Final ID: Sa205
Resuscitation and Antiarrhythmic Effects of Artificial Oxygen Carrier of HbV in Perioperative Severe Hemorrhagic Shock during Total Pneumonectomy Model
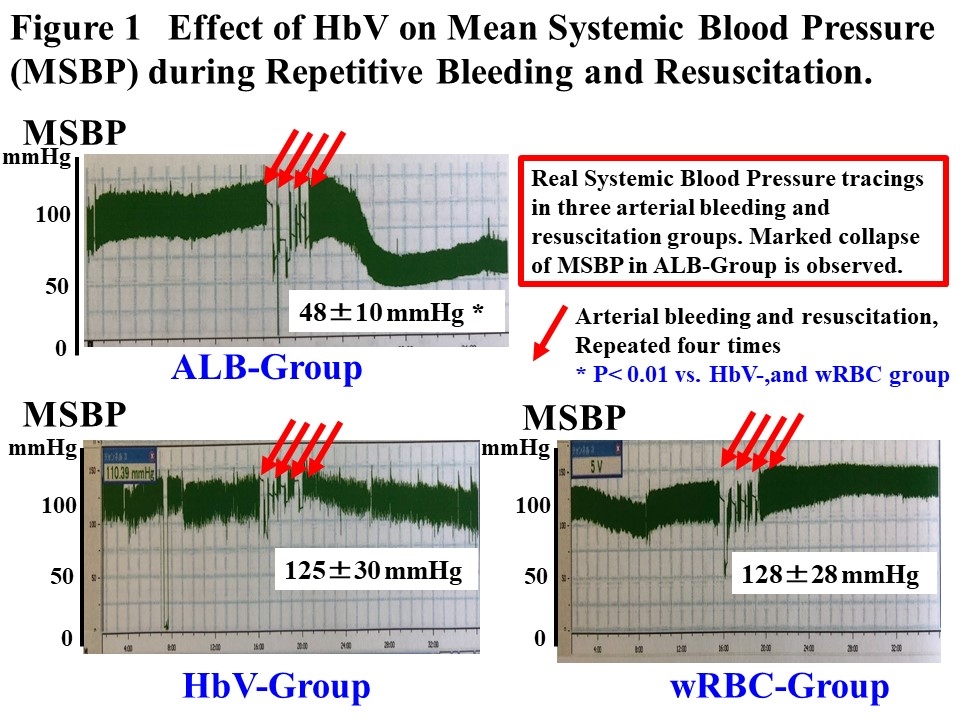
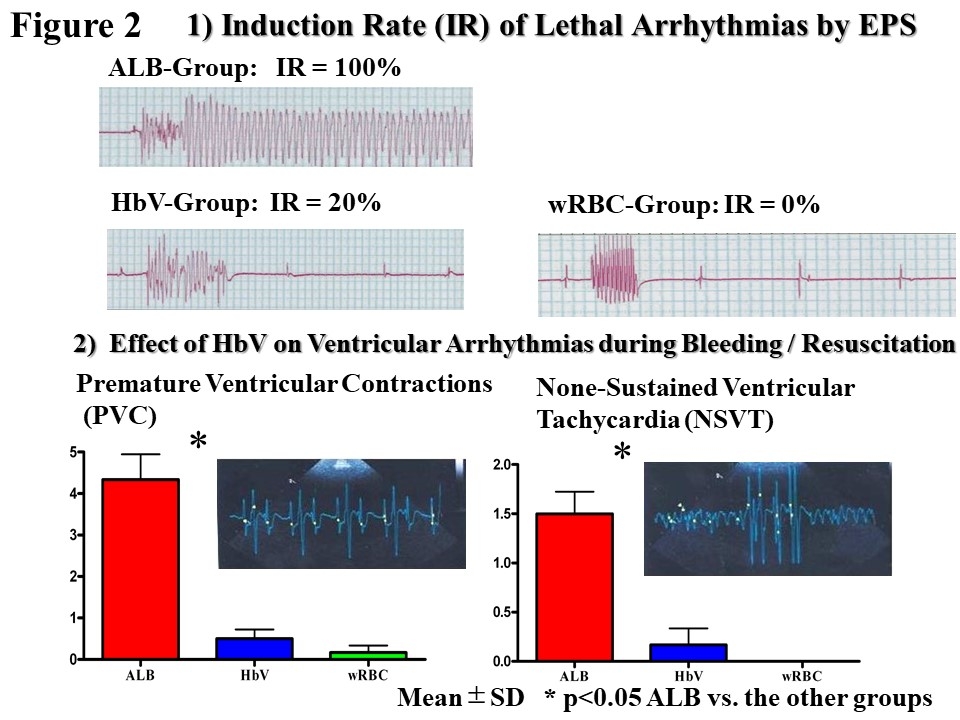
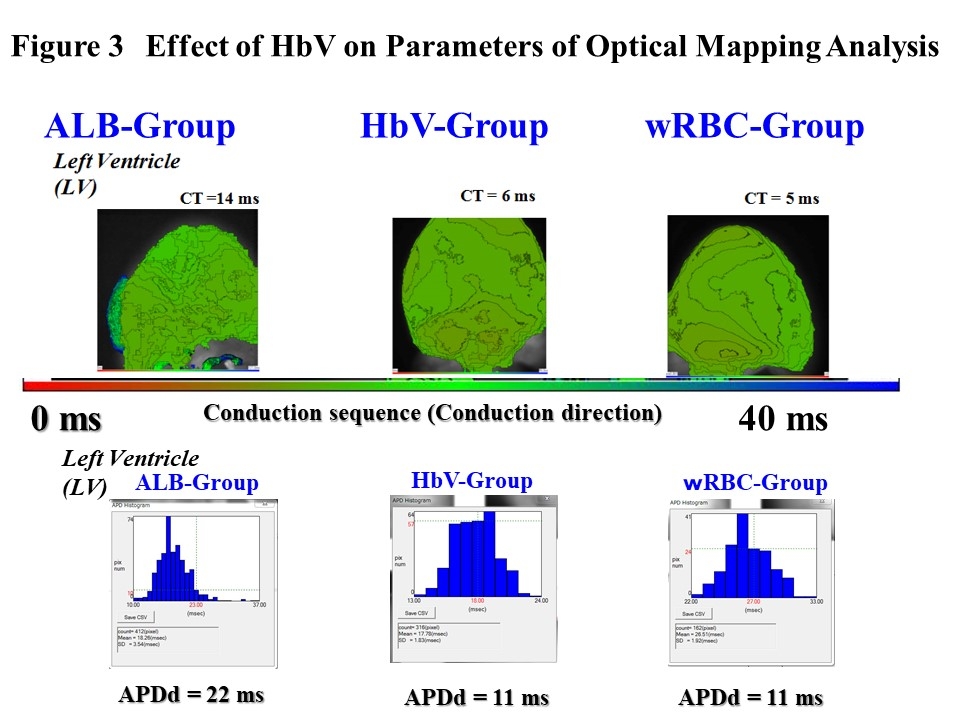
Abstract Body: Perioperative bleeding is fetal complication of thoracic surgery (0.3-1.8% of all lung resection). We reported effects of Liposome-encapsulated hemoglobin vesicle (HbV) in hemorrhagic shock. Phase I clinical trial of HbV was successfully performed. For future clinical trials, we investigated resuscitation and antiarrhythmic effects of HbV in pneumonectomy model by using optical mapping analysis (OMP) with Langendorff's method. Left total pneumonectomy was performed in SD rats (N=30). Immediately after pneumonectomy, repetitive 50% blood hemorrhage and resuscitation were conducted. HbV-administration (HbV-group), washed red blood cell-administration (wRBC-group), and 5% albumin-administration (ALB-group) were studied. Right mean ventricular pressure (RMVBP) and systemic mean blood pressure (SMBP) were measured. OMP including lethal arrhythmia (SVT/VF) induction by electrophysiological study (EPS) was performed. Ventricular arrhythmia (PVC/NSVT) numbers were counted. Blood chemistry of ALT, AST, CPK, Cr, troponin I (TnI) and lactate (LT) were measured. Tissue HIF1alpha expression were examined in heart, lung, liver, kidney and spleen. RMVBP increased to 20±4 to 45±3 mmHg by pneumonectomy, presumably worsening systemic circulation and proarrhythmic effect. Observation for 40 min after resuscitation showed that SMBP remained normal in HbV-group and wRBC-group, but not in ALB-group (Fig. 1). SVT/VF induction and PVC/NSVTs were observed in ALB-group, but suppressed in HbV-group and wRBC-group (Fig. 2). The values of action potential duration dispersion (APDd; index of lethal arrhythmias) in LV determined by OMP was comparable in the HbV-group and wRBC-group (APDd; HbV-group, wRBC-group vs. ALB-group;12±4,14±3 vs. 24±4* ms, P<0.01, Fig. 3). ALT, CPK, TnI and LT were increased in ALB-group only, but not those in HbV- and wRBC-group (values after resuscitation, HbV-group, wRBC-group vs. ALB-group; ALT, 28±8, 24±6 vs. 72±6* U/L; CPK, 241±61,154±76 vs. 732±175* U/L; TnI, 0.21±0.07, 0.21±0.06 vs. 3.54±0.84*ng/mL; LT, 0.8±0.2, 1.1±0.1 vs. 2.6±0.6* mmol/L; *P<0.01). HIF1alpha staining was observed in heart, liver and kidney only in ALB-group, but not in HbV- and wRBC-groups. Conclusions: HbV effectively preserves cardiac circulatory function due to anti-shock effect even in RVMBP overload, and it has anti-hypoxic effect leading to prevent lethal arrhythmias in perioperative hemorrhagic shock following total lung resection, which is useful finding in future HbV trials.
More abstracts on this topic:
AI-based prediction of mortality in patients with ventricular tachycardia
Bandyopadhyay Sabyasachi, Narayan Sanjiv, Sadri Shirin, Brennan Kelly, Ganesan Prash, Clopton Paul, Ruiperez-campillo Samuel, Peralta Esteban, Sillett Charlie, Rogers Albert
1-Year Outcomes After Cardioversion With and Without Anticoagulation in Patients With Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion: A Propensity-Matched AnalysisThangjui Sittinun, Trongtorsak Angkawipa, Kewcharoen Jakrin, Thyagaturu Harshith, Watson Hangyu, Mensah Samuel, Balla Sudarshan, Navaravong Leenhapong