Final ID: Sa207
Early Nebulized Inhaled Nitroglycerin Enhances Carotid Blood Flow Without Compromising Coronary Perfusion Pressure During CPR in a Swine Cardiac Arrest Model
Abstract Body: Introduction/Background: Pulmonary vasodilators reduce pulmonary vascular resistance and may improve blood flow during CPR. However, most are not available outside of an ICU setting. Nitroglycerin is an inexpensive pulmonary vasodilator that EMS widely uses to treat chest pain.
Research Questions/Hypothesis: We hypothesized that nebulized, inhaled nitroglycerin (NIN) would improve carotid blood flow (CBF) without reducing coronary perfusion (CPP) or arterial pressures.
Goals/Aims: The principal aim of this investigation was to assess the hemodynamic effects of NIN administered during CPR in a swine model of cardiac arrest.
Methods/Approach: N=17 Mixed breed Yorkshire swine (54+5 kg) were sedated, intubated, and placed under isoflurane general anesthesia. Following instrumentation with arterial and right atrial pressure catheters as well as a carotid flow probe, the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) was titrated to achieve a PaO2 of 80-100 mmHg. Ventricular fibrillation (VF) was then induced with a pacing catheter, and the ventilator turned off. After 7 minutes of untreated VF, mechanical chest compressions with a LUCAS device were initiated. Three minutes later, mechanical ventilation was resumed at prearrest settings with 100% FiO2. Two minutes later, 5 mL of either nebulized normal saline (NNS controls, n=9) or 10 mg of nitroglycerin (NIN treatment, n=8) was delivered through a nebulizer placed in line with the endotracheal tube, by random allocation. After 4 minutes of nebulized treatment, IV epinephrine (0.15 mg/kg) was administered, followed 2 minutes later by defibrillation. NIN or nebulized NS was continued until the volume was fully delivered, while standard ALS resuscitation proceeded until ROSC or 40 min of arrest had elapsed. Data were analyzed using mixed effects models.
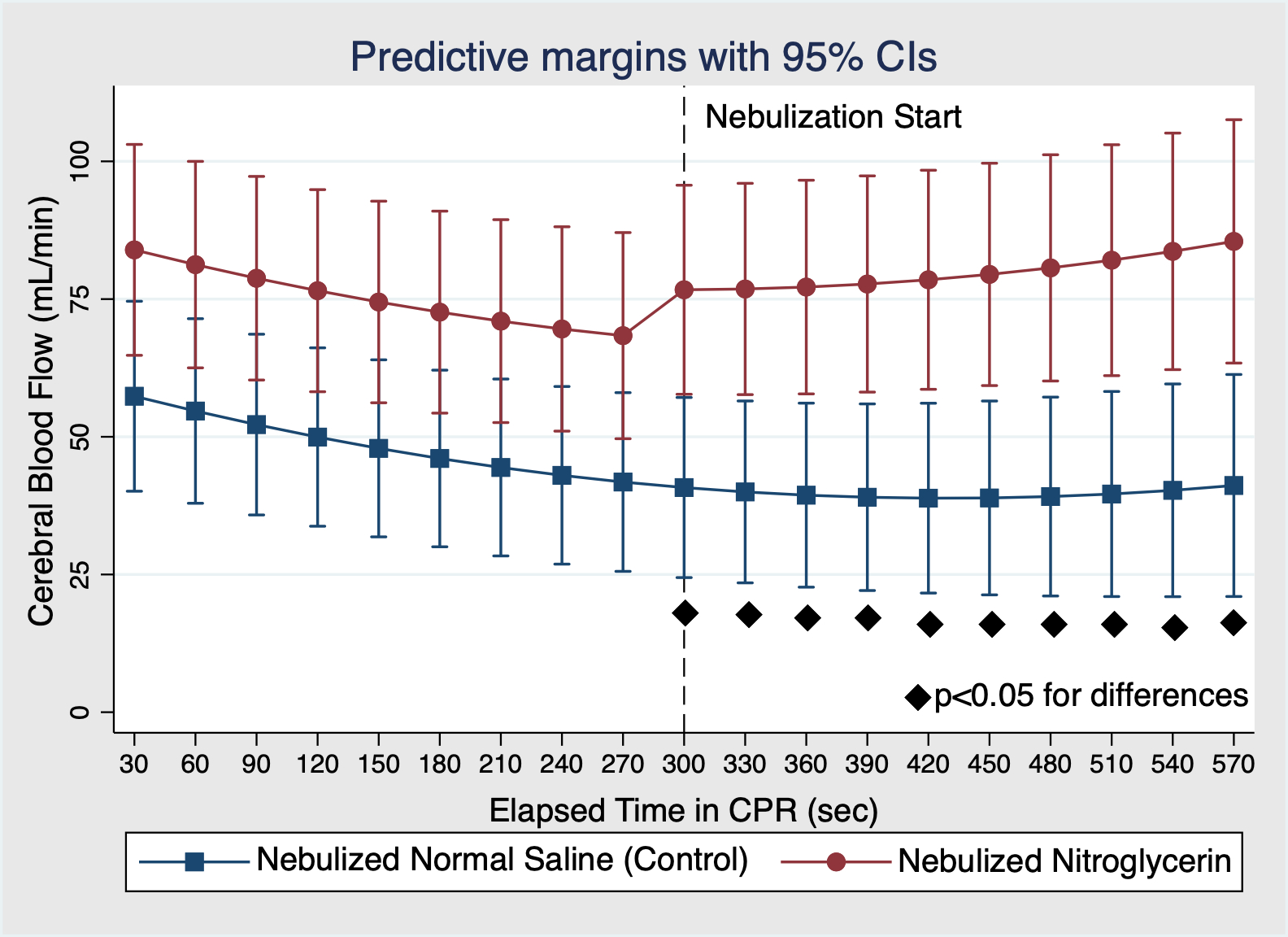
Results/Data: Prearrest hemodynamic and blood gas variables were similar between groups. There were no statistically significant differences in systolic or diastolic arterial pressures or CPP. However, there was a statistically significant increase in CBF following NIN (Figure). After 4 minutes of treatment, CBF in NIN-treated animals was approximately double that of NNS controls: 85 mL/min (95% CI 63-108 mL/min) vs 41 mL/min (95% CI 21-61 mL/min), respectively. ROSC was achieved in 3/9 (33%) NNS controls and in 5/8 (63%) of NIN-treated animals (p=0.23).
Conclusions: In this small study, early NIN treatment resulted in superior CBF without decreasing arterial pressures or CPP.
Research Questions/Hypothesis: We hypothesized that nebulized, inhaled nitroglycerin (NIN) would improve carotid blood flow (CBF) without reducing coronary perfusion (CPP) or arterial pressures.
Goals/Aims: The principal aim of this investigation was to assess the hemodynamic effects of NIN administered during CPR in a swine model of cardiac arrest.
Methods/Approach: N=17 Mixed breed Yorkshire swine (54+5 kg) were sedated, intubated, and placed under isoflurane general anesthesia. Following instrumentation with arterial and right atrial pressure catheters as well as a carotid flow probe, the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) was titrated to achieve a PaO2 of 80-100 mmHg. Ventricular fibrillation (VF) was then induced with a pacing catheter, and the ventilator turned off. After 7 minutes of untreated VF, mechanical chest compressions with a LUCAS device were initiated. Three minutes later, mechanical ventilation was resumed at prearrest settings with 100% FiO2. Two minutes later, 5 mL of either nebulized normal saline (NNS controls, n=9) or 10 mg of nitroglycerin (NIN treatment, n=8) was delivered through a nebulizer placed in line with the endotracheal tube, by random allocation. After 4 minutes of nebulized treatment, IV epinephrine (0.15 mg/kg) was administered, followed 2 minutes later by defibrillation. NIN or nebulized NS was continued until the volume was fully delivered, while standard ALS resuscitation proceeded until ROSC or 40 min of arrest had elapsed. Data were analyzed using mixed effects models.
Results/Data: Prearrest hemodynamic and blood gas variables were similar between groups. There were no statistically significant differences in systolic or diastolic arterial pressures or CPP. However, there was a statistically significant increase in CBF following NIN (Figure). After 4 minutes of treatment, CBF in NIN-treated animals was approximately double that of NNS controls: 85 mL/min (95% CI 63-108 mL/min) vs 41 mL/min (95% CI 21-61 mL/min), respectively. ROSC was achieved in 3/9 (33%) NNS controls and in 5/8 (63%) of NIN-treated animals (p=0.23).
Conclusions: In this small study, early NIN treatment resulted in superior CBF without decreasing arterial pressures or CPP.
More abstracts on this topic:
Improving Bystander CPR Knowledge and Preparedness Among Secondary School Students and Healthcare Workers in Ikare-Akoko, Nigeria.
Oturoko Mayowa, Chang Mary
Improving CPR Quality Through Feedback Devices: A Randomized Simulation Trial Among Critical and Non-Critical Care NursesPolastri Thatiane, Peres Heloisa, Tobase Lucia, Timerman Sergio, Vattimo Maria De Fatima, Coelho Filipe Utuari De Andrade