Final ID: Sa203
Association between dynamic cerebral perfusion indices by NIRS and cerebral microvascular flow during CPR in a porcine cardiac arrest model
Abstract Body: [Background] Maintaining cerebral blood flow during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) significantly impacts the neurological outcome of patients after cardiac arrest. However, dynamic indicator of cerebral blood flow during CPR is not established. Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) can continuously detect cerebral blood volume changes in a non-invasive way. The aim of this study is to compare cerebral perfusion during CPR obtained by NIRS-based assessment of continuous cerebral perfusion indices (CPI) with cerebral microvascular flow (CMF) using laser doppler flowmetry (LDF) in a ventricular fibrillation (VF) porcine model with free intracranial pressure (ICP).
[Methods] CPI and CMF during CPR were measured in 5 swine (40± 3 kg). After craniotomy and head up condition to create free ICP environment, NIRS probe was placed on brain surface directly in the middle of the craniotomy. In the upper left or right corner of the craniotomy, an LDF probe was inserted to measure cortical CMF. Aortic blood pressure (ABP) was measured at same time to assess the quality of chest compression. Following baseline measurements, VF was electrically induced. After the interval of 6 min untreated VF, CPR was continued for 24 min, during which mechanical and manual CPR was alternated at every 4 min intervals. To make a variety of cerebral blood flow by chest compressions, high quality CPR was performed during Mechanical CPR while low quality CPR was purposely performed during manual. CPI, CMF and ABP were measured continuously during CPR. Each median value in 5 sec was regarded as trend. Correlations between CPI and CMF, as well as CPI and ABP, were analyzed by Pearson correlation coefficient and Spearman's rank correlation.
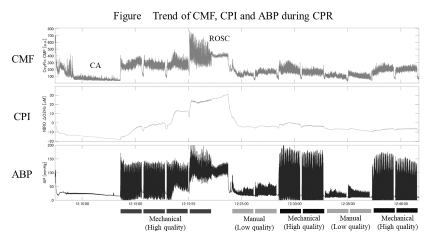
[Results] Poor data measurements were observed in 2 out of 5 cases for CPI and in 3 cases for CMF. One of 5 cases were eligible for analysis. The followability of CPI to CMF and ABP during CPR was good. CPI and CMF tended to increase during high quality CPR, while both CPI and CMF decreased during low quality CPR (Figure). Pearson's correlation coefficient and Spearman's rank correlation coefficient between CPI and CMF during CPR of analyzable data were 0.71 (p < 0.001) and 0.52 (p < 0.001), respectively. Similarly, CPI and ABP were 0.86 (p<0.001) and 0.67 (p<0.001).
[Conclusions] It was suggested that CPI by NIRS can reflect the CMF during CPR with free ICP environment.
[Methods] CPI and CMF during CPR were measured in 5 swine (40± 3 kg). After craniotomy and head up condition to create free ICP environment, NIRS probe was placed on brain surface directly in the middle of the craniotomy. In the upper left or right corner of the craniotomy, an LDF probe was inserted to measure cortical CMF. Aortic blood pressure (ABP) was measured at same time to assess the quality of chest compression. Following baseline measurements, VF was electrically induced. After the interval of 6 min untreated VF, CPR was continued for 24 min, during which mechanical and manual CPR was alternated at every 4 min intervals. To make a variety of cerebral blood flow by chest compressions, high quality CPR was performed during Mechanical CPR while low quality CPR was purposely performed during manual. CPI, CMF and ABP were measured continuously during CPR. Each median value in 5 sec was regarded as trend. Correlations between CPI and CMF, as well as CPI and ABP, were analyzed by Pearson correlation coefficient and Spearman's rank correlation.
[Results] Poor data measurements were observed in 2 out of 5 cases for CPI and in 3 cases for CMF. One of 5 cases were eligible for analysis. The followability of CPI to CMF and ABP during CPR was good. CPI and CMF tended to increase during high quality CPR, while both CPI and CMF decreased during low quality CPR (Figure). Pearson's correlation coefficient and Spearman's rank correlation coefficient between CPI and CMF during CPR of analyzable data were 0.71 (p < 0.001) and 0.52 (p < 0.001), respectively. Similarly, CPI and ABP were 0.86 (p<0.001) and 0.67 (p<0.001).
[Conclusions] It was suggested that CPI by NIRS can reflect the CMF during CPR with free ICP environment.
More abstracts on this topic:
Evaluation Of The Use Of Assistive Technology In Teaching Basic Life Support For People With Hearing Impairment
Bueno Claudia, Gomes Ester, Da Silva Almeida Gildecley, Martin Joelma, Varao Thawanny, Mattei De Araujo Juliana, Santos De Santana Bruna Rutiele, Da Silva Francielly, Costa Joenny, Cunha Carneiro Maria Angelica, Da Silva Ferreira Laíse Jorrana, Farias Pinho Gustavo
Association Between Kidney Function and Severity of White Matter Hyperintensity: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities StudyLittig Lauren, Krothapalli Neeharika, Wong Ka-ho, Kim Yvonne, Smith Harper, De Havenon Adam