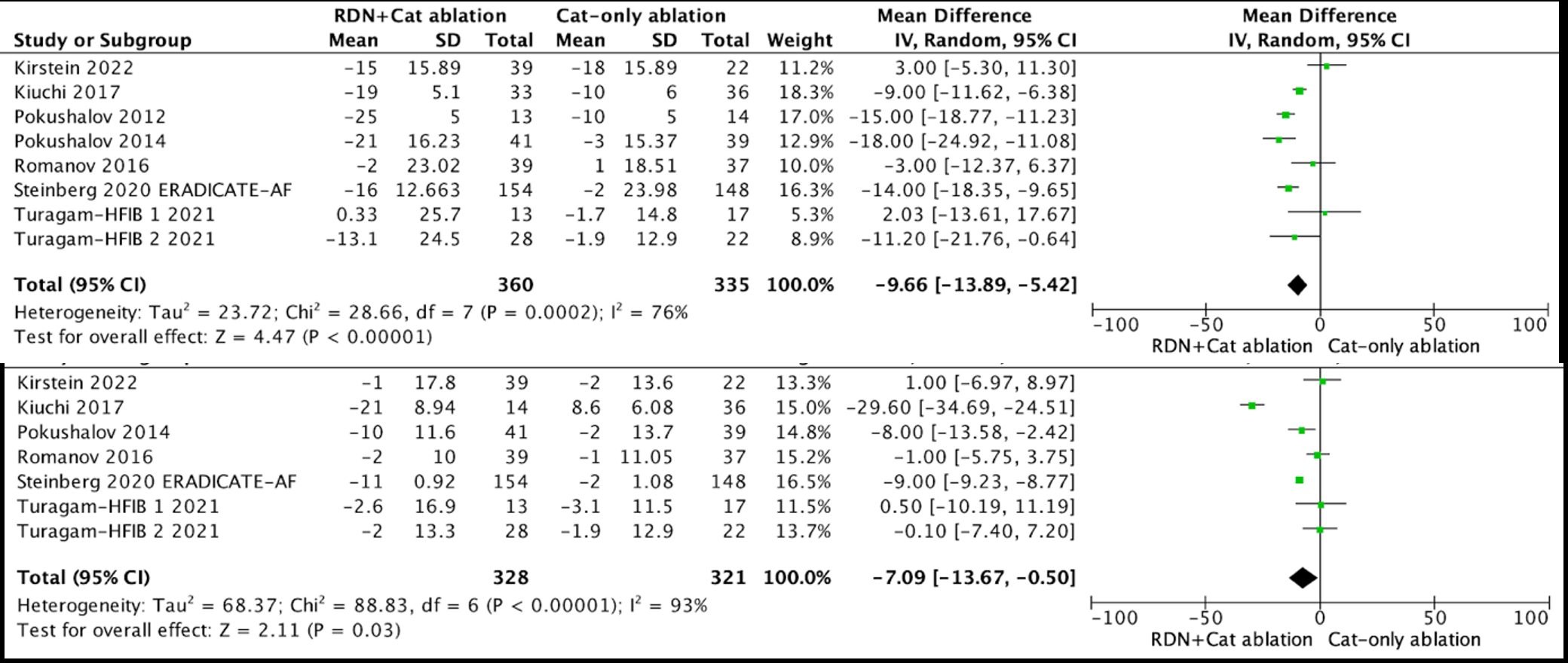
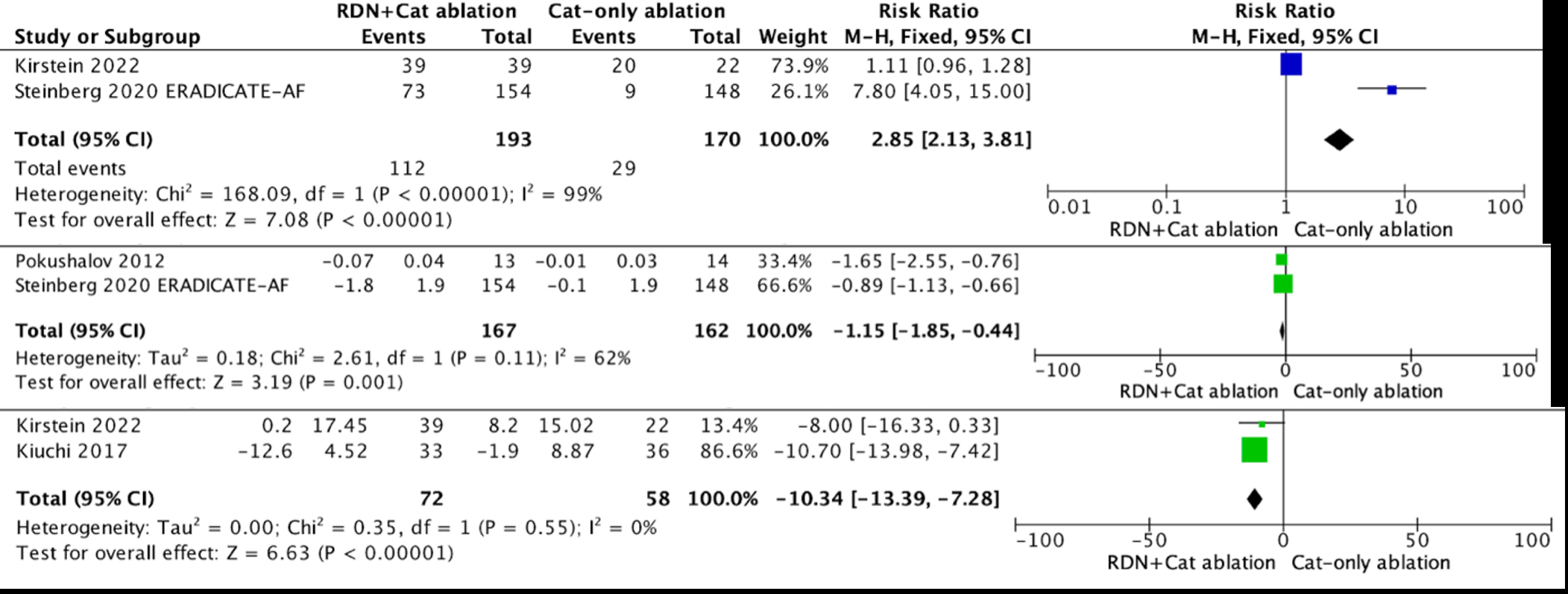
Results: From 409 studies identified, 8 studies and 695 patients were included. Meta-analysis showed a significant reduction in atrial fibrillation recurrence with the combination therapy (HR 0.66 [95% CI=0.55 – 0.79], p=0.00001). Blood pressure outcomes were superior in the combination group, with reductions in both systolic (MD = -9.66 mmHg [95% CI: -13.89, -5.42], p=0.00001) and diastolic pressures (MD = -7.09 mmHg [95% CI: -13.67, -0.50], p=0.003). Cardiovascular structural changes, such as left atrial size (RR 2.85 [95% CI: 2.13, 3.81], p=0.00001) and interventricular septal thickness (MD = -1.15 [95% CI: -1.85, -0.44], p=0.003), also favored the combination therapy. Kidney function, measured by eGFR was better preserved (MD = -10.34 [95% CI: -13.39, -7.28], p<0.00001).
Conclusion: The combination of RDN and CA is more effective than CA alone in reducing the recurrence of AF, with additional benefits in blood pressure control, cardiovascular structural improvements, and renal function preservation.
Aim: To evaluate the efficacy of combining Renal Denervation and Cardiac Ablation compared to Cardiac Ablation Alone in reducing AF recurrence.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted following the PRISMA-2020 guidelines, A search for randomized controlled clinical trials was carried out in PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Scopus, and ScienceDirect until March 2024. Specifically, about adult patients aged 18 years and above diagnosed with AF and drug-resistant hypertension undergoing renal denervation and or cardiac ablation. The primary outcome was the recurrence of AF. The secondary outcomes were effects on systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, cardiovascular structural changes, glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). In addition, periprocedural events and major complication events. Dichotomous outcomes were calculated using relative risk (RR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). For continuous variables, the results were shown considering the mean difference (MD) and standard deviation with 95% CI.
Results: From 409 studies identified, 8 studies and 695 patients were included. Meta-analysis showed a significant reduction in atrial fibrillation recurrence with the combination therapy (HR 0.66 [95% CI=0.55 – 0.79], p=0.00001). Blood pressure outcomes were superior in the combination group, with reductions in both systolic (MD = -9.66 mmHg [95% CI: -13.89, -5.42], p=0.00001) and diastolic pressures (MD = -7.09 mmHg [95% CI: -13.67, -0.50], p=0.003). Cardiovascular structural changes, such as left atrial size (RR 2.85 [95% CI: 2.13, 3.81], p=0.00001) and interventricular septal thickness (MD = -1.15 [95% CI: -1.85, -0.44], p=0.003), also favored the combination therapy. Kidney function, measured by eGFR was better preserved (MD = -10.34 [95% CI: -13.39, -7.28], p<0.00001).
Conclusion: The combination of RDN and CA is more effective than CA alone in reducing the recurrence of AF, with additional benefits in blood pressure control, cardiovascular structural improvements, and renal function preservation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Artificial-Intelligence Based Tracking of Atrial Fibrillation Waves that Exit Pulmonary Veins Predicts Response to Ablation
Anbazhakan Suhaas, Abad Juan Ricardo Carlos, Ruiperez-campillo Samuel, Rodrigo Miguel, Narayan Sanjiv
A novel ECG algorithm using stepwise approach for accurate localization of premature ventricular contraction and ventricular tachycardia: SMART-PVC/VTKhalaph Moneeb, Lucas Philipp, Sciacca Vanessa, Beyer Sebastian, Moersdorf Maximilian, Sohns Christian, Guckel Denise, Sommer Philipp, Trajkovska Nadica, Deneke Thomas, Didenko Maxim, El Hamriti Mustapha, Imnadze Guram, Fink Thomas, Braun Martin, Bergau Leonard