Final ID: WP194
Deep-learning Based Artefact Removal From Relative Non-contrast Computed Tomography Maps To Identify Early Hypodensity Changes After Acute Ischemic Stroke
Abstract Body: Introduction: A semi-automated method that compares voxel density with the contra-lateral hemisphere to generate ratio, or relative Non-Contrast CT (rNCCT) maps for identifying hypodensity changes was developed. In addition to being sensitive to stroke related hypodensities, these maps are also sensitive to motion artefacts and naturally occurring asymmetry in densities across hemispheres. We assessed the value of a deep-learning based model to segment and remove these artefacts and for identifying ischemic core of baseline NCCT.
Methods: We included data from 268 acute ischemic stroke patients with a large vessel occlusion from the ongoing CT perfusion to Predict Response to Recanalization in Ischemic Stroke Project 2 study. NCCT scans acquired at the primary stroke center were used to create rNCCT maps. These maps detect regions with at least 1% relative hypodensity difference compared to the contralateral region. A trained observer who had insight of arterial occlusion location manually annotated artefacts. We trained a no new UNet using the NCCT, rNCCT, and flipped NCCT images to detect artefacts from the rNCCT maps. To assess the extent to which our model falsely identified ischemic regions as artefact, we determined the overlap between the automatically segmented artefact on the rNCCT map and the manually segmented ischemic core on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) acquired at the comprehensive stroke center before treatment.
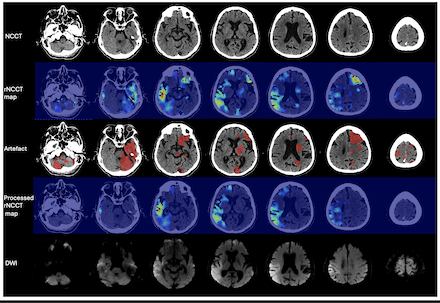
Results: The best performing model was the ensemble of the five cross-validation folds of 3d low- and high-resolution models based on dice similarity coefficient. Figure 1 provides an example of our model’s artefact segmentation and the processed rNCCT map after artefact removal. For the 54 patients (20% of study population) in our test set, our model achieved a median Dice similarity coefficient of 0.95 (IQR: 0.91-0.97) and a median false positive volume of 6.1 (3.2-11) ml. In the 30 patients with available DWI scans, 30% of patients had any overlap (>=1 voxel) between the segmented artefact and DWI ischemic core with a median overlap volume of 0.69 (IQR: 0.32-2.3) ml.
Conclusion: We demonstrate the use of a deep-learning based model to automatically segment artefacts from rNCCT maps. Our model circumvents time-invasive manual removal of artefacts from the rNCCT map and thereby simplifies segmentation of the ischemic core on baseline NCCT. Validation with external datasets is necessary before use in routine stroke evaluation.
Methods: We included data from 268 acute ischemic stroke patients with a large vessel occlusion from the ongoing CT perfusion to Predict Response to Recanalization in Ischemic Stroke Project 2 study. NCCT scans acquired at the primary stroke center were used to create rNCCT maps. These maps detect regions with at least 1% relative hypodensity difference compared to the contralateral region. A trained observer who had insight of arterial occlusion location manually annotated artefacts. We trained a no new UNet using the NCCT, rNCCT, and flipped NCCT images to detect artefacts from the rNCCT maps. To assess the extent to which our model falsely identified ischemic regions as artefact, we determined the overlap between the automatically segmented artefact on the rNCCT map and the manually segmented ischemic core on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) acquired at the comprehensive stroke center before treatment.
Results: The best performing model was the ensemble of the five cross-validation folds of 3d low- and high-resolution models based on dice similarity coefficient. Figure 1 provides an example of our model’s artefact segmentation and the processed rNCCT map after artefact removal. For the 54 patients (20% of study population) in our test set, our model achieved a median Dice similarity coefficient of 0.95 (IQR: 0.91-0.97) and a median false positive volume of 6.1 (3.2-11) ml. In the 30 patients with available DWI scans, 30% of patients had any overlap (>=1 voxel) between the segmented artefact and DWI ischemic core with a median overlap volume of 0.69 (IQR: 0.32-2.3) ml.
Conclusion: We demonstrate the use of a deep-learning based model to automatically segment artefacts from rNCCT maps. Our model circumvents time-invasive manual removal of artefacts from the rNCCT map and thereby simplifies segmentation of the ischemic core on baseline NCCT. Validation with external datasets is necessary before use in routine stroke evaluation.
More abstracts on this topic:
An Innovative telemonitoring-wearable device with third heart sound detection for early detection of worsening heart failure
Masuda Hirotada, Ekuni Shota, Misumi Yusuke, Akazawa Yasuhiro, Sakata Yasushi, Miyagawa Shigeru
10-Year Trends in Last Known Well to Arrival Time in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients: 2014-2023Ferrone Nicholas, Sanmartin Maria, O'hara Joseph, Jimenez Jean, Ferrone Sophia, Wang Jason, Katz Jeffrey, Sanelli Pina
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)