Final ID: WP181
Effect of RapidAI Imaging Software Implementation on Workflow Metrics in Acute Ischemic Stroke Care
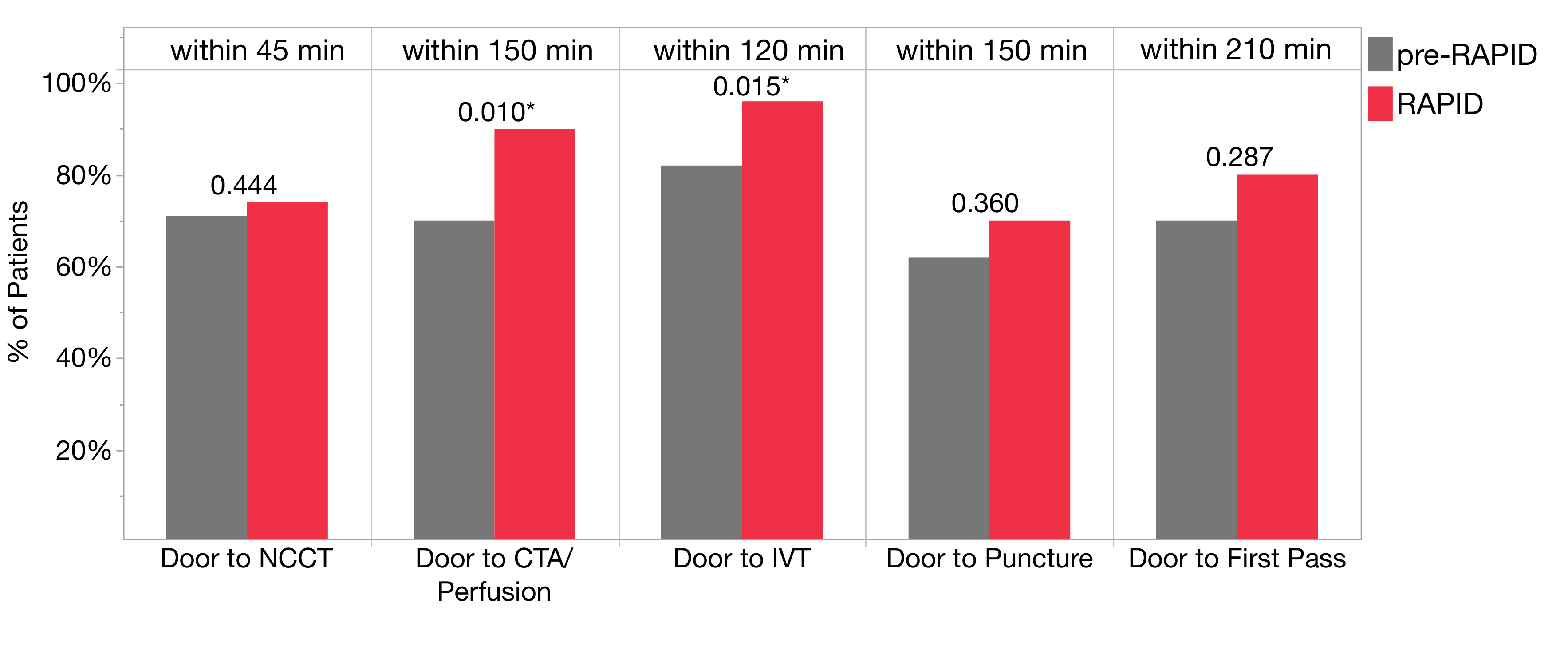
Methods: In this retrospective observational study, we analyzed consecutive patients who presented to our hospital ER with acute ischemic stroke and who were treated with Intravenous Thrombolysis (IVT) or mechanical thrombectomy between December 20, 2014, and April 20, 2024. Patients were divided into pre-RAPID (n =186) and post-RAPID (n =264) groups based on the implementation date of the RAPID system (September 1, 2019). We compared Door to Non-contrast CT (NCCT), Door to CT Angiography (CTA) / Perfusion Imaging, Door to IVT, and Door to Puncture / first pass for thrombectomy, between the two groups using Fisher’s exact test.
Results: For Door to CT, no significant difference was observed between pre-RAPID and post-RAPID groups; 74% of patients in the post-RAPID group and 71% in the pre-RAPID group received NCCT within 45 minutes (p = 0.44). Significant improvements were observed in Door to CTA/Perfusion times; 90% of patients received vessel or perfusion imaging within 150 minutes post-RAPID compared to 70% pre-RAPID (p = 0.01), and 87% received imaging within 120 minutes post-RAPID compared to 70% pre-RAPID (p = 0.031). For Door to IVT, 96% of patients received treatment within 120 minutes post-RAPID compared to 82% pre-RAPID (p = 0.015). For thrombectomy, there was a trend toward faster door to puncture post-RAPID; 70% of patients were treated within 150 minutes post-RAPID compared to 62% pre-RAPID (p = 0.36), and 90% were treated within 210 minutes post-RAPID compared to 81% pre-RAPID (p = 0.12). Similarly, a trend toward faster Door to First Pass times was observed post-RAPID, with 88% treated within 240 minutes compared to 80% pre-RAPID (p = 0.20).
Conclusions: RapidAI Implementation was associated with significant improvements in key workflow metrics, notably in Door to Vessel/Perfusion Imaging and Door to IVT. These findings suggest that RAPID enhances the efficiency of patient care delivery in acute ischemic stroke. Further studies with larger sample sizes are warranted.
More abstracts on this topic:
Montalvan Victor, Hendley Katie, Zurasky John, Albers Greg, Tan Yuanyuan, Marginean Horia, Neves Gabriel, Ota Riichi, Hernandez Roberto, Barnes Robert, Brister Rorie, Chintakayala Laxmi
Computed-Tomography (CT) Based Imaging Scores in Basilar Artery Occlusions – A Comparison of Predictive Abilities for Functional OutcomesLun Ronda, Goldman Yassen Adam, Hsieh Kevin Li-chun, Giurgiutiu Dan-victor, Gibson Dan, Carrera Emmanuel, Alemseged Fana, Faizy Tobias, Fiehler Jens, Pileggi Marco, Campbell Bruce, Shah Parshva, Heit Jeremy, Albers Gregory, Franco Lia Carolina, Cereda Carlo, Mlynash Michael, Yuen Nicole, Qureshi Abid, Hinduja Archana, Dehkharghani Seena
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.