Final ID: Su607
Which would be major? witnessed collapse or bystander resuscitation?
Abstract Body: Background
Witnessed collapse and bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) are two variables commonly used to predict outcomes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). Some published studies have shown that bystander CPR were not significantly associated with outcomes after confounders adjusted. This may imply that witnessed collapse would be a superior prognostic factors beyond bystander CPR.
Hypothesis
Witnessed collapse and bystander CPR may not contribute equally to prehospital return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), and the former may be major.
Aims
To investigate four prediction models for prehospital ROSC using stratification of the witnessed collapse and bystander CPR.
Methods
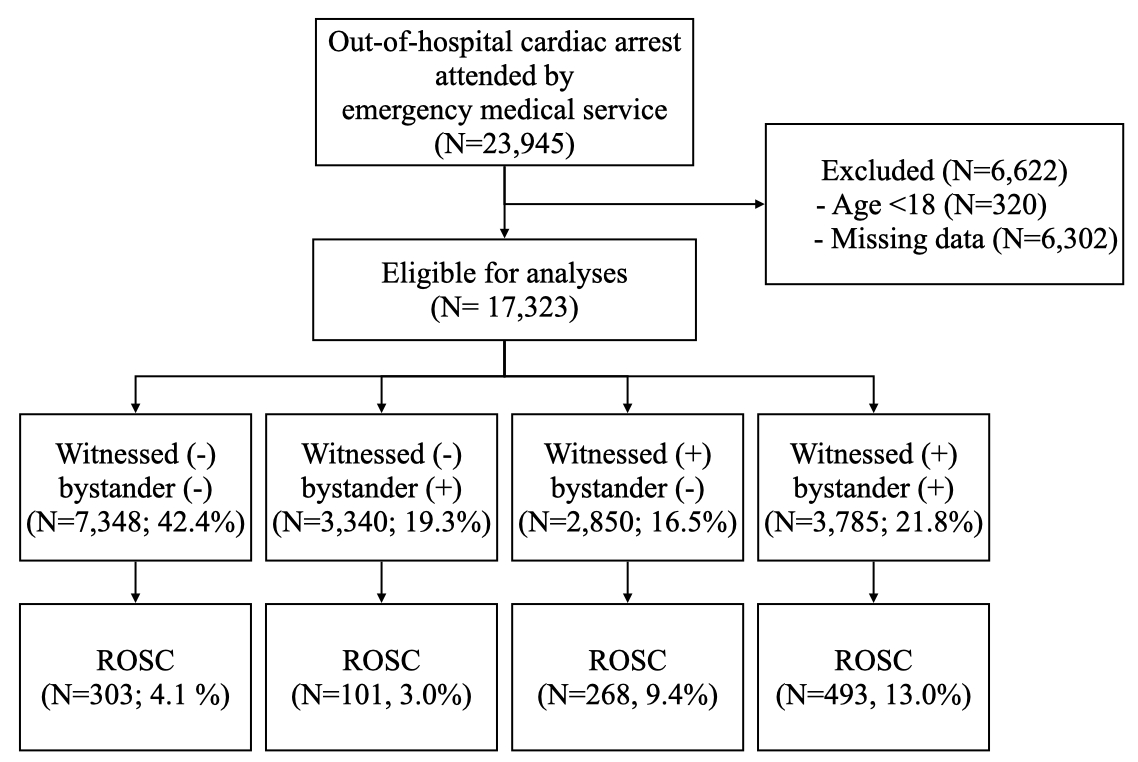
The study enrolled OHCA patients treated by the emergency medical service (EMS) from January 2010 to December 2022 in three EMS systems in Taiwan. Data were extracted from the records of each medical service encounter, including patient demographics, dispatch timing, prehospital management, witnessed collapse and bystander CPR. The primary outcome was any prehospital ROSC. Patients were stratified into four groups by witnessed collapse (with/without) and bystander CPR (with/without) status, namely W+B+, W-B+, W+B- and W-B-. Prehospital ROSC prognostication were identified using multivariable logistic regression analysis.
Results
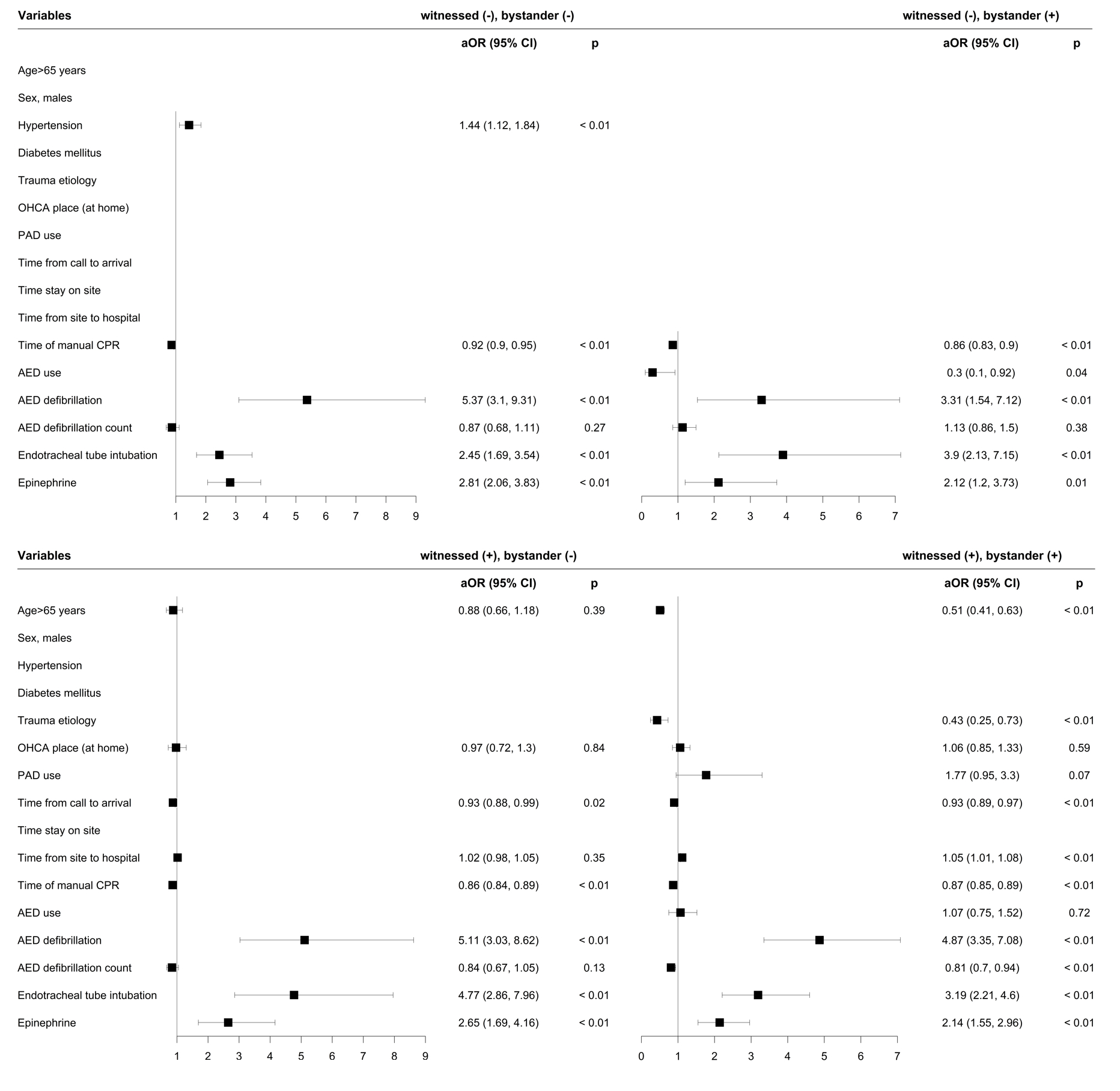
The analysis comprised 17,323 patients, among whom 1,165 (6.7%) achieved prehospital ROSC. The W+B+ group demonstrated the highest prehospital ROSC rate at 13.0%, as compared with the other groups significantly (9.0%, 3.4%, and 4.1%, as depicted in Image 1). Stratification of the prehospital ROSC model (Image 2) indicated that the W+B+ group had several common predictors including age, traumatic arrest, no-flow time, public access defibrillation (PAD), and resuscitation events. However, certain predictors in other groups were removed during regression process. Notably, no-flow time significantly influenced prehospital ROSC only in the W+B+ and W+B- groups. Conversely, in the W-B- group, most variables had minimal impact on prehospital ROSC, reflecting the limited effectiveness of traditional predictors within this subgroup.
Conclusion
The significance of witnessed collapse as a prognostic factor may be equal to or even greater than that of bystander CPR. Further studies are needed to confirm.
Witnessed collapse and bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) are two variables commonly used to predict outcomes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). Some published studies have shown that bystander CPR were not significantly associated with outcomes after confounders adjusted. This may imply that witnessed collapse would be a superior prognostic factors beyond bystander CPR.
Hypothesis
Witnessed collapse and bystander CPR may not contribute equally to prehospital return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), and the former may be major.
Aims
To investigate four prediction models for prehospital ROSC using stratification of the witnessed collapse and bystander CPR.
Methods
The study enrolled OHCA patients treated by the emergency medical service (EMS) from January 2010 to December 2022 in three EMS systems in Taiwan. Data were extracted from the records of each medical service encounter, including patient demographics, dispatch timing, prehospital management, witnessed collapse and bystander CPR. The primary outcome was any prehospital ROSC. Patients were stratified into four groups by witnessed collapse (with/without) and bystander CPR (with/without) status, namely W+B+, W-B+, W+B- and W-B-. Prehospital ROSC prognostication were identified using multivariable logistic regression analysis.
Results
The analysis comprised 17,323 patients, among whom 1,165 (6.7%) achieved prehospital ROSC. The W+B+ group demonstrated the highest prehospital ROSC rate at 13.0%, as compared with the other groups significantly (9.0%, 3.4%, and 4.1%, as depicted in Image 1). Stratification of the prehospital ROSC model (Image 2) indicated that the W+B+ group had several common predictors including age, traumatic arrest, no-flow time, public access defibrillation (PAD), and resuscitation events. However, certain predictors in other groups were removed during regression process. Notably, no-flow time significantly influenced prehospital ROSC only in the W+B+ and W+B- groups. Conversely, in the W-B- group, most variables had minimal impact on prehospital ROSC, reflecting the limited effectiveness of traditional predictors within this subgroup.
Conclusion
The significance of witnessed collapse as a prognostic factor may be equal to or even greater than that of bystander CPR. Further studies are needed to confirm.
More abstracts on this topic:
Agency Epinephrine Dosing Intervals and Patient Characteristics in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A National EMS Study
Defilippo Michael, Braude Darren, Root Christopher, Covert Harold, Fisher Benjamin, Huebinger Ryan
Chest Compression Quality Phenotypes and ROSC in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac ArrestRaya Krishnamoorthy Banu Priya, Daya Mohamud, Nichol Graham, Stephens Shannon, Carlson Jestin, Panchal Ashish, Wang Henry, Nassal Michelle, Gage Christopher, Kamholz Jacob, Elola Andoni, Aramendi Elisabete, Jaureguibeitia Xabier, Idris Ahamed, Aufderheide Tom