Final ID: TP2
Association between Statin therapy for preventing recurrent stroke in patients with ischemic stroke: A Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Background
Statins are effective in reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. It has shown to reduce the risk of stroke and is cardioprotective in nature. However, statin might elevate the risk of hemorrhagic stroke and hence it's critically important to evaluate its efficacy and safety among stroke patients.
Objective
This study aims to investigate the association of statin based therapies with outcomes for patients with stroke.
Methods
We performed a systematic literature search on PubMed, EMBASE, and ClinicalTrials.gov for relevant randomized controlled trials (RCTs) from inspection until August 10th, 2024, without any language restrictions. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were pooled using a random-effect model, and a p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
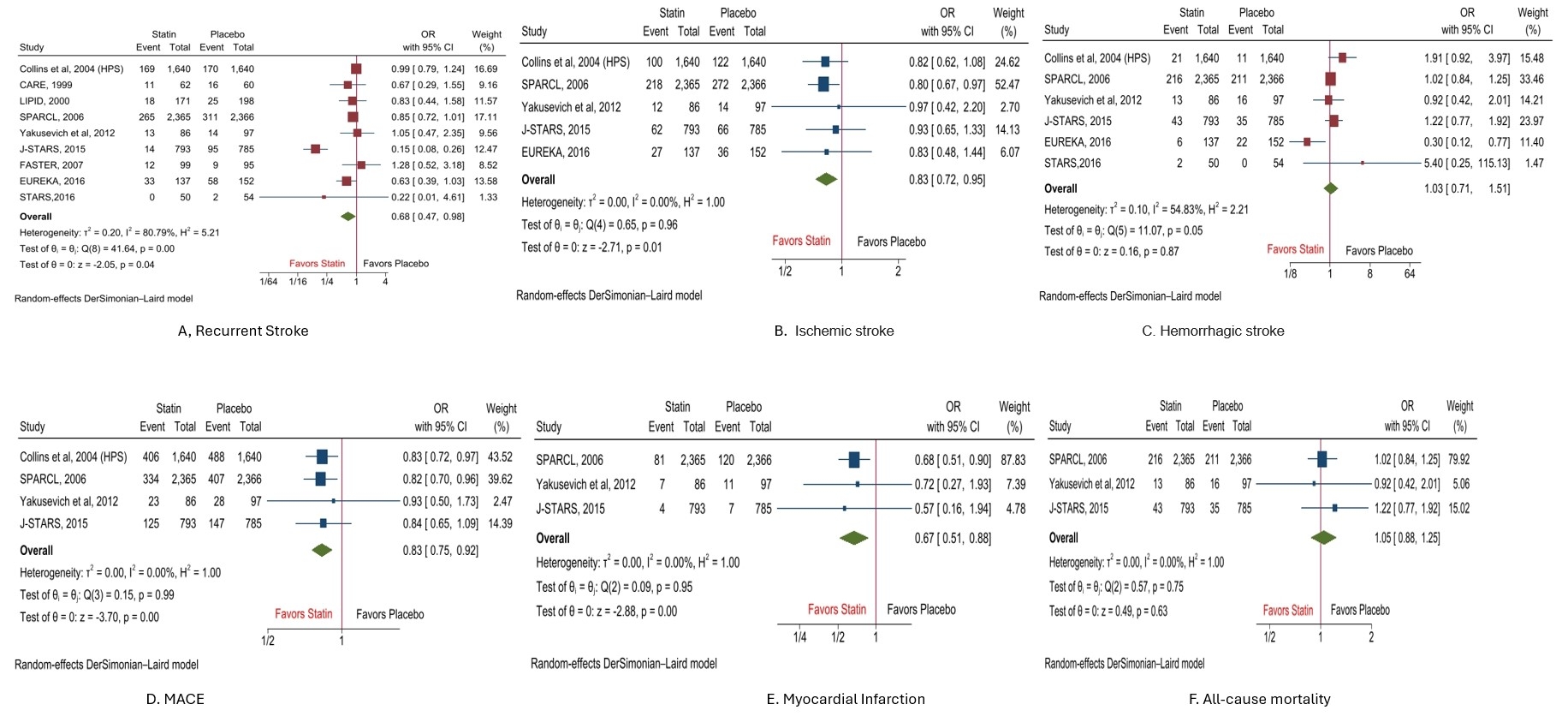
A total of 9 randomized controlled trials with 10, 850 patients (5403 patients in the statin group, and 5447 patients in the placebo group) were included in the analysis. Mean age of patients was 65 years and mean follow up duration was 3.6 years.
Pooled analysis of primary outcomes showed that statin group of patients were having lower odds of recurrent stroke (OR, 0.68(95%CI: 0.47-0.98), P=0.04), ischemic stroke (OR, 0.83(95%CI: 0.72-0.95), P=0.01), major adverse cardiovascular events (OR, 0.83(95%CI: 0.75-0.92), P<0.001), and myocardial infarction (OR, 0.67(95%CI: 0.51-0.88), P<0.001). However, the risk of all-cause mortality (OR, 1.05(95%CI: 0.88-1.25), P=0.63), and hemorrhagic stroke (OR, 1.03(95%CI: 0.71-1.51), P=0.87) was comparable between both group of patients.
Conclusion
This study findings suggest that statins significantly reduced the risk of recurrent stroke, ischemic stroke, and MACE. However, the risk of hemorrhagic stroke was comparable between both groups of patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
Kaloth Srivarsha, Fitzgerald Nurgul, Bacalia Karen Mae, Kalbag Aparna, Setoguchi Soko
A multifaceted family intervention for blood pressure management in rural China: an open label, parallel group, cluster randomized trial (Healthy Family Program)Jiang Chao, Dong Jianzeng, Cai Jun, Anderson Craig, Du Xin, Tang Yangyang, Han Rong, Song Yanna, Wang Chi, Lin Xiaolei, Yi Yang, Rodgers Anthony, Ma Changsheng
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.