Final ID: DP39
Short-term Outcomes of Atrial Fibrillation Patients Undergoing Carotid Stent Placement or Carotid Endarterectomy in the United States
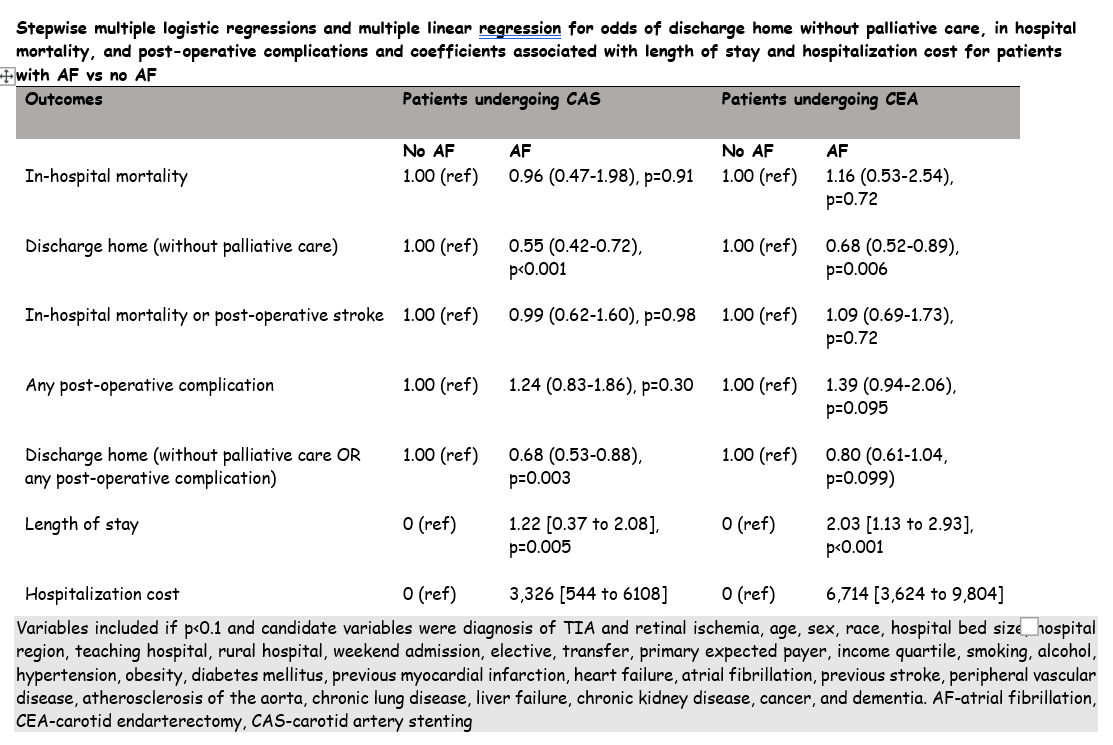
Abstract Body: Background:Patients with atrial fibrillation were excluded from clinical trials evaluating carotid artery stent(CAS) or carotid endarterectomy (CEA).We performed this analysis to identify the prevalence of atrial fibrillation and associated outcomes in symptomatic internal carotid artery stenosis patients undergoing CAS or CEA.Methods:We analyzed the data from the National inpatient sample (NIS) between January 2016 to December 2021. We used the ICD-10 to identify patients hospitalized with diagnosis of stroke, TIA, or retinal ischemia with stenosis of carotid artery who underwent CAS or CEA. We divided patients based on presence or absence of atrial fibrillation. We ascertained the end points of intra-procedural and post-procedural cerebral infarction, hemorrhage, discharge home and death in CAS and CEA patients with atrial fibrillation. We compared the endpoints between patients who underwent CAS and those who underwent CEA after propensity score matching.Results:Atrial fibrillation was present in 3,785 (18.3%) of 20,645 patients underwent either CAS or CEA between 2016 and 2021 [18.0% versus 18.8% for CAS or CEA, respectively, p=0.50]. The proportions of patients who developed acute myocardial infarction, respiratory failure, acute kidney injury, or required blood transfusion was higher in patients with atrial fibrillation in both CAS and CEA groups. There was no difference in odds of post-operative stroke and/or death in patients with atrial fibrillation (compared with those without atrial fibrillation) who were treated with CAS (OR 0.99, 95% CI 0.62-1.60, p=0.98) and those treated with CEA (OR 1.09, 95% CI 0.69-1.73, p=0.72) in the multivariate analysis after adjusting for confounders. The length of stay and hospitalization cost was significantly higher in patients with atrial fibrillation (compared with those without atrial fibrillation who were treated with CAS and those treated with CEA). There was no difference in post-operative stroke and/or death (10.7% versus 8.7%, p=0.41) and discharge home (32.4% versus 26.8%, p=0.13) in atrial fibrillation patients who underwent CEA with compared to those underwent CAS in propensity matched analysis.Conclusion:Approximately 1 in 5 patients with symptomatic internal carotid artery stenosis who undergo CAS or CEA have atrial fibrillation in the United States, we did not identify any higher risk of post-operative stroke and/or death in atrial fibrillation patients irrespective of which procedure was undertaken
More abstracts on this topic:
Associations Between Absolute Blood Eosinophil Count and Subclinical Atherosclerotic Plaque in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Mathis Nyla, Mcclelland Robyn, Stein James, Johansson Mats, Tattersall Matthew, Hansen Spencer, Dasiewicz Alison, Esnault Stephane, Siddiqui Salman, Mathur Sameer, Jarjour Nizar, Denlinger Loren
A Fat Chance: Paradoxical Embolic Stroke from Lipomatous Hypertrophy of the Interatrial SeptumKalathoor Abraham
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)