Final ID: DP15
Increased Severity of Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption is Associated with Greater Burden of Cerebrovascular Disease in Asymptomatic Patients
Abstract Body: Background: White matter hyperintensities (WMH) of presumed vascular origin can be associated with vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. However, WMH are also seen in asymptomatic subjects. Blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption is thought to play a role in the formation of WMH. In this study we measured BBB disruption in and around areas of WMH in asymptomatic subjects and compared it with the volume of WMH to test the hypothesis that more severe BBB disruption would be associated with a larger burden of WMH.
Methods: Subjects being followed in the GeneSTAR study, an ongoing study of families enriched for vascular risk factors and cardiovascular disease, were included in this study if they had been scanned with dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC), FLAIR and T1 MRI. FLAIR/T1 images were segmented to create WMH masks. Penumbra masks were made by dilating the WMH masks by 4 voxels to create a region of interest that reflects the normal appearing white matter adjacent to the WMH. BBB disruption was measured using DSC images voxel-by-voxel by isolating signal changes due to leakage of gadolinium contrast agent through the BBB. The BBB metric K2 was calculated and expressed as the fraction of the recorded signal that originates from the leakage of contrast through the BBB. To identify hotspots of BBB disruption, 100 voxels with the highest BBB leakage for each patient were averaged to create a BBB metric from the same volume of tissue for each subject. BBB was compared with WMH volume using linear regression.
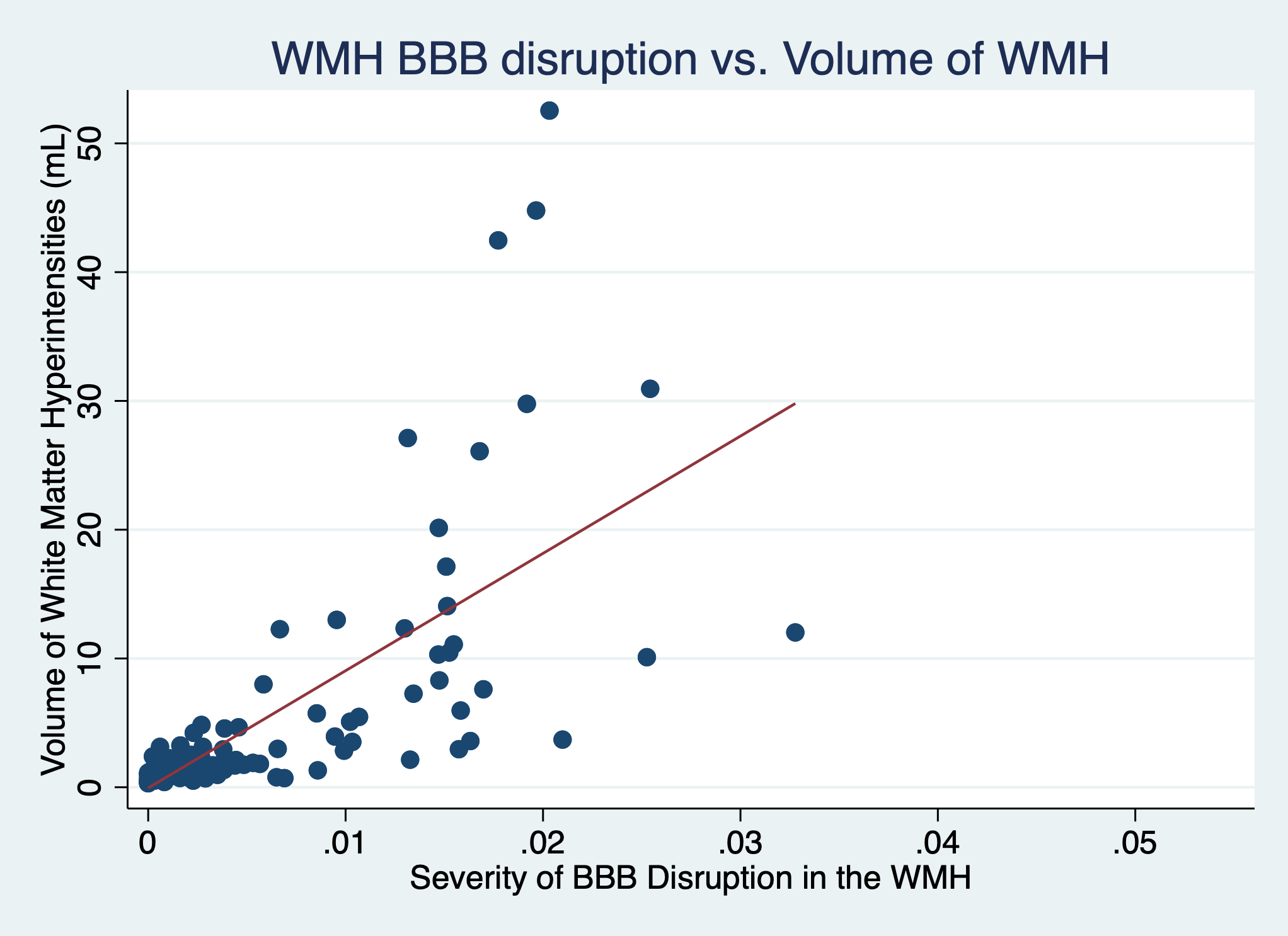
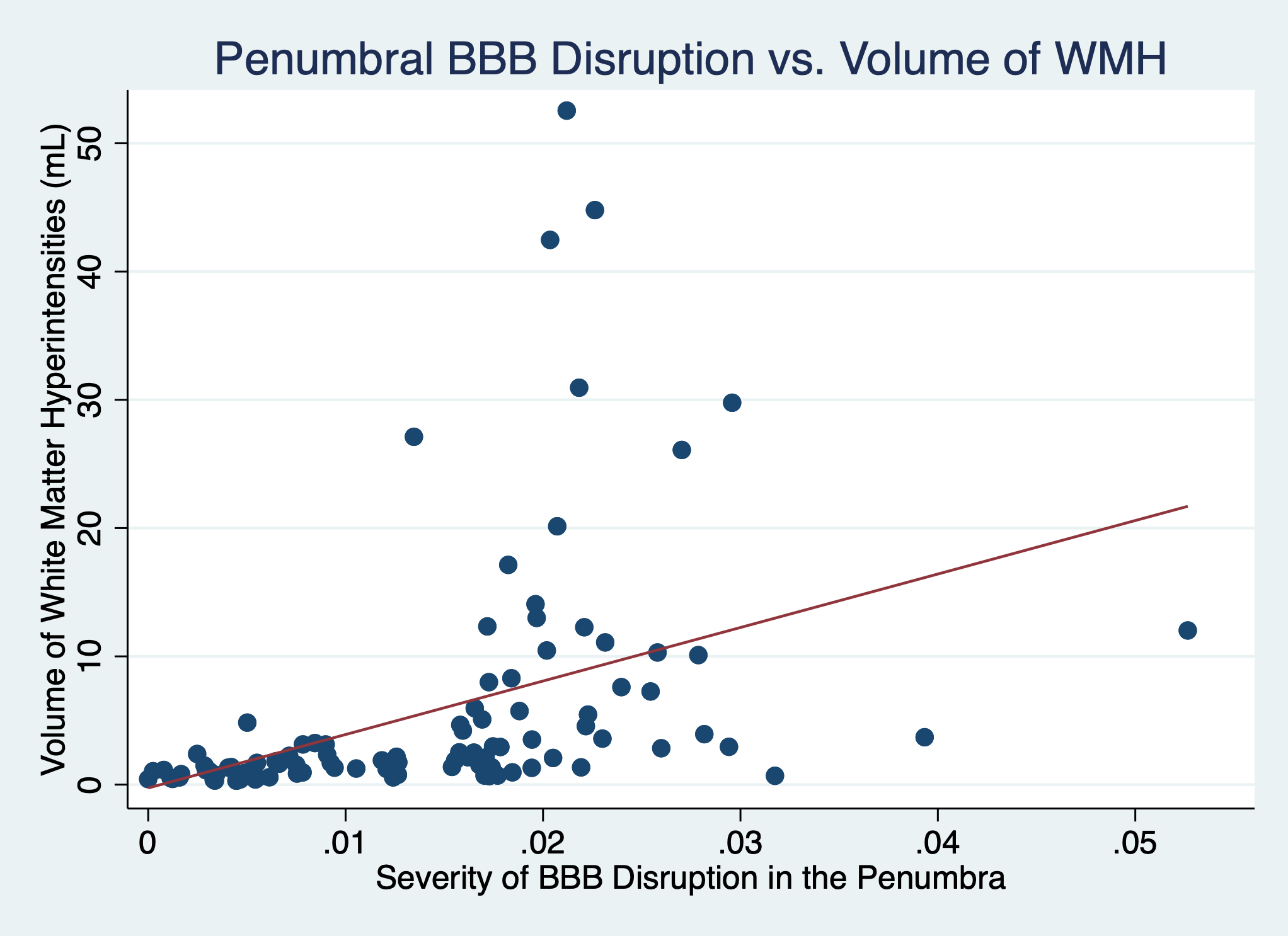
Results: There were 102 asymptomatic subjects included in the analysis, average age 63.2, of which 61% were women. BBB disruption measured in the WMH highly correlated with the volume of WMH (r2=0.47, p<0.001) suggesting that BBB disruption accounts for almost half of the disease burden (figure 1). BBB disruption measured in the penumbra also correlated with the WMH volume (r2=0.17, p<0.001) and although the association with WMH volume was weaker, the severity of BBB disruption was on average higher than when measured in the WMH (figure 2).
Conclusions: In this population of asymptomatic subjects, the burden of WMH was largely accounted for by the severity of their BBB disruption within the lesions. In areas adjacent to the WMH, BBB disruption was also apparent but may be more indicative of future WMH progression.
Methods: Subjects being followed in the GeneSTAR study, an ongoing study of families enriched for vascular risk factors and cardiovascular disease, were included in this study if they had been scanned with dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC), FLAIR and T1 MRI. FLAIR/T1 images were segmented to create WMH masks. Penumbra masks were made by dilating the WMH masks by 4 voxels to create a region of interest that reflects the normal appearing white matter adjacent to the WMH. BBB disruption was measured using DSC images voxel-by-voxel by isolating signal changes due to leakage of gadolinium contrast agent through the BBB. The BBB metric K2 was calculated and expressed as the fraction of the recorded signal that originates from the leakage of contrast through the BBB. To identify hotspots of BBB disruption, 100 voxels with the highest BBB leakage for each patient were averaged to create a BBB metric from the same volume of tissue for each subject. BBB was compared with WMH volume using linear regression.
Results: There were 102 asymptomatic subjects included in the analysis, average age 63.2, of which 61% were women. BBB disruption measured in the WMH highly correlated with the volume of WMH (r2=0.47, p<0.001) suggesting that BBB disruption accounts for almost half of the disease burden (figure 1). BBB disruption measured in the penumbra also correlated with the WMH volume (r2=0.17, p<0.001) and although the association with WMH volume was weaker, the severity of BBB disruption was on average higher than when measured in the WMH (figure 2).
Conclusions: In this population of asymptomatic subjects, the burden of WMH was largely accounted for by the severity of their BBB disruption within the lesions. In areas adjacent to the WMH, BBB disruption was also apparent but may be more indicative of future WMH progression.
More abstracts on this topic:
4D Flow MRI Evaluation of Cardiovascular Risk-Related Alterations in Heart-Brain Hemodynamics in Cognitively Healthy Aging Adults
Najafi Anahita, Rogalski Emily, Jarvis Kelly, Richter Adam, Lytchakov Anna, Benson Theresa, Jin Ning, Davids Rachel, Schnell Susanne, Ragin Ann, Weintraub Sandra
Apparent Thalamostriate Vein and Brush Sign on Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging as Predictors of Infarct Growth at the Lenticulostriate Artery TerritoryYoshimura Shota, Yamaguchi Susumu, Matsuo Takayuki
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)