Final ID: Sa204
Mitochondrial transplantation improves hemodynamics after cardiac arrest and resuscitation in pigs
Abstract Body: Introduction: Mitochondrial transplantation (MTx) is an innovative technology that has the potential to attenuate ischemia-reperfusion injury and improve outcomes. Our recent studies have demonstrated that MTx significantly enhances survival and neurological outcomes after resuscitation in a rat model of cardiac arrest (CA).
Objective: This study aims to evaluate whether MTx, applied immediately after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), can improve cardiovascular parameters during the acute phase following CA and resuscitation using a pig ventricular fibrillation (VF)-induced CA model.
Methods: Sixteen LWD pigs (age 3-4 weeks, weight 29-34 kg) were subjected to VF-induced CA via intravenous potassium chloride injection. Eight minutes after CA, mechanical ventilation with 100% O2, mechanical chest compressions, and administration of epinephrine and defibrillation according to the current ACLS guidelines with minor modifications. Three pigs that did not achieve ROSC within 20 minutes were excluded from the analysis. Among the remaining 13 pigs, 7 received intravenous respiration buffer as a vehicle (vehicle group, n=7) and 6 received intravenous MTx immediately after ROSC (MTx group, n=6). The donor mitochondria were freshly isolated from rectus femoris muscle of healthy pigs a few hours before MTx. The animals were observed until 240 minutes after ROSC.
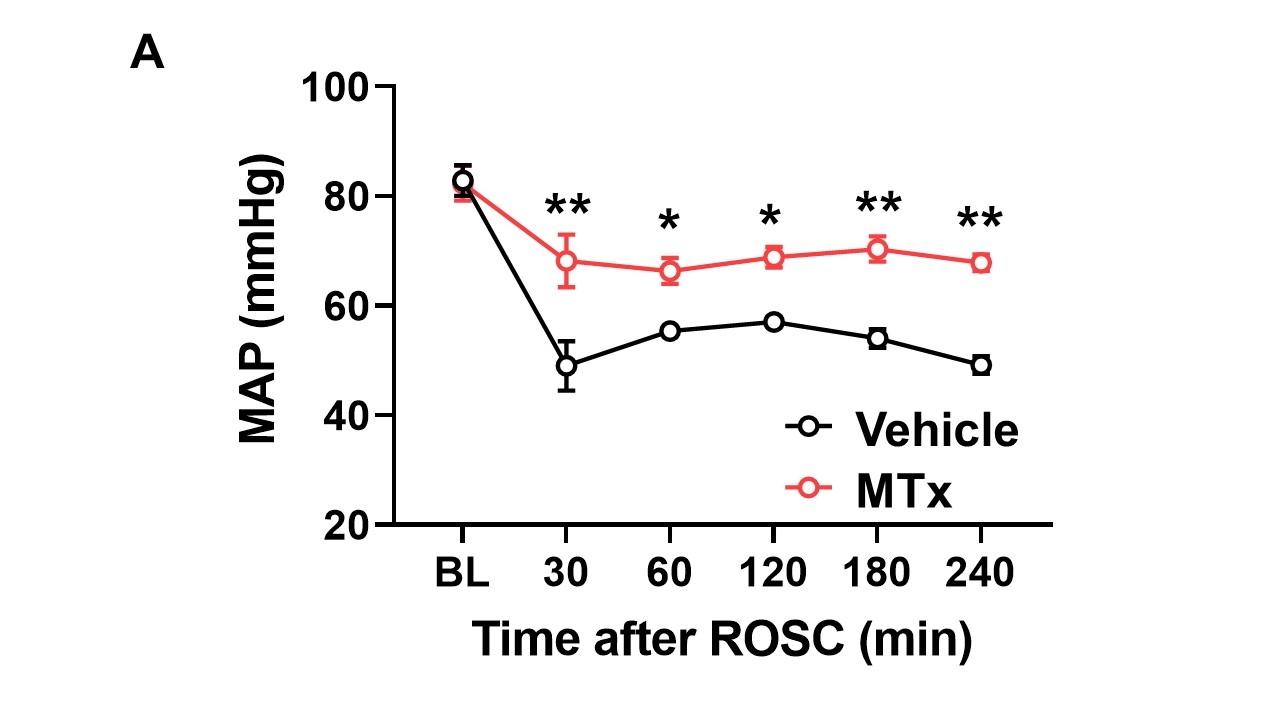
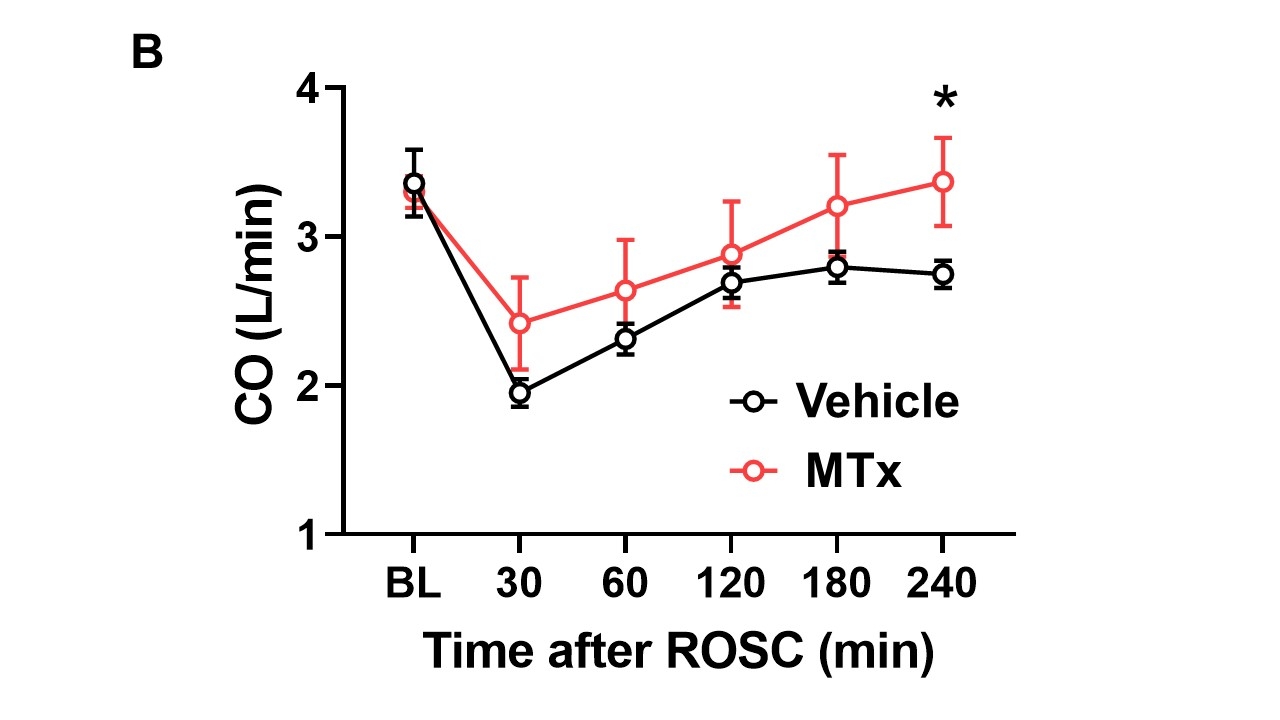
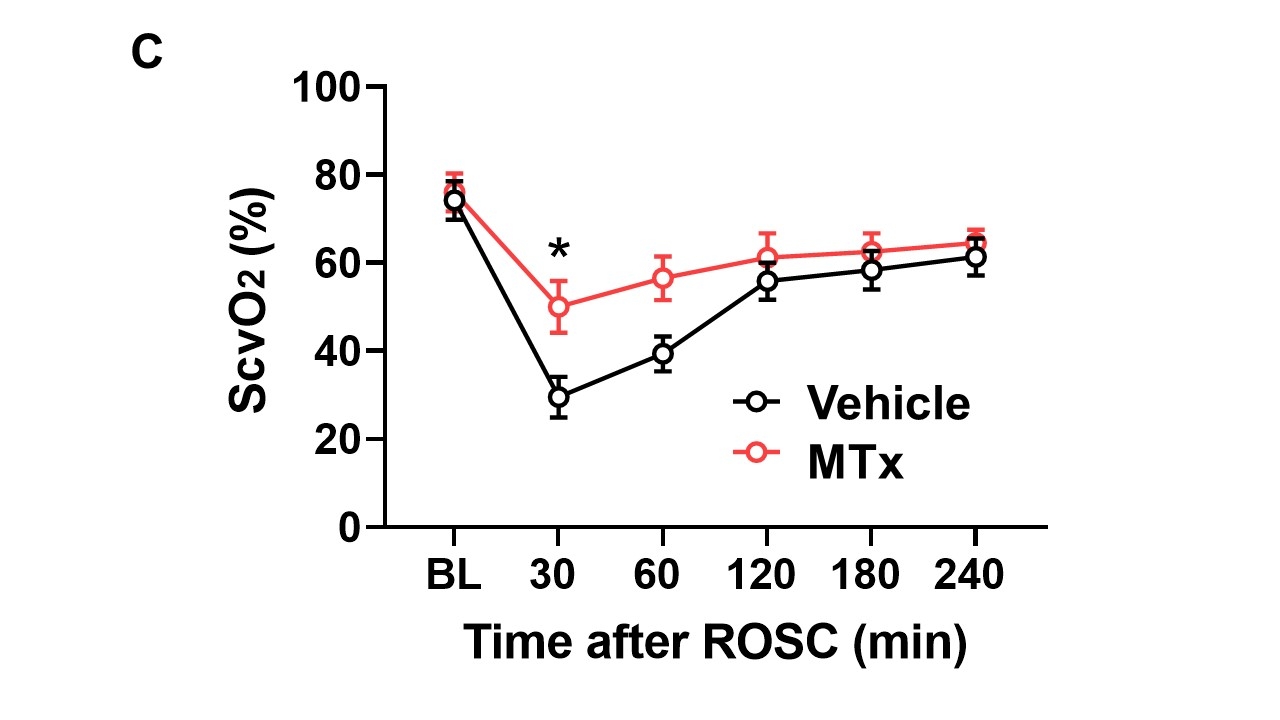
Results: All pigs successfully went into VF-CA after potassium administration. The time to ROSC was 370 ± 184 seconds in the vehicle group and 420 ± 62 seconds in the MTx group, with no significant difference between the two groups. The vehicle group showed a significant decrease in mean arterial pressure (MAP) compared to baseline after ROSC, while the MTx group prevented the decrease in MAP, maintaining significantly higher MAP than the vehicle group (Fig A). Transpulmonary thermodilution revealed that MTx maintained stroke volume and cardiac output (CO) at 240 minutes after ROSC, which were significantly higher than those in the vehicle group (Fig B). Blood gas analysis revealed significantly higher central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) in the MTx group compared to the vehicle group at 30 minutes after ROSC (Fig C).
Conclusions: Intravenous administration of MTx immediately after ROSC improved cardiovascular parameters and maintained the oxygen supply-demand balance in a pig model of CA. MTx shows promising potential for attenuating cardiovascular instability and improving overall outcomes after CA.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate whether MTx, applied immediately after return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), can improve cardiovascular parameters during the acute phase following CA and resuscitation using a pig ventricular fibrillation (VF)-induced CA model.
Methods: Sixteen LWD pigs (age 3-4 weeks, weight 29-34 kg) were subjected to VF-induced CA via intravenous potassium chloride injection. Eight minutes after CA, mechanical ventilation with 100% O2, mechanical chest compressions, and administration of epinephrine and defibrillation according to the current ACLS guidelines with minor modifications. Three pigs that did not achieve ROSC within 20 minutes were excluded from the analysis. Among the remaining 13 pigs, 7 received intravenous respiration buffer as a vehicle (vehicle group, n=7) and 6 received intravenous MTx immediately after ROSC (MTx group, n=6). The donor mitochondria were freshly isolated from rectus femoris muscle of healthy pigs a few hours before MTx. The animals were observed until 240 minutes after ROSC.
Results: All pigs successfully went into VF-CA after potassium administration. The time to ROSC was 370 ± 184 seconds in the vehicle group and 420 ± 62 seconds in the MTx group, with no significant difference between the two groups. The vehicle group showed a significant decrease in mean arterial pressure (MAP) compared to baseline after ROSC, while the MTx group prevented the decrease in MAP, maintaining significantly higher MAP than the vehicle group (Fig A). Transpulmonary thermodilution revealed that MTx maintained stroke volume and cardiac output (CO) at 240 minutes after ROSC, which were significantly higher than those in the vehicle group (Fig B). Blood gas analysis revealed significantly higher central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) in the MTx group compared to the vehicle group at 30 minutes after ROSC (Fig C).
Conclusions: Intravenous administration of MTx immediately after ROSC improved cardiovascular parameters and maintained the oxygen supply-demand balance in a pig model of CA. MTx shows promising potential for attenuating cardiovascular instability and improving overall outcomes after CA.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Case of Adalimumab-Induced Cardiac Tamponade in a Patient with Psoriatic Arthritis
Raval Akhinav, Tran Minh, Saini Ishveen, Rea Mark
Checkpoint Kinase 1 Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Maintaining SIRT1-Dependent Mitochondrial HomeostasisYang Tongtong, Zhou Liu-hua, Shan Tiankai, Wang Hao, Wang Liansheng