Final ID: WMP22
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Markers of Brain Health to Assess Functional Outcome After Acute Ischemic Stroke: a Quantitative Comparison Study
Brain health facilitates resilience to withstand detrimental effects of neurological diseases. Magnetic resonance imaging markers that quantify brain health may hence improve clinical modeling of functional outcome after acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Here, we aimed to compare the modeling performance of four quantitative brain health measures in a large, multicenter clinical setting.
Methods
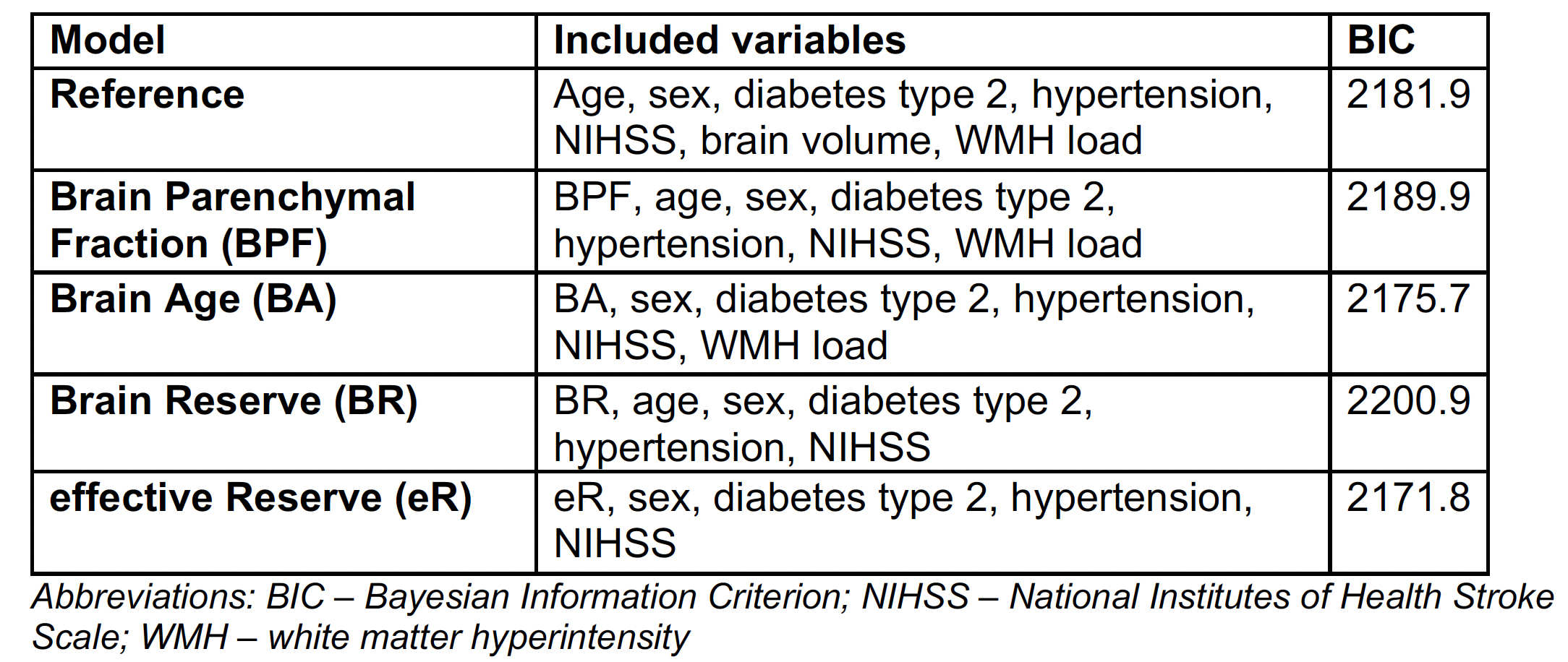
We analyzed 2,223 adult AIS survivors from the MRI-GENIE study, an international multicenter cohort (17 centers; 2003 - 2011) with acute T2-FLAIR imaging. We used dedicated deep learning enabled automated pipelines to assess white matter hyperintensity volume (WMHv), brain volume, and intracranial volume (ICV). We assessed the following brain health markers: 1) Brain Parenchymal Fraction (BPF, defined as brain volume relative to ICV), 2) Brain Age (BA, estimated using radiomics in an ElasticNet linear regression model), 3) Brain Reserve (BR, defined as normal appearing brain volume relative to ICV), and 4) effective Reserve (eR, defined as a latent variable calculated through structural equation modeling based on age, WMH load and brain volume with coefficients estimated in an independent cohort). We evaluated the brain health markers in separate logistic regression models of poor outcome (modified Rankin Scale score 3-5 at 90 days) adjusting for sex, diabetes type 2, hypertension, stroke severity (NIHSS), and age, brain volume and WMH load if not used to determine the respective brain health measure (see Table 2). Models were compared in terms of goodness of fit using Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC).
Results
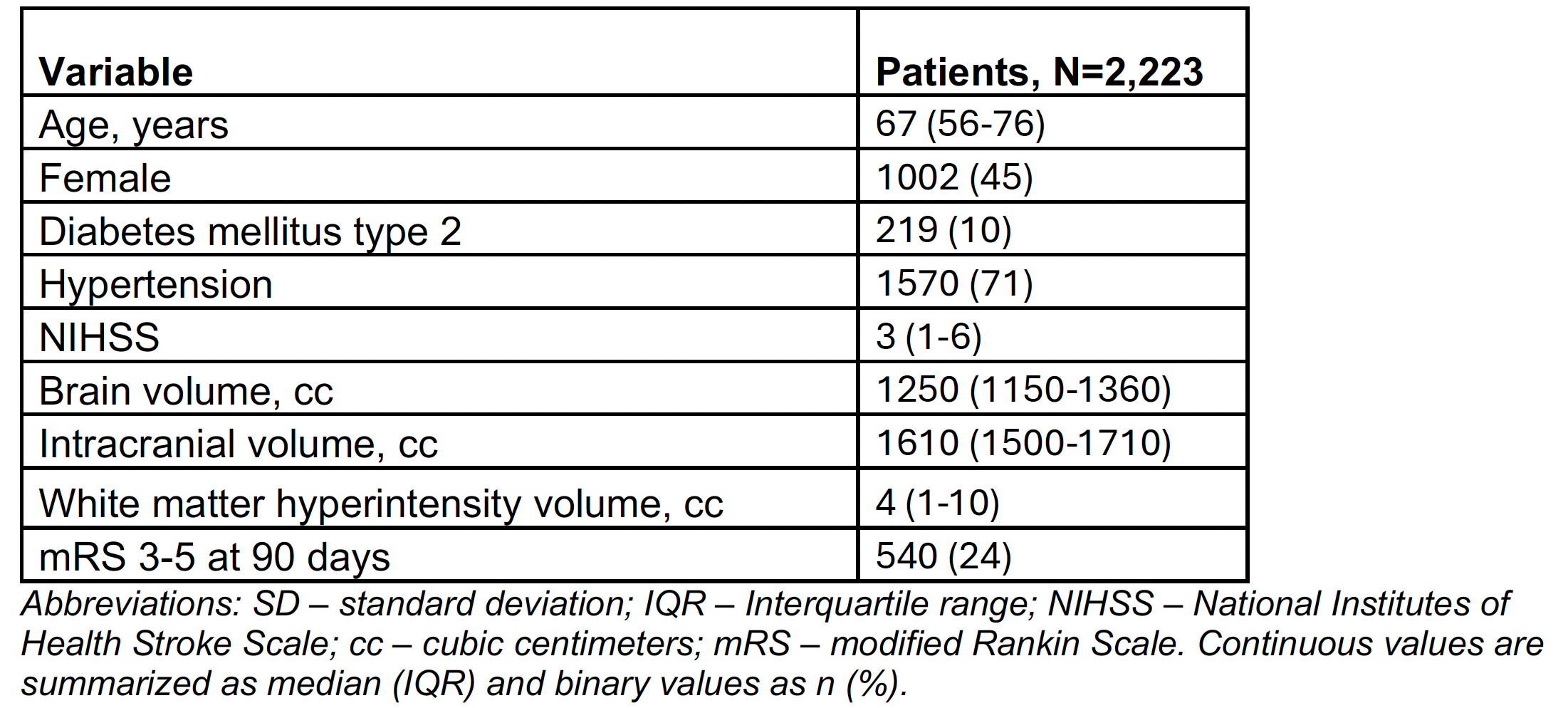
Of 2,223 patients with complete data (median age 67 years, 45% female), median NIHSS at admission was 3, and 24% of patients had poor outcomes (see Table 1). The model utilizing eR (BIC=2171.8), showed the lowest BIC values, providing moderate statistical evidence to outperform the BA model (BIC=2175.7, ΔBIC > 2), and very strong (ΔBIC > 10) statistical evidence to outperform all other models (see Table 2).
Conclusions
In conclusion, incorporating eR as a quantitative measure of brain health, determined from routinely acquired clinical imaging, has the potential to improve personalized patient prognostication and modeling of functional outcome after AIS.
More abstracts on this topic:
Mallavarapu Monica, Kim Hyun Woo, Iyyangar Ananya, Salazar-marioni Sergio, Yoo Albert, Giancardo Luca, Sheth Sunil, Jeevarajan Jerome
A Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating Vitamin D Normalization on Major Adverse Cardiovascular-Related Events Among Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients: The TARGET-D TrialMay Heidi, Colipi Dominique, Whiting Tyler, Muhlestein Joseph, Le Viet, Anderson Jeffrey, Babcock Daniel, Wayman Libby, Bair Tami, Knight Stacey, Knowlton Kirk, Iverson Leslie
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.