Final ID: Su1006
Mean Arterial Pressure During the First 72 hours after Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation is not Associated with Survival to Discharge and Neurologic Outcomes in Children with Cardiac Disease
Abstract Body: Introduction
While studies have shown an association between post-cardiac arrest hypotension and mortality after conventional CPR in children, there is a lack of evidence regarding optimal mean arterial pressure (MAP) targets after ECPR.
Hypothesis
Amongst children with cardiac disease undergoing ECPR, the lowest MAP < 5th percentile for age during the first 72 hours after return of circulation (ROC) is associated with decreased survival to hospital discharge (SHD) with favorable neurologic outcome (FNO).
Methods:
This is a single center retrospective cohort study of children admitted to a pediatric cardiac intensive care unit (CICU) from 2010 to 2022 that underwent ECPR. Chi-square test was used to analyze the association of the lowest MAP values, percentile adjusted for age, during the 72 hours post-ROC with SHD with FNO (defined by Pediatric Cerebral Performance Category [PCPC] score of 1,2 or 3 or no change in PCPC from baseline). Our secondary outcomes included acute composite injury (defined by the presence of seizures in the first 72 hours or neuroimaging injury within 14 days post arrest), and abnormal EEG background (defined as moderate or severe). As an exploratory analysis, we used Wilcoxon Rank Sum test to analyze the association of burden of MAP < 5th percentile for age with our outcomes.
Results:
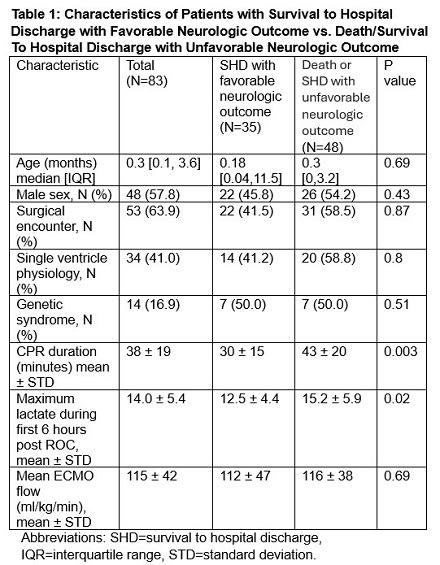
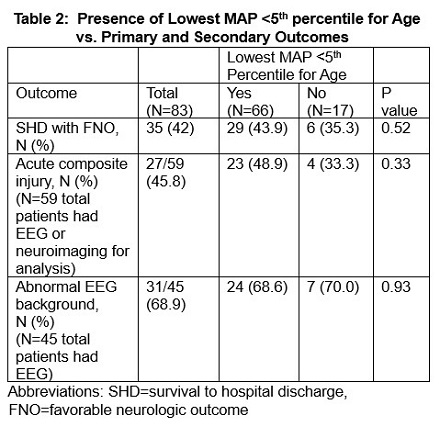
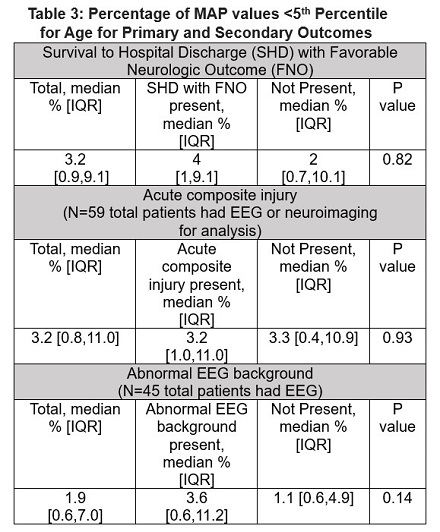
We analyzed 83 index ECPR events. SHD with FNO was observed for 35 index events (42%). Table 1 displays the characteristics of patients with SHD with FNO compared to those who died or had SHD without FNO. Patients with SHD with FNO had shorter duration of CPR and lower maximum lactate during the first 6 hours post ROC compared to both survivors without FNO and non-survivors. The majority of the cohort (79.5%) experienced a lowest MAP < 5th percentile for age during the first 72 hours post-ROC. Table 2 and 3 reveal no associations between MAP < 5th percentile for age and primary or secondary outcomes.
Conclusion
This retrospective cohort study of children with cardiac disease undergoing ECPR reveals no association between MAP < 5th percentile for age during the 72 hours post-ROC and our primary outcome of SHD with FNO as well as secondary outcomes of acute composite injury and abnormal EEG background. Given heterogeneity in the cardiac population as well as the high incidence of hypotension <5th percentile for age in our cohort, further investigation is warranted into whether certain subgroups may benefit from targeting higher MAP values after ECPR.
While studies have shown an association between post-cardiac arrest hypotension and mortality after conventional CPR in children, there is a lack of evidence regarding optimal mean arterial pressure (MAP) targets after ECPR.
Hypothesis
Amongst children with cardiac disease undergoing ECPR, the lowest MAP < 5th percentile for age during the first 72 hours after return of circulation (ROC) is associated with decreased survival to hospital discharge (SHD) with favorable neurologic outcome (FNO).
Methods:
This is a single center retrospective cohort study of children admitted to a pediatric cardiac intensive care unit (CICU) from 2010 to 2022 that underwent ECPR. Chi-square test was used to analyze the association of the lowest MAP values, percentile adjusted for age, during the 72 hours post-ROC with SHD with FNO (defined by Pediatric Cerebral Performance Category [PCPC] score of 1,2 or 3 or no change in PCPC from baseline). Our secondary outcomes included acute composite injury (defined by the presence of seizures in the first 72 hours or neuroimaging injury within 14 days post arrest), and abnormal EEG background (defined as moderate or severe). As an exploratory analysis, we used Wilcoxon Rank Sum test to analyze the association of burden of MAP < 5th percentile for age with our outcomes.
Results:
We analyzed 83 index ECPR events. SHD with FNO was observed for 35 index events (42%). Table 1 displays the characteristics of patients with SHD with FNO compared to those who died or had SHD without FNO. Patients with SHD with FNO had shorter duration of CPR and lower maximum lactate during the first 6 hours post ROC compared to both survivors without FNO and non-survivors. The majority of the cohort (79.5%) experienced a lowest MAP < 5th percentile for age during the first 72 hours post-ROC. Table 2 and 3 reveal no associations between MAP < 5th percentile for age and primary or secondary outcomes.
Conclusion
This retrospective cohort study of children with cardiac disease undergoing ECPR reveals no association between MAP < 5th percentile for age during the 72 hours post-ROC and our primary outcome of SHD with FNO as well as secondary outcomes of acute composite injury and abnormal EEG background. Given heterogeneity in the cardiac population as well as the high incidence of hypotension <5th percentile for age in our cohort, further investigation is warranted into whether certain subgroups may benefit from targeting higher MAP values after ECPR.
More abstracts on this topic:
Comparing visual attention and CPR quality among physicians with variable experience levels in simulated pediatric CPR
Zubrow Michael, Chipman Micheline, Mayer Erika, Ferguson Michael
Adapting Chest Compressions to Variable Chest Dynamics in Out-of-Hospital CPRUriguen Jose Antonio, Leturiondo Mikel, Daya Mohamud, Russell James