Final ID: MDP1284
Carotid Plaque Inflammation Is Associated with Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is prevalent in patients with atherosclerotic coronary and carotid artery disease and is associated with elevated plasma inflammatory markers, such as Interleukin (IL)-6. In carotid artery atherosclerosis, macrophages are considered a local marker of inflammation.
Hypothesis
We hypothesize that AF is independently associated with carotid plaque inflammation.
Aims
In patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy (CEA), we aimed to determine whether carotid plaques inflammation is associated with AF.
Approach
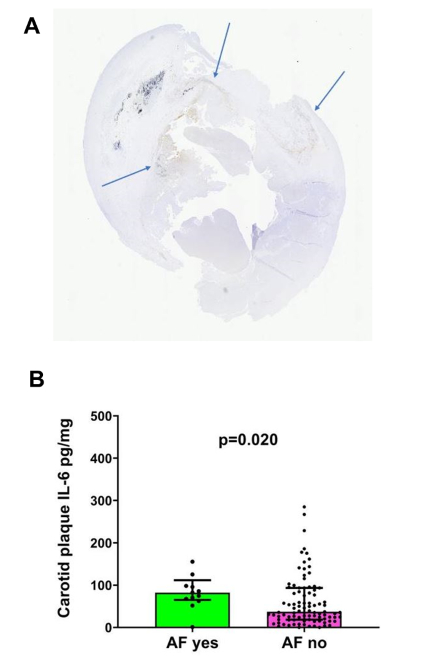
In this prospective cohort study, consecutive patients with carotid artery disease undergoing CEA were enrolled. From the plaques removed during surgery, fixed in formalin and embedded in paraffin blocks, sections were stained with antibodies against CD68 to detect macrophages (Fig.1A). Digital copies of the slides were created by Motic Easy Scan and histologically annotated with QuPath. The percentage of CD68+ cells was defined as (CD68+ positive cells/total nuclei) x 100. Flash-frozen plaque segments were analyzed by ELISA for IL-6 concentration. Baseline demographics and clinical data, including AF diagnosis, were extracted from the electronic health records.
Results
A total of 106 patients undergoing CEA, with a median age of 73 [67-78] years and comprising 83 (78.3%) males, were included in the study. AF was diagnosed prior to CEA in 13 (12.3%) patients. Univariate logistic regression showed that plaque CD68+ cell content was associated with AF (OR 1.048 [95% CI 1.010 – 1.088]; p = 0.013).
Additionally, in Mann-Whitney test IL-6 levels were significantly over twofold higher in plaques of patients with AF compared to those without AF (82.4 [64.9-111.7] pg/mg vs 37.0 [18.4-93.3] pg/mg; p=0.020) (Fig. 1B).
Conclusions
The current study demonstrates an association between carotid atherosclerotic plaque macrophage content, IL6 levels and AF, supporting the role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of AF in these patients. Further studies are needed to determine the potential of plaque inflammation as a therapeutic target in AF.
Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is prevalent in patients with atherosclerotic coronary and carotid artery disease and is associated with elevated plasma inflammatory markers, such as Interleukin (IL)-6. In carotid artery atherosclerosis, macrophages are considered a local marker of inflammation.
Hypothesis
We hypothesize that AF is independently associated with carotid plaque inflammation.
Aims
In patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy (CEA), we aimed to determine whether carotid plaques inflammation is associated with AF.
Approach
In this prospective cohort study, consecutive patients with carotid artery disease undergoing CEA were enrolled. From the plaques removed during surgery, fixed in formalin and embedded in paraffin blocks, sections were stained with antibodies against CD68 to detect macrophages (Fig.1A). Digital copies of the slides were created by Motic Easy Scan and histologically annotated with QuPath. The percentage of CD68+ cells was defined as (CD68+ positive cells/total nuclei) x 100. Flash-frozen plaque segments were analyzed by ELISA for IL-6 concentration. Baseline demographics and clinical data, including AF diagnosis, were extracted from the electronic health records.
Results
A total of 106 patients undergoing CEA, with a median age of 73 [67-78] years and comprising 83 (78.3%) males, were included in the study. AF was diagnosed prior to CEA in 13 (12.3%) patients. Univariate logistic regression showed that plaque CD68+ cell content was associated with AF (OR 1.048 [95% CI 1.010 – 1.088]; p = 0.013).
Additionally, in Mann-Whitney test IL-6 levels were significantly over twofold higher in plaques of patients with AF compared to those without AF (82.4 [64.9-111.7] pg/mg vs 37.0 [18.4-93.3] pg/mg; p=0.020) (Fig. 1B).
Conclusions
The current study demonstrates an association between carotid atherosclerotic plaque macrophage content, IL6 levels and AF, supporting the role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of AF in these patients. Further studies are needed to determine the potential of plaque inflammation as a therapeutic target in AF.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Fat Chance: Paradoxical Embolic Stroke from Lipomatous Hypertrophy of the Interatrial Septum
Kalathoor Abraham
Artificial Intelligence-estimated Probability of Aortic Stenosis Is an Independent Predictor of Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients with Carotid Artery Disease After Carotid EndarterectomyMahmoudi Hamidabad Negin, Kalina Samuel, Nogami Kai, Lerman Lilach, Nardi Valentina, Lerman Amir