Final ID: TP171
Automated Large Vessel Occlusions Detection: Improved Diagnostic Accuracy in MCA M2 Segment Using Deep Learning
Abstract Body: Introduction
Integrating AI into clinical practice enables precise diagnosis and could potentially enhance outcomes for patients with large vessel occlusion (LVO). Although advancements in AI have shown promise in enhancing diagnostic accuracy, several studies have reported very low sensitivities when including MCA-M2 occlusions, resulting in unbalanced performance across different LVO segments. Therefore, continuous retraining and evaluation of these evolving technologies in clinical settings are essential. This study aims to analyze the real-world performance of the latest version of an FDA-approved and CE-marked AI software for LVO detection in computed tomography angiograms (CTAs), specifically designed to provide balanced performance across all LVO segments.
Methods
This retrospective, multicenter, multinational, and blinded study analyzed anonymized CTA scans from 7 clinical sources across Europe and the USA, acquired using 40 scan models from 5 different CT vendors. The improved version of CINA-LVO (Avicenna.AI, La Ciotat, France) uses deep learning to accurately detect ICA, MCA-M1 and proximal MCA-M2 without impairment, specifically with MCA-M2 segments. Its diagnostic performance was assessed against the ground truth, which was determined through the consensus of three US board-certified senior neuroradiologists who analyzed each LVO segment.
Results
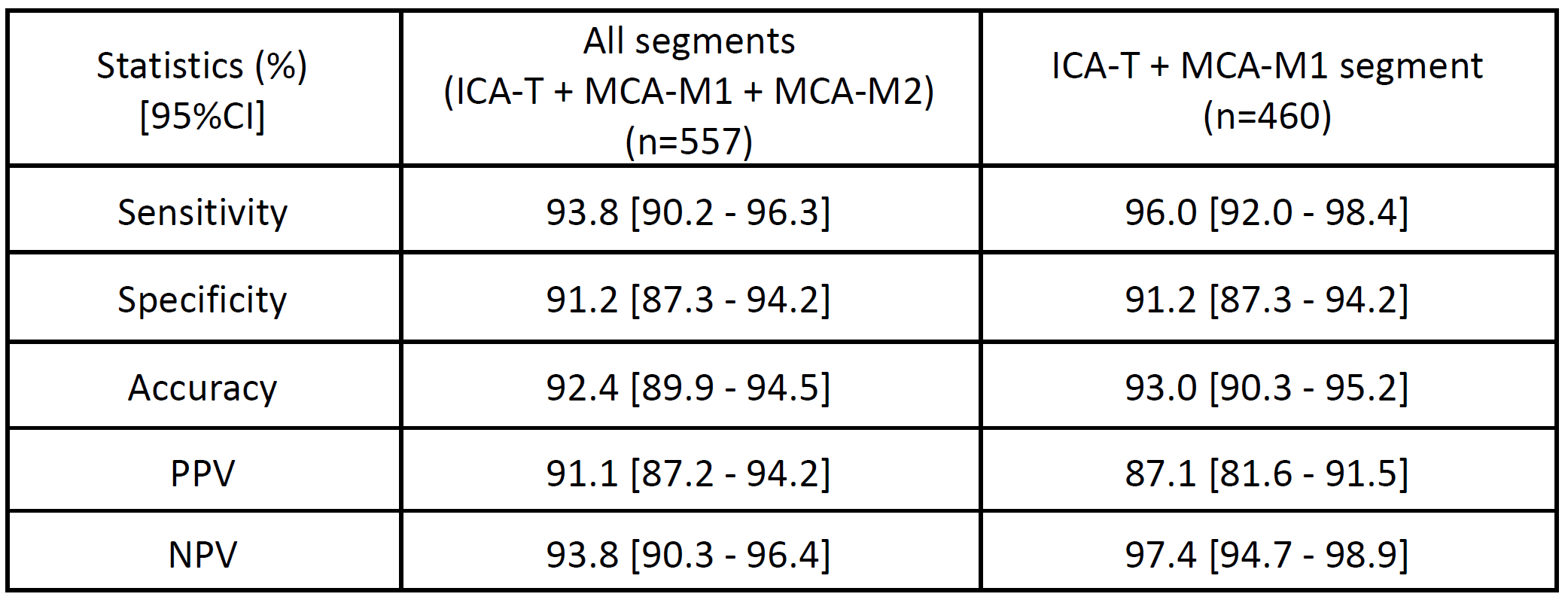
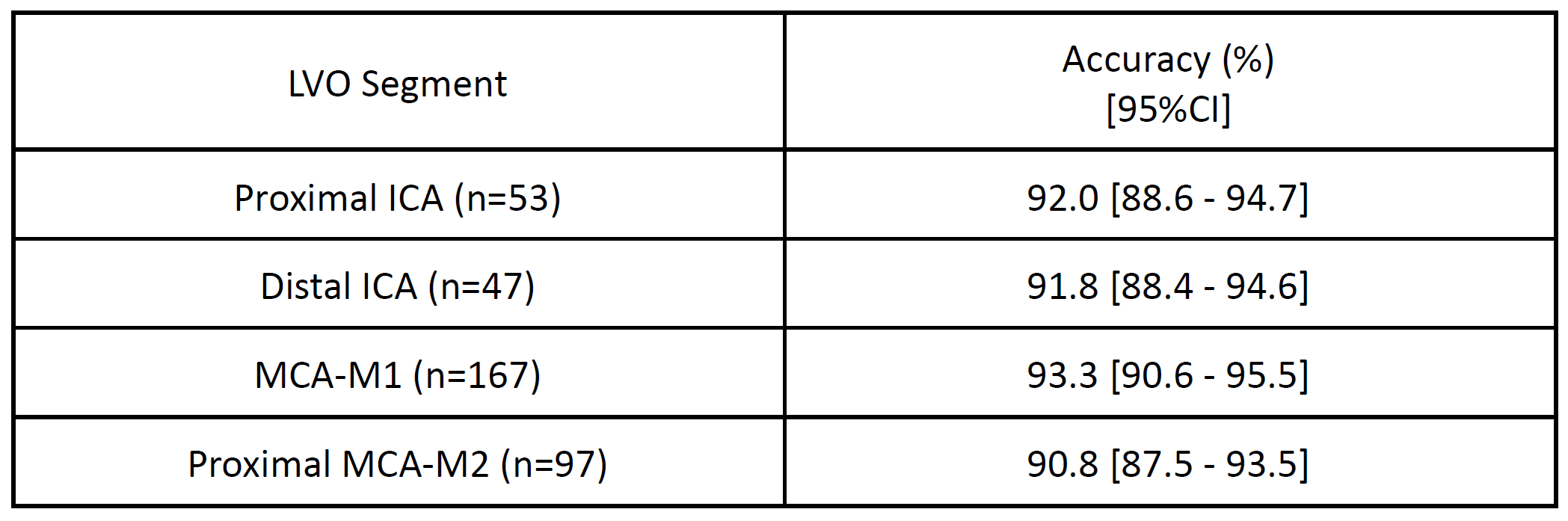
A total of 557 scans (mean age 66.2 ± 20.5 [SD] years old, 50.3% female, 49.0% positive for LVO) were included. Overall sensitivity and specificity including M2 occlusions (all 557 cases) were 93.8% (95%CI: 90.2%-96.3%) and 91.2% (95%CI: 87.3%-94.2%), respectively. The PPV and NPV were 91.1% and 93.8%, respectively (see Table 1). Moreover, the detection accuracy for LVO exceeded 90% across all LVO segments, including the proximal and distal internal carotid artery and the M1 and proximal M2 segments of the middle cerebral artery (see Table 2). There were no statistically significant differences between the accuracy of each LVO segment (p-value>0.05).
Conclusions
Unlike previous studies, our results demonstrate balanced performance across all LVO segments, with no impairment in diagnostic accuracy from the inclusion of M2 occlusions in the analysis. These promising findings suggest that the integration of continuously improved AI tools into clinical practice could substantially enhance clinical workflow and diagnostic accuracy for patients with LVO.
Integrating AI into clinical practice enables precise diagnosis and could potentially enhance outcomes for patients with large vessel occlusion (LVO). Although advancements in AI have shown promise in enhancing diagnostic accuracy, several studies have reported very low sensitivities when including MCA-M2 occlusions, resulting in unbalanced performance across different LVO segments. Therefore, continuous retraining and evaluation of these evolving technologies in clinical settings are essential. This study aims to analyze the real-world performance of the latest version of an FDA-approved and CE-marked AI software for LVO detection in computed tomography angiograms (CTAs), specifically designed to provide balanced performance across all LVO segments.
Methods
This retrospective, multicenter, multinational, and blinded study analyzed anonymized CTA scans from 7 clinical sources across Europe and the USA, acquired using 40 scan models from 5 different CT vendors. The improved version of CINA-LVO (Avicenna.AI, La Ciotat, France) uses deep learning to accurately detect ICA, MCA-M1 and proximal MCA-M2 without impairment, specifically with MCA-M2 segments. Its diagnostic performance was assessed against the ground truth, which was determined through the consensus of three US board-certified senior neuroradiologists who analyzed each LVO segment.
Results
A total of 557 scans (mean age 66.2 ± 20.5 [SD] years old, 50.3% female, 49.0% positive for LVO) were included. Overall sensitivity and specificity including M2 occlusions (all 557 cases) were 93.8% (95%CI: 90.2%-96.3%) and 91.2% (95%CI: 87.3%-94.2%), respectively. The PPV and NPV were 91.1% and 93.8%, respectively (see Table 1). Moreover, the detection accuracy for LVO exceeded 90% across all LVO segments, including the proximal and distal internal carotid artery and the M1 and proximal M2 segments of the middle cerebral artery (see Table 2). There were no statistically significant differences between the accuracy of each LVO segment (p-value>0.05).
Conclusions
Unlike previous studies, our results demonstrate balanced performance across all LVO segments, with no impairment in diagnostic accuracy from the inclusion of M2 occlusions in the analysis. These promising findings suggest that the integration of continuously improved AI tools into clinical practice could substantially enhance clinical workflow and diagnostic accuracy for patients with LVO.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Real-world Evaluation of Longitudinal Healthcare Expenses in a Health System Registry of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease Enabled by the 21st Century Cures Act
Dhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Pedroso Aline, Rajpura Jigar, Mehanna Sherif, Tonnu-mihara Ivy, Khera Rohan
3D Aortic Geometry is Informative for Risk of Adverse Aortic EventsPirruccello James
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.
Rate this abstract
(Maximum characters: 500)