Final ID: MDP1554
Cardiac Consequences of Acute Mania: A Case of Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TCM) is a transient condition characterized by left ventricular dysfunction, often triggered by stress, although its exact pathogenesis remains unclear. We are presenting a case of TCM triggered by an acute manic episode, shedding light on the interplay between psychological states and cardiac function. Additionally, this case underscores the heightened risk of QT prolongation and ventricular fibrillation associated with antipsychotic medications.
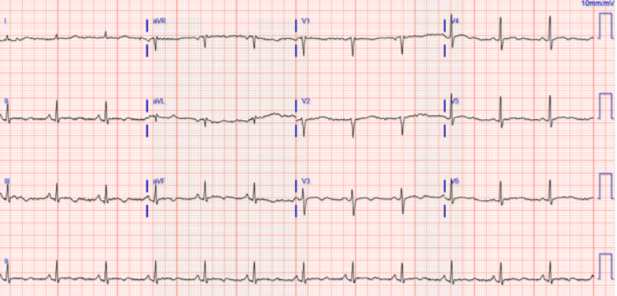
Case Description: A 32-year-old female with a history of bipolar I disorder was admitted to the psychiatric unit for an acute manic episode and was immediately started on Olanzapine. On the second day of admission, the patient collapsed and was found to be in ventricular fibrillation. After three cycles of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and two direct current shocks, the patient achieved a return of spontaneous circulation and sinus rhythm. She was intubated and transferred to the ICU, where an EKG revealed a QTc of 497 ms (Figure.2). A follow-up EKG after 12 hours showed dynamic T-wave inversions and a prolonged QTc of 615 ms (Figure.1). Echocardiography indicated apical akinesis with severely decreased systolic function, with an ejection fraction of 30%. CT coronary angiography was normal. The patient was diagnosed with Takotsubo cardiomyopathy and started on metoprolol. On the fourth day of admission, an automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator was implanted. At six-month follow-up, the patient's EKG showed a normal QTc of 420 ms (Figure. 2), and echocardiography demonstrated an improved ejection fraction of 55%.
Conclusion: This case supports the hypothesis of catecholamine-induced myocardial stunning as a primary mechanism of TCM, illustrated here in the context of acute mania. Physicians should consider TCM as a potential complication of acute mania. Screening EKGs in patients experiencing manic episodes could be beneficial. If abnormalities are detected, serial EKGs, echocardiography, and medication adjustments may help prevent this potentially fatal consequence of acute mania. Although Olanzapine is not strongly linked to QTc prolongation compared to some other atypical antipsychotics, diligent electrocardiographic monitoring and close observation for any QTc prolongation are crucial. These measures play a pivotal role in preventing potentially fatal consequences associated with cardiac arrhythmias.
Case Description: A 32-year-old female with a history of bipolar I disorder was admitted to the psychiatric unit for an acute manic episode and was immediately started on Olanzapine. On the second day of admission, the patient collapsed and was found to be in ventricular fibrillation. After three cycles of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and two direct current shocks, the patient achieved a return of spontaneous circulation and sinus rhythm. She was intubated and transferred to the ICU, where an EKG revealed a QTc of 497 ms (Figure.2). A follow-up EKG after 12 hours showed dynamic T-wave inversions and a prolonged QTc of 615 ms (Figure.1). Echocardiography indicated apical akinesis with severely decreased systolic function, with an ejection fraction of 30%. CT coronary angiography was normal. The patient was diagnosed with Takotsubo cardiomyopathy and started on metoprolol. On the fourth day of admission, an automatic implantable cardioverter-defibrillator was implanted. At six-month follow-up, the patient's EKG showed a normal QTc of 420 ms (Figure. 2), and echocardiography demonstrated an improved ejection fraction of 55%.
Conclusion: This case supports the hypothesis of catecholamine-induced myocardial stunning as a primary mechanism of TCM, illustrated here in the context of acute mania. Physicians should consider TCM as a potential complication of acute mania. Screening EKGs in patients experiencing manic episodes could be beneficial. If abnormalities are detected, serial EKGs, echocardiography, and medication adjustments may help prevent this potentially fatal consequence of acute mania. Although Olanzapine is not strongly linked to QTc prolongation compared to some other atypical antipsychotics, diligent electrocardiographic monitoring and close observation for any QTc prolongation are crucial. These measures play a pivotal role in preventing potentially fatal consequences associated with cardiac arrhythmias.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Recalled Experience of Death Among Cardiac Arrest Survivors Is Associated with Improved Psychological Outcomes
Goins Imani, Ingram Cambell, Wei Lijing, Gonzales Anelly, He Tun, Moore Sacha, Parnia Sam
Depression and anxiety increase risk of chronic kidney disease via gain of CVD risk factors with an accentuated effect among women and non-white individualsAbikaram Krystel, Assefa Alula, Ahmad Taha, Radfar Azar, Seligowski Antonia, Nigwekar Sagar, Tawakol Ahmed, Osborne Michael, Saeed Fatima, Abohashem Shady, Lau Hui Chong, Khalil Maria, Arora Gagan, Bellinge Jamie, Civieri Giovanni, Aldosoky Wesam