Final ID: WP262
Prediction of Final Ischemic Infarct Volume Via Virtual Noncontrast Imaging After Stroke Thrombectomy
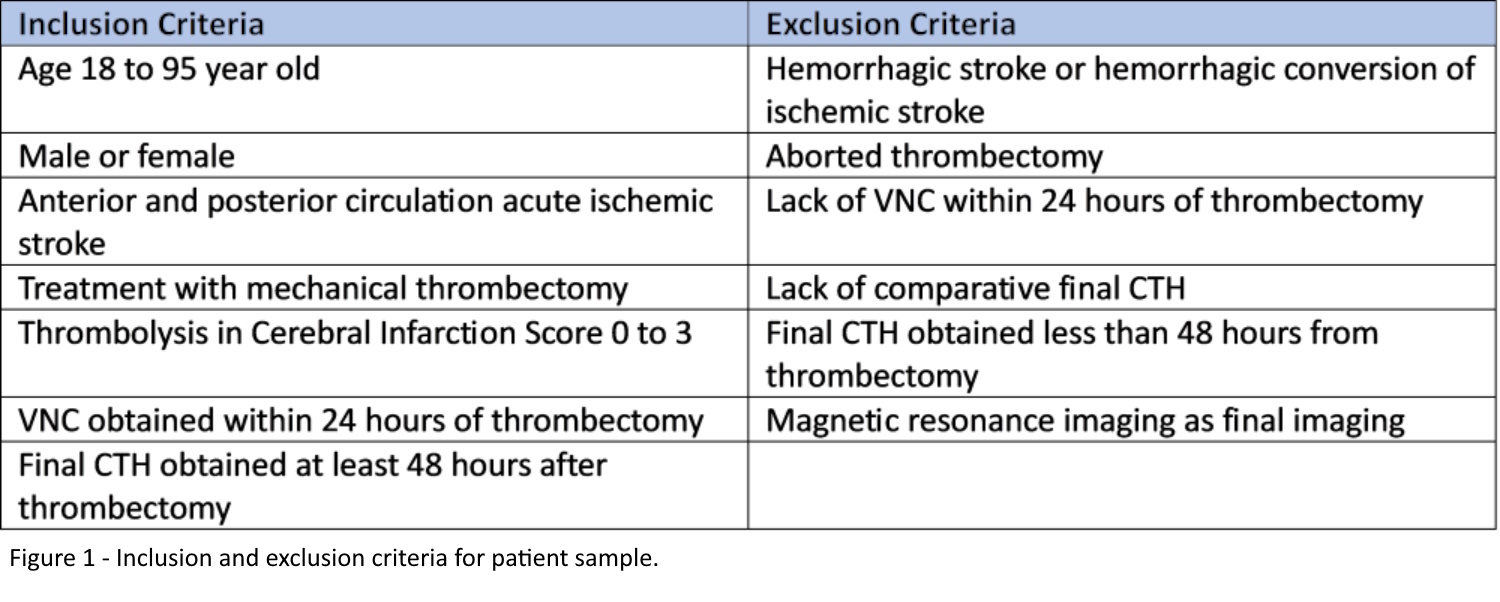
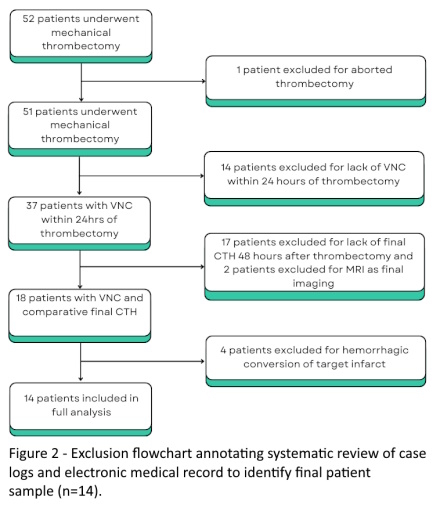
Methods: This is a retrospective, observational, single-center study of 14 patients who underwent mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke between January 2023 and August 2024. Inclusion and exclusion criteria and exclusion flowchart are listed in Figure 1 and 2, respectively. Demographics, National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) and mRS data were extracted from the electronic medical record. Infarct volumes on initial VNC and final CTH were measured using the ABC/2 or ABC/3 formula for ellipsoid or irregular infarcts, respectively. Statistical analysis was conducted with a paired t-test (p-value <0.05) to compare matched volume differences.
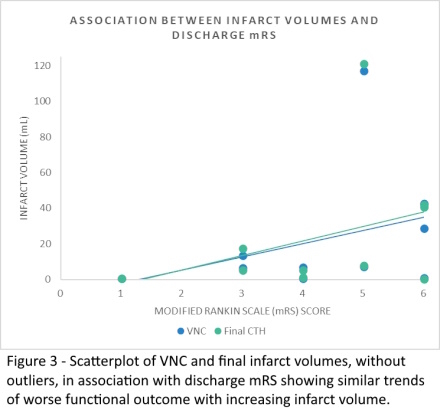
Results: Patient sample was 50% male and 50% female. Age ranged from 45 to 94 years old with a mean of 71. Mean and median initial NIHSS was 19 with a range 4 to 29. Mean discharge NIHSS was 21. VNC underestimated final infarct volume by a mean difference of 4.68 milliliters in a full sample analysis. This mean difference was statistically significant (p-value 0.038) indicating VNC volume may not reliably predict the final infarct volume in the full sample. However, analysis without outliers yielded a statistically insignificant difference (p-value 0.3102) indicating VNC volume may be a reliable predictor in smaller infarcts. Figure 3 depicts increasing infarct volumes on VNC or final CTH trended towards worse mRS indicating VNC may have a role in prognostication.
Conclusion: VNC may be a predictor of final infarct volume in patients with small infarct sizes with minimum cerebral edema. Limitations of this study include small sample size and cerebral edema as a confounder in large infarct volume measurements. Further studies correlating VNC infarct with final MRI infarct volume and functional outcome are needed.
More abstracts on this topic:
Narangoli Adeeb, Sila Cathy, Opaskar Amanda, Xiong Wei, Degeorgia Michael, Duncan Kelsey, Ray Abhishek, Hu Yin, Sunshine Jeffrey, Bambakidis Nicholas, Sarraj Amrou, Yaghmoor Bassam, Pujara Deep, Alshaibi Faisal, Saidi Yazid, Shafiq Ameena, Albedaiwi Mohammed, Al Mostaneer Alhassin, Sundararajan Sophia
Blood pressure trends during first forty-eight hours post arterial ischemic stroke in children with cardiac diseaseQuesnel Elya, Guerguerian Anne-marie, Chin Norbert, Linds Alexandra, Sheng Min, Pulcine Elizabeth, Moharir Mahendranath, Deveber Gabrielle, Dlamini Nomazulu
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.