Final ID: WP147
The Impact of Electronic Consent on Participant Recruitment in an Acute Ischemic Stroke Clinical Trial
Obtaining timely informed consent is a key barrier in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) clinical trial recruitment. Electronic consent (eConsent) allows electronic delivery and documentation of the informed consent process which may optimize recruitment. eConsent utilization in AIS clinical trials, however, is limited and understudied. We report eConsent adoption in MOST, a Phase III AIS clinical trial, and studied the impact on recruitment.
Methods:
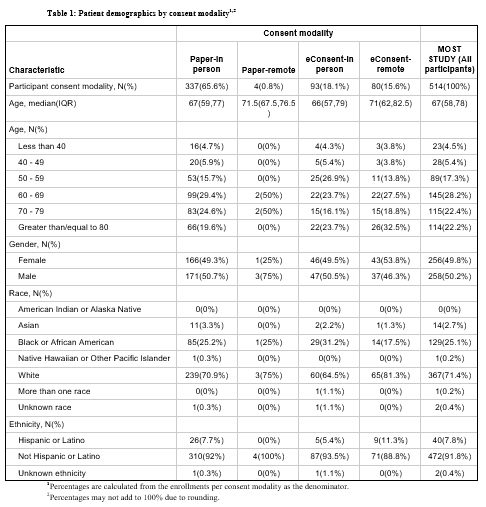
Study databases were reviewed to determine informed consent modality for each participant: paper-in person, paper-remote, eConsent-in person, eConsent-remote (remote consent occurred when the study team and participant/legally authorized representative were in different physical locations). eConsent adoption trends, participant demographics, and diversity were reported using descriptive statistics. We utilized chi-square and Kruskal Wallis tests to compare individual site enrollment, remote consent utilization, baseline-neuroimaging-to-randomization times, data clarification requests (DCRs), and reportable unanticipated events (UEs), across consent modalities.
Results
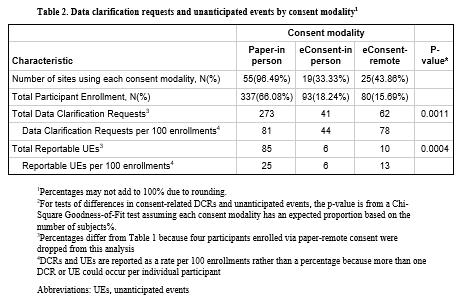
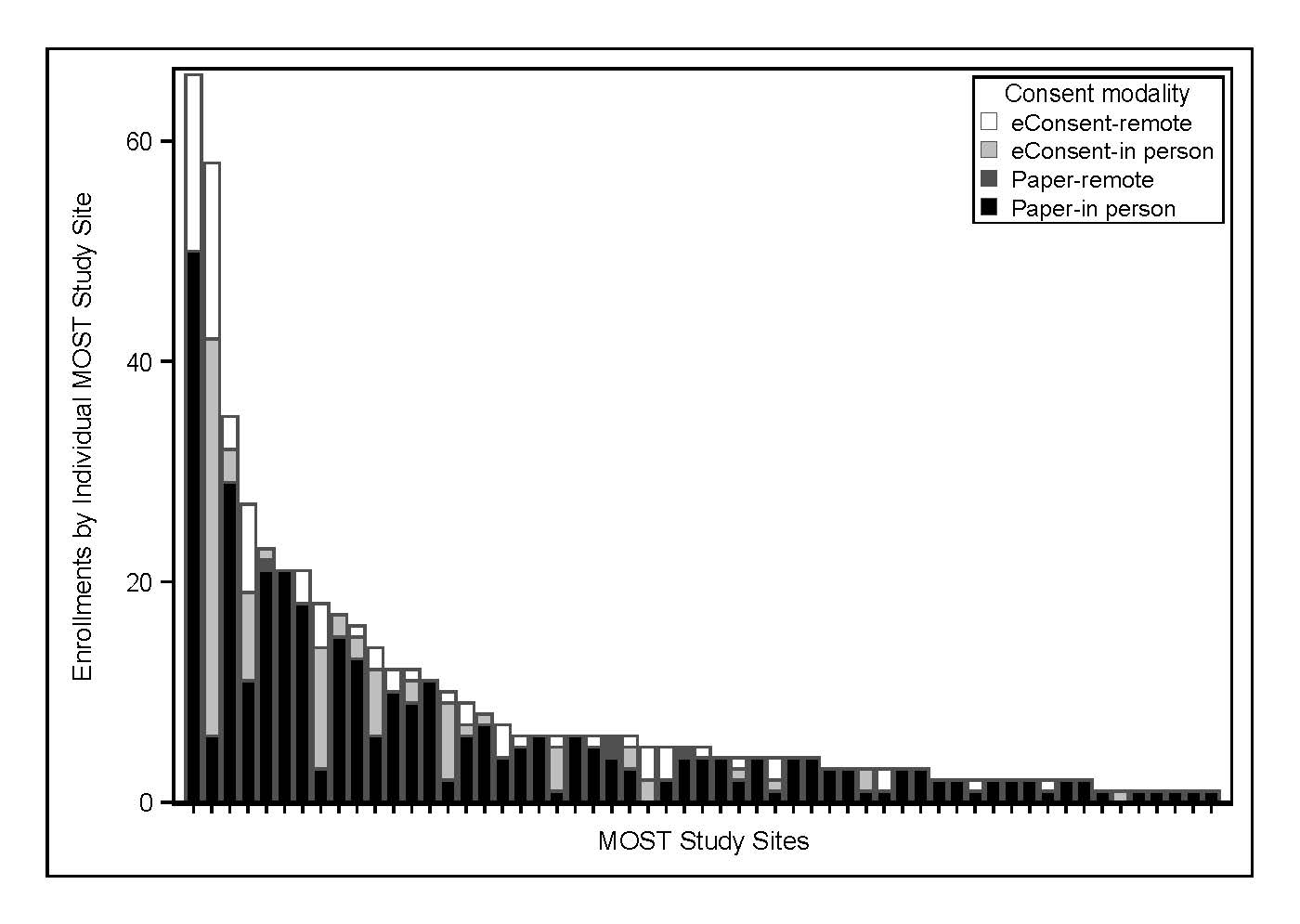
eConsent was utilized for 173 (33.7%) out of 514 participants. 32 of 57 sites (56.1%) utilized eConsent at least once: those sites had higher median enrollment than non-eConsent sites (7.5 [IQR 5-17] vs 3 [IQR 2-4], p<0.001). eConsent was completed remotely more frequently than paper consent (46.2% vs 1.2%, p<0.001). Participant diversity and baseline-neuroimaging-to-randomization times were similar between eConsent-in person and paper-in person consent (median 58.5 min [IQR 46.5-72.5] vs median 55 min [IQR 39-70]). Consent documentation adherence was superior with eConsent-in person compared to paper-in person including decreased DCRs (44 vs 81 per 100 participants, p<0.001) and reportable UEs (6 vs 25 per 100 participants, p<0.001).
Conclusion
eConsent in MOST was associated with higher individual site enrollment, higher remote consent rates, and improved consent documentation adherence over paper consent. Our study outlines the potential advantages of eConsent adoption in future AIS clinical trials and stroke research networks.
More abstracts on this topic:
Wang Henry, Bosson Nichole, Leonard Julie, Ward Caleb, Nishijima Daniel, Adelgais Kathleen, Remick Katherine, Gaither Joshua, Colella Riccardo, Swanson Doug, Goldkind Sara, Stephens Shannon, Hansen Matthew, Jacobsen Kammy, Brown Brittany, Elsholz Cara, Frey Jennifer, Vanburen John, Gausche-hill Marianne, Shah Manish
Drop It Like It’s Hot: Partnering with Teleneurology to Decrease Treatment TimesNielsen Danielle
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.