Final ID: Sa1001
Epinephrine for In-hospital Cardiac Arrest: Effect and Time to Return of Spontaneous Circulation
Abstract Body: Introduction:
Epinephrine is the mainstay of drug treatment during cardiac arrest and it is firmly established that it promotes Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC). In this study we aimed to describe the effect and occurrence of ROSC after administering epinephrine to hospitalized patients with primary pulseless electrical activity (PEA), i.e., administered during PEA as the first recorded arrest rhythm.
Method:
We investigated 78 episodes of primary PEA registered between Aug. 2018 and Oct. 2022 at St. Olav University Hospital (Trondheim, Norway). In 36 episodes, the first dose of epinephrine was administered during primary PEA and registered with minute precision. We created different time dependent covariate profiles for the effect of epinephrine, starting at 0 (time of administration), rising linearly to 1 (presumed maximum effect) and decreasing to 0 immediately thereafter. Time to presumed maximum effect started at 5 seconds (s) after administration and increased in steps of 5s until 300s. We entered each of these different covariate profiles into separate Cox regression models using time to ROSC as outcome obtaining in total 60 Hazard ratios (HR) from all the models.
Results:
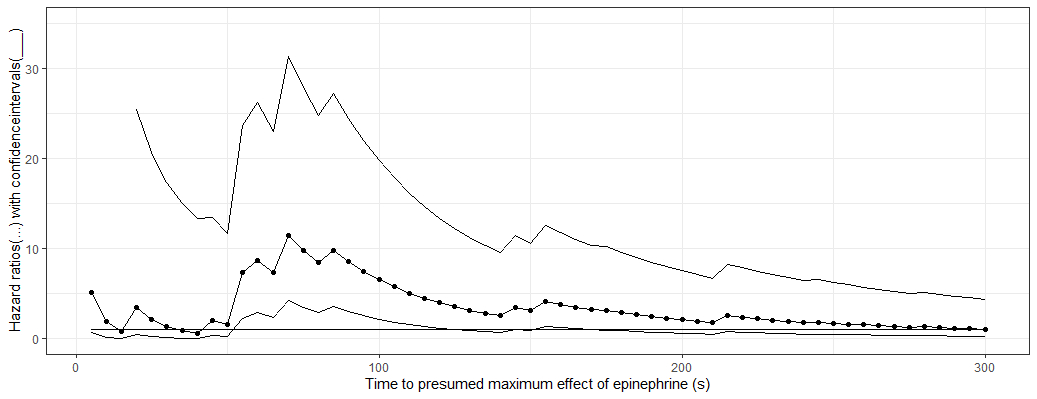
Median time to epinephrine administration was 185s (range 80 to 310) after start of resuscitation. In total, 23 patients obtained ROSC after the administration of epinephrine and 15 patients obtained ROSC without epinephrine. The different hazard ratios (y-axis) were plotted against the location of the maximum point of the covariate profile (x-axis) in Fig. 1. HR peaked twice, at 70 and 155s, 11.4(p< 0.001) and 4.1(p= 0.013), respectively.
Discussion: This study indicates a strong effect of epinephrine during primary PEA 1-2 min after administration. This information may provide the treating team with useful insight on what to expect after administering epinephrine. In addition, the actual effect may be even larger, as the sickest patients (expected to respond less well to epinephrine) are more often monitored and thus recieve epinephrine earlier.
Epinephrine is the mainstay of drug treatment during cardiac arrest and it is firmly established that it promotes Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC). In this study we aimed to describe the effect and occurrence of ROSC after administering epinephrine to hospitalized patients with primary pulseless electrical activity (PEA), i.e., administered during PEA as the first recorded arrest rhythm.
Method:
We investigated 78 episodes of primary PEA registered between Aug. 2018 and Oct. 2022 at St. Olav University Hospital (Trondheim, Norway). In 36 episodes, the first dose of epinephrine was administered during primary PEA and registered with minute precision. We created different time dependent covariate profiles for the effect of epinephrine, starting at 0 (time of administration), rising linearly to 1 (presumed maximum effect) and decreasing to 0 immediately thereafter. Time to presumed maximum effect started at 5 seconds (s) after administration and increased in steps of 5s until 300s. We entered each of these different covariate profiles into separate Cox regression models using time to ROSC as outcome obtaining in total 60 Hazard ratios (HR) from all the models.
Results:
Median time to epinephrine administration was 185s (range 80 to 310) after start of resuscitation. In total, 23 patients obtained ROSC after the administration of epinephrine and 15 patients obtained ROSC without epinephrine. The different hazard ratios (y-axis) were plotted against the location of the maximum point of the covariate profile (x-axis) in Fig. 1. HR peaked twice, at 70 and 155s, 11.4(p< 0.001) and 4.1(p= 0.013), respectively.
Discussion: This study indicates a strong effect of epinephrine during primary PEA 1-2 min after administration. This information may provide the treating team with useful insight on what to expect after administering epinephrine. In addition, the actual effect may be even larger, as the sickest patients (expected to respond less well to epinephrine) are more often monitored and thus recieve epinephrine earlier.
More abstracts on this topic:
Calmodulin Kinase II is a Mutation-Specific Driver of Disease in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hauck Garrett, Vasquez Catherine, Lynn Melissa, Klass Matthew, Langlais Paul, Hamilton Shanna, Tardiff Jil
Agency Epinephrine Dosing Intervals and Patient Characteristics in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A National EMS StudyDefilippo Michael, Braude Darren, Root Christopher, Covert Harold, Fisher Benjamin, Huebinger Ryan