Final ID: 48
Effect of Remote Ischemic Conditioning on Functional Outcomes in Patients With Supratentorial Intracerebral Hemorrhage: The Final Results of RICH-2 Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Methods: In this investigator-initiated, multicentre, prospective, randomized, sham-controlled, outcome-blinded parallel-group trial conducted in 20 centers in China, patients (age 18 to 80 years) with supratentorial ICH presenting within 24-48 h of ictus who do not need surgical therapy were randomly allocated (1:1, stratified by baseline NIHSS and clot size) to receive RIC or sham RIC for 7 consecutive days after randomization in addition to best medical management. The primary outcome was a score of 0-2 on the modified Rankin Scale at 90 days, analyzed in the intention-to-treat population. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04657133.
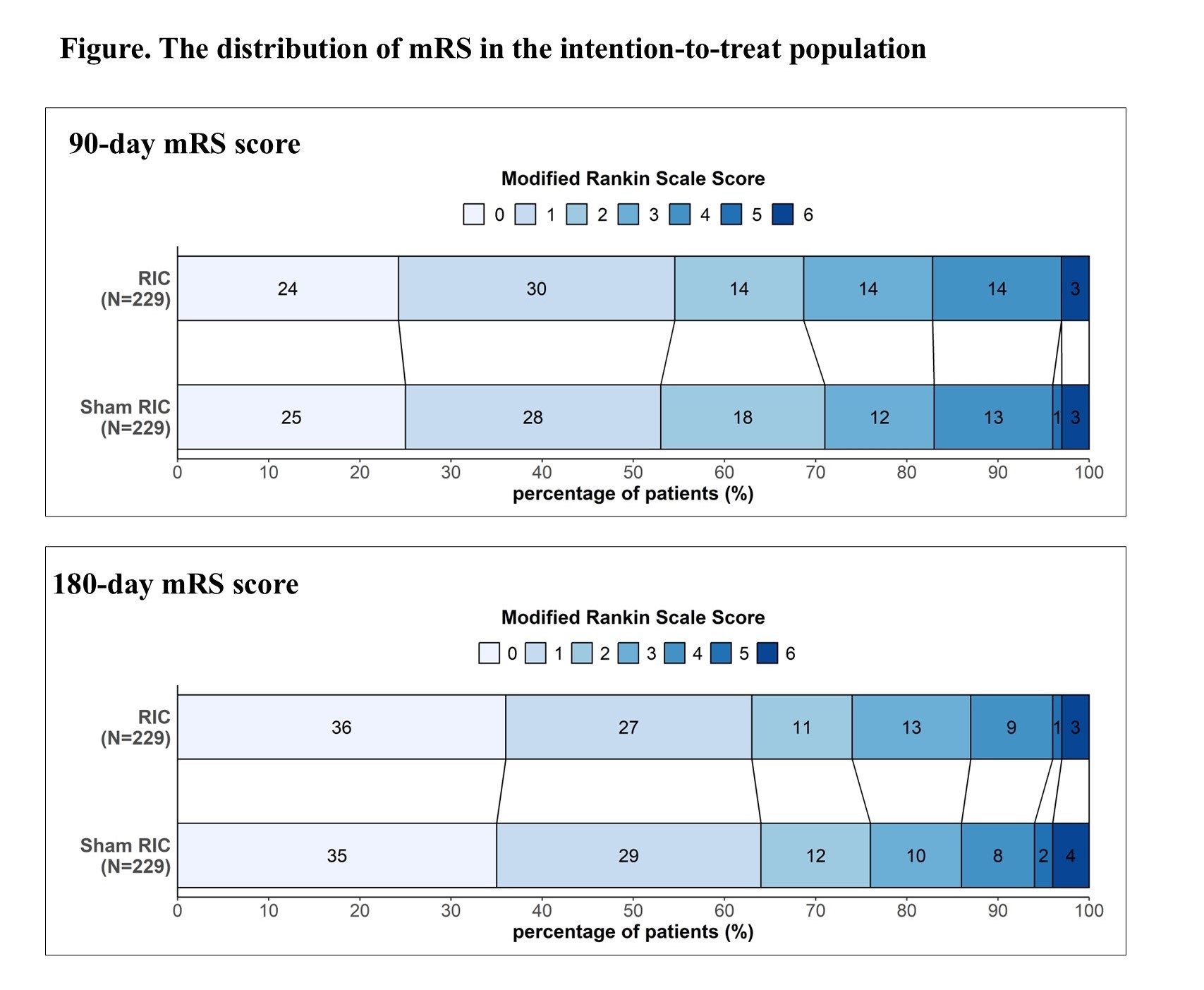
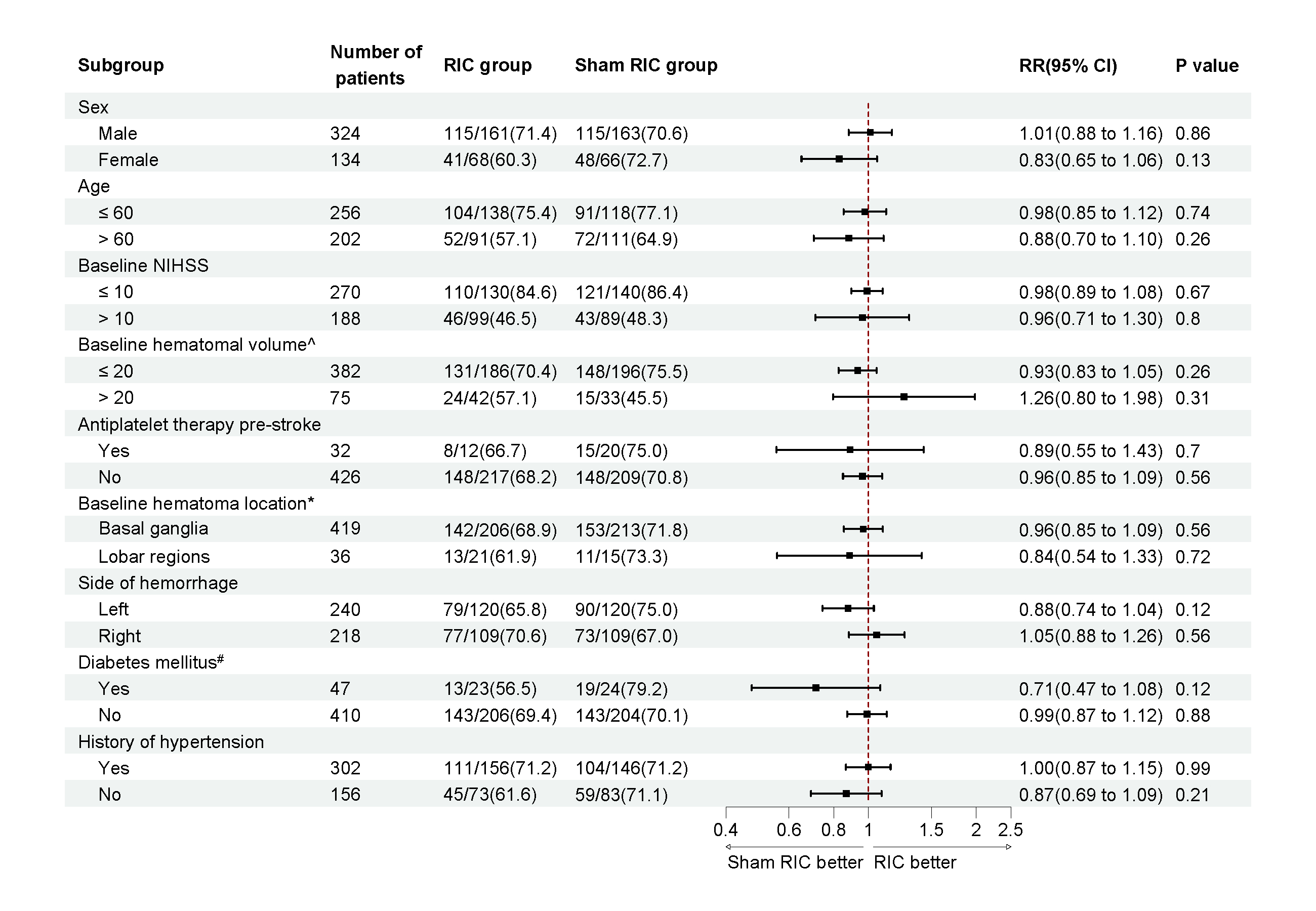
Results: Between Apr 22, 2021, and Oct 30, 2023, 458 patients were randomly assigned, with 229 in each group. 134 (29.3%) were women, and 324 (70.7%) were men, the median age was 58 years (IQR 51-68), the median NIHSS score was 9.0 (IQR 7.0-13.0), and the median hematoma volume was 12.6 mL (IQR 10.0-18.0). 156 (68.1%) of 229 patients in the RIC group and 163 (71.2%) of 229 patients in the sham group had a mRS score of 0-2 at 90 days (adjusted RR 0.98; 95% CI 0.88-1.09; adjusted p=0.69). Prespecified subgroup analysis showed a trend in favor of RIC in patients with clot size larger than 20 ml (RR 1.26, 95% CI 0.80-1.98, p=0.31). At 180-day follow-up, 169 (73.8%) of 229 patients receiving RIC and 175 (76.4%) of 229 patients receiving sham RIC achieved a mRS score of 0-2 (adjusted RR 0.98; 95% CI 0.89-1.08; adjusted p=0.64). Serious adverse events occurred in 16 (7.0%) of 229 patients receiving RIC and 12 (5.2%) of 229 patients receiving sham RIC (adjusted RR 1.29, 95% CI, 0.63-2.67, p=0.48). No important unexpected adverse events or side effects of RIC were observed.
Conclusions: RIC did not improve the proportion of patients who achieved functional independence 90 days after ICH in patients who did not need surgical therapy. Further studies of RIC in this population should target patients with large clot sizes and address the RIC protocol.
More abstracts on this topic:
Anderson Darci, Gaudio Hunter, Morton Sarah, Menezes Forti Rodrigo, Baker Wesley, Kilbaugh Todd, Morgan Ryan, Ko Tiffany, Herrmann Jeremy, Senthil Kumaran, Crozier Aidan, Mason Mckenna, Seeney Alyssa, Ranieri Nicolina, Goto Rika, Krishna Akshatha
Cardiovascular Events in Hospitalized Patients with Malignant Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Nationwide AnalysisPhilip Anil, Banga Akshat, Saeed Muhammad Subhan, Briones-zamora Killen H., Briones-claudett Killen H., Kohli Saksham, Khullar Rohit, George Lina James, Mautong Hans, John Kevin, Varma Revati, Kini Saurav, Khalid Abdullah, Saha Shubhashis, Caputi Zuniga Angelo
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.