Final ID: Su404
Time difference between pad placement in double versus single external defibrillation: a live patient simulation model
Abstract Body: BACKGROUND: Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) cause significant patient morbidity and mortality. Double sequential external defibrillation (DSED) represents an alternative treatment for OHCA patients, but the use is currently reserved for patients in refractory ventricular fibrillation. However, OHCA patients may achieve return of spontaneous circulation earlier with the use of DSED as the initial treatment.
AIMS: To compare the necessary times needed to establish pad placement in DSED compared to standard pad placement in a live patient simulation model.
METHODS: This study was an observational cohort study with ambulance personnel and live patient models. Two-member teams established two defibrillators ready for rhythm analysis. Time spent for standard pad placement and DSED was registered in the same procedure. The procedure was performed on two patient categories, with BMI 20,9 (patient A) and BMI 32,8 (patient B). All team members performed the procedure on both patient categories.
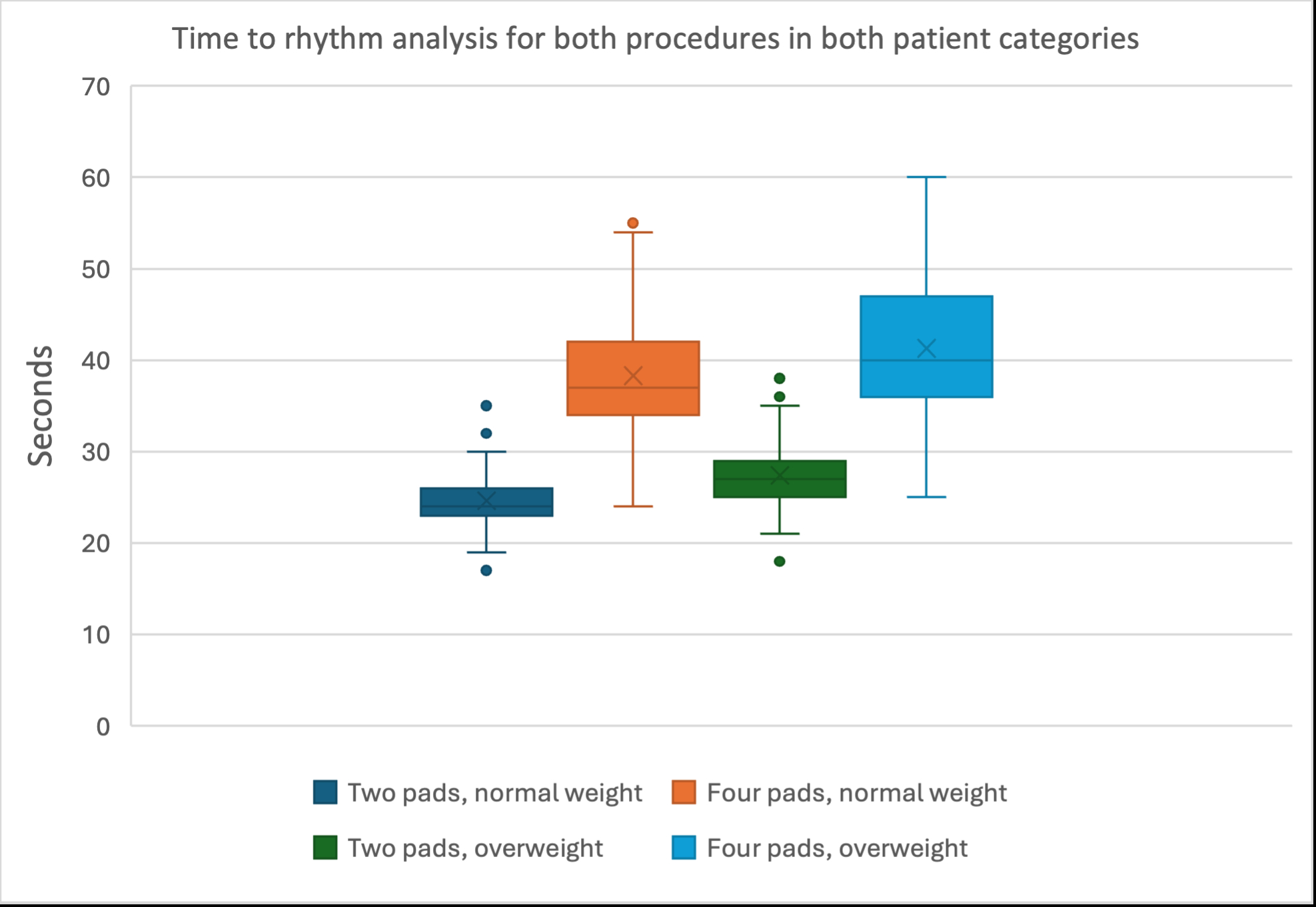
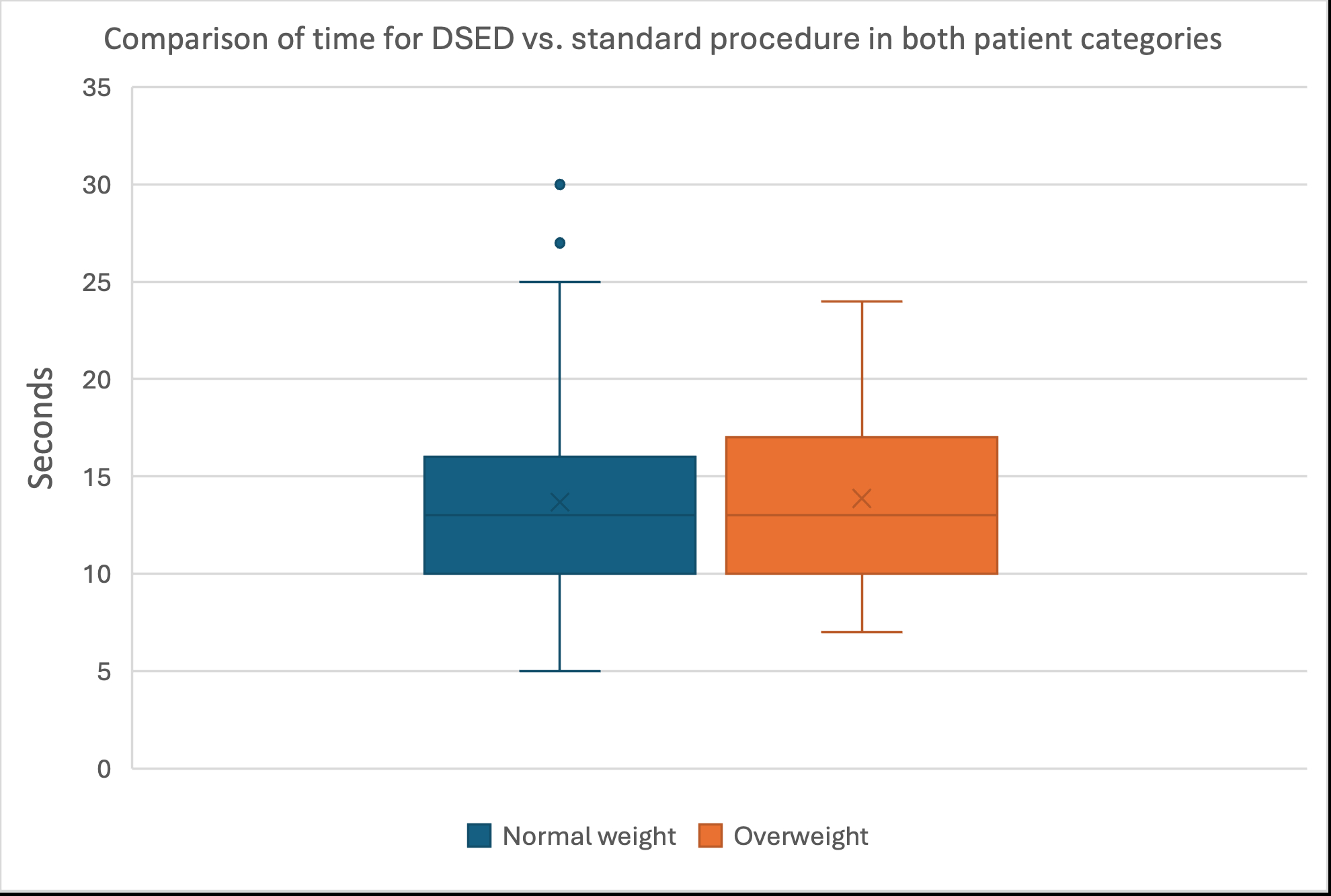
RESULTS: In total, 108 procedures were performed on both patient categories. Mean difference in time needed for DSED versus standard pad placement was 13.7 ± 4.8 seconds for patient A, and 13.9 ± 4.6 seconds for patient B. There was no significant difference in time spent between the two patient categories (p=0.725).
CONCLUSION: The necessary time to establish DSED versus standard defibrillation pad placement was short. This may support clinical studies on DSED as initial treatment for OHCA patients without risk of significant increase in time to first defibrillation.
AIMS: To compare the necessary times needed to establish pad placement in DSED compared to standard pad placement in a live patient simulation model.
METHODS: This study was an observational cohort study with ambulance personnel and live patient models. Two-member teams established two defibrillators ready for rhythm analysis. Time spent for standard pad placement and DSED was registered in the same procedure. The procedure was performed on two patient categories, with BMI 20,9 (patient A) and BMI 32,8 (patient B). All team members performed the procedure on both patient categories.
RESULTS: In total, 108 procedures were performed on both patient categories. Mean difference in time needed for DSED versus standard pad placement was 13.7 ± 4.8 seconds for patient A, and 13.9 ± 4.6 seconds for patient B. There was no significant difference in time spent between the two patient categories (p=0.725).
CONCLUSION: The necessary time to establish DSED versus standard defibrillation pad placement was short. This may support clinical studies on DSED as initial treatment for OHCA patients without risk of significant increase in time to first defibrillation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Abdominal Aortic Compression with Ultrasound is Safe and Demonstrates Effect on Cardiac Output in Healthy Volunteers on Non-Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring
Jafry Zan, Truong Natalie, Dinh Vi, Joe Yuna
Airway Opening Index is Associated with Return of Spontaneous Circulation in Swine and Humans with Cardiac ArrestBhandari Shiv, Coult Jason, Sharpe Zachary, Rea Thomas, Neumar Robert, Hsu Cindy, Counts Catherine, Sayre Michael, Johnson Nicholas