Final ID: TP276
Impact of Educational Attainment and Social Support on Stroke Recurrence in a South Texas Community
Abstract Body: Background: Lower educational attainment (EA) and smaller social network are each associated with a greater risk for incident stroke. However, the relationship between EA, social support (SS), and recurrent stroke is less clear.
Objectives: To evaluate the association of EA and SS with stroke recurrence. We also assessed whether SS modifies the effect of EA on recurrence. We hypothesize that EA and SS each protect against recurrence and additively interact to further decrease risk.
Methods: Within the Brain Attack Surveillance in Corpus Christi (BASIC) project, we identified patients, age >45, with first-ever ischemic or hemorrhagic strokes from 2008-2019. Structured interviews were conducted to collect levels of EA (<, =, or > high school) and SS. Pre-stroke SS was measured by a 7-item scale (0-14, higher=more support). Multiple imputation was used for missing data on exposures and covariates. Complete case analysis was additionally performed. Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves for recurrence-free survival were plotted by EA level and SS quartile. Multivariate Cox models assessed the association of SS and EA with recurrence after adjustment for multiple covariates.
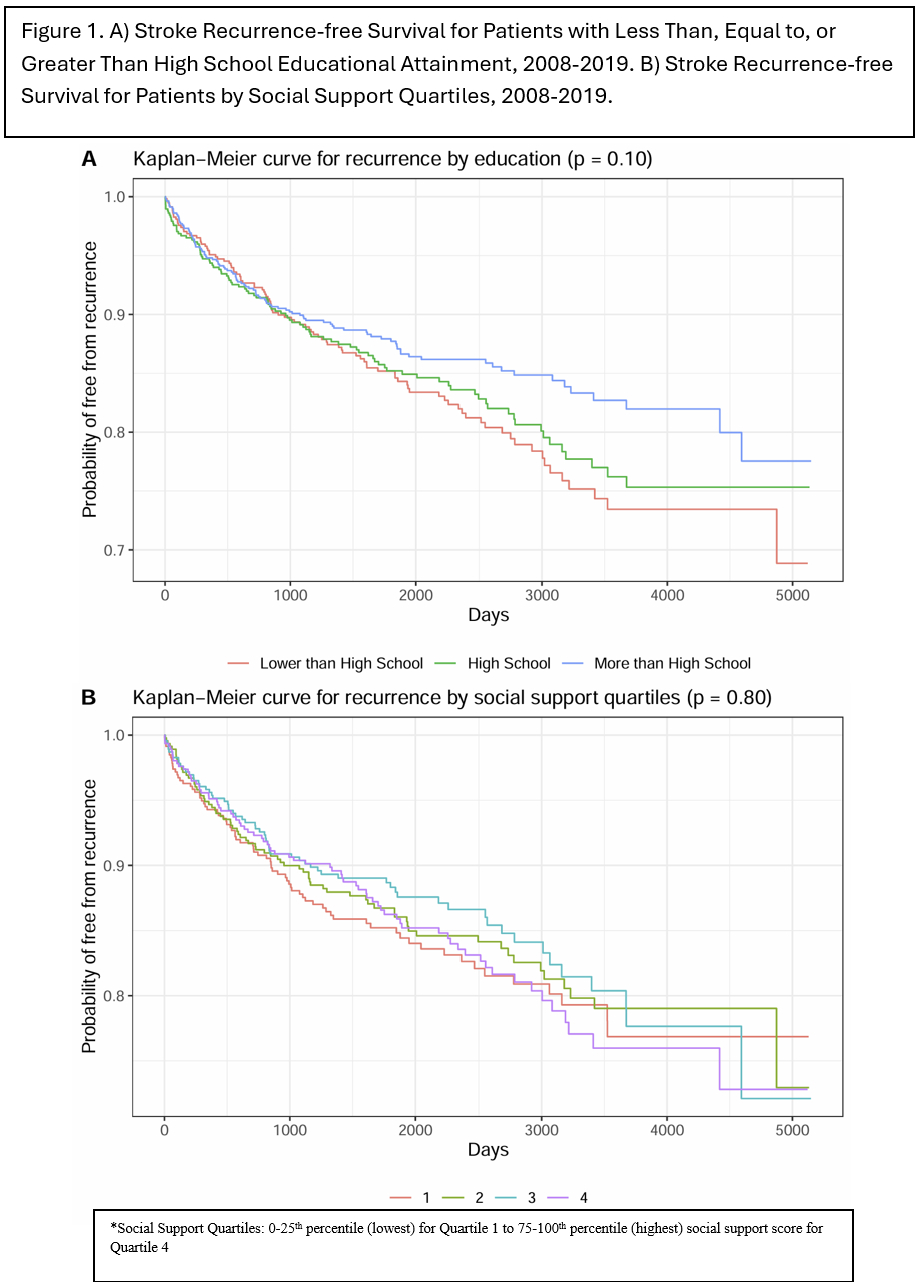
Results: Of 1,959 patients with incident stroke between 2008-2019, 305 had a recurrent stroke. In unadjusted KM analyses, higher EA was non-significantly associated with lower recurrence (p=0.10; Figure 1A), and SS was not associated with recurrence (Figure 1B). In both unadjusted and fully adjusted Cox models, neither EA, SS, nor the interaction of SS on EA were significantly associated with recurrence. In fully adjusted models, Mexican-American ethnicity, diabetes, and high cholesterol were associated with higher recurrence. Female sex (HR 0.66, 95% CI 0.50-0.87) and marriage (HR 0.74, 95% CI 0.56-0.97) were associated with lower recurrence risk. Complete case analysis yielded no substantive difference in results.
Conclusions: Though we observed a trend toward reduced recurrence risk among patients with higher EA in unadjusted KM analysis, no association emerged between EA or SS after adjustment for covariates. We did observe associations between both female sex and marriage with reduced recurrence risk.
Objectives: To evaluate the association of EA and SS with stroke recurrence. We also assessed whether SS modifies the effect of EA on recurrence. We hypothesize that EA and SS each protect against recurrence and additively interact to further decrease risk.
Methods: Within the Brain Attack Surveillance in Corpus Christi (BASIC) project, we identified patients, age >45, with first-ever ischemic or hemorrhagic strokes from 2008-2019. Structured interviews were conducted to collect levels of EA (<, =, or > high school) and SS. Pre-stroke SS was measured by a 7-item scale (0-14, higher=more support). Multiple imputation was used for missing data on exposures and covariates. Complete case analysis was additionally performed. Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves for recurrence-free survival were plotted by EA level and SS quartile. Multivariate Cox models assessed the association of SS and EA with recurrence after adjustment for multiple covariates.
Results: Of 1,959 patients with incident stroke between 2008-2019, 305 had a recurrent stroke. In unadjusted KM analyses, higher EA was non-significantly associated with lower recurrence (p=0.10; Figure 1A), and SS was not associated with recurrence (Figure 1B). In both unadjusted and fully adjusted Cox models, neither EA, SS, nor the interaction of SS on EA were significantly associated with recurrence. In fully adjusted models, Mexican-American ethnicity, diabetes, and high cholesterol were associated with higher recurrence. Female sex (HR 0.66, 95% CI 0.50-0.87) and marriage (HR 0.74, 95% CI 0.56-0.97) were associated with lower recurrence risk. Complete case analysis yielded no substantive difference in results.
Conclusions: Though we observed a trend toward reduced recurrence risk among patients with higher EA in unadjusted KM analysis, no association emerged between EA or SS after adjustment for covariates. We did observe associations between both female sex and marriage with reduced recurrence risk.
More abstracts on this topic:
Descriptive Analysis of Geographic and Sociodemographic Patterns in Poor Cardiovascular Health Across U.S. Census Tracts
Abadi Azar, Flores Melissa, Hailu Elleni, Ghosh Arnab, Wickliffe Jeffrey, Dooley Erin, Gabriel Kelley, Levitan Emily
An Evaluation of Bystander CPR by Race, Accounting for Social Drivers of HealthLane Nina, Crowe Remle, Salcido David
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)