Final ID: TP179
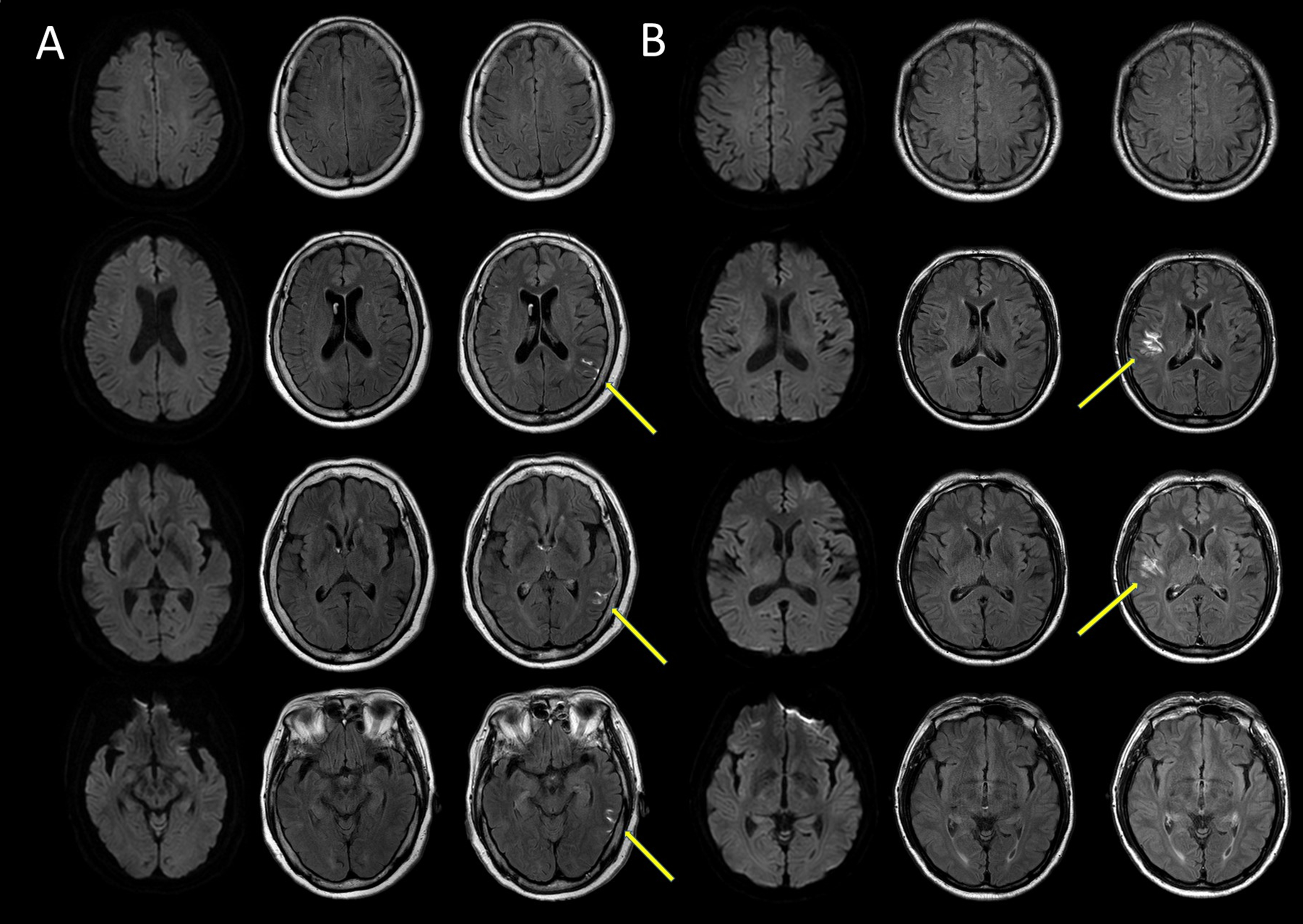
Hyperintense Acute Reperfusion Marker Sign in Patients with Diffusion Weighted Image-negative Transient Ischemic Attack
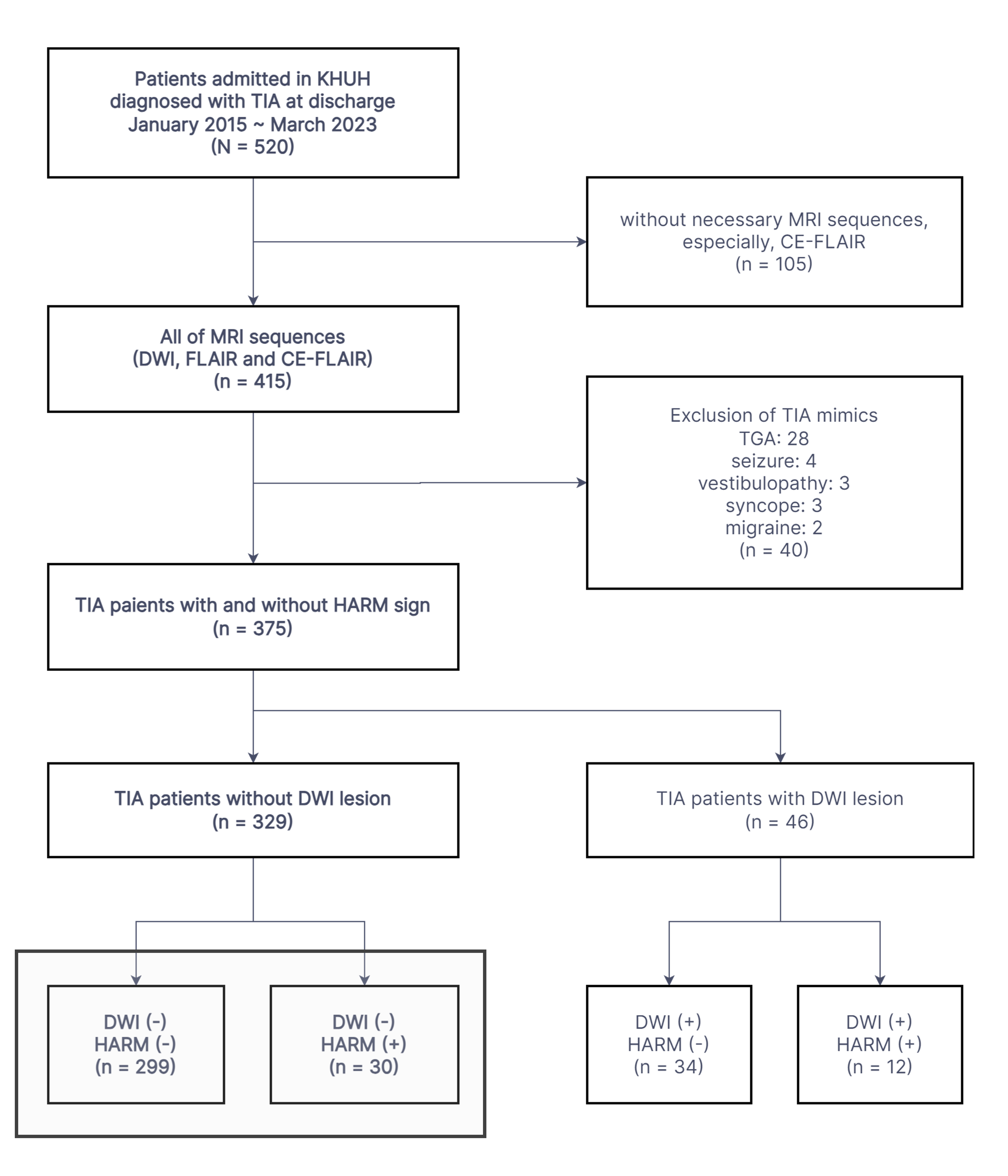
Methods: We included 329 consecutive patients with DWI-negative TIA and divided them into two groups according to the HARM sign: 299 patients in the HARM(-) group and 30 patients in the HARM(+) group. Clinical information, brain imaging, and follow-up data were gathered from medical records and phone calls and compared using the HARM sign.
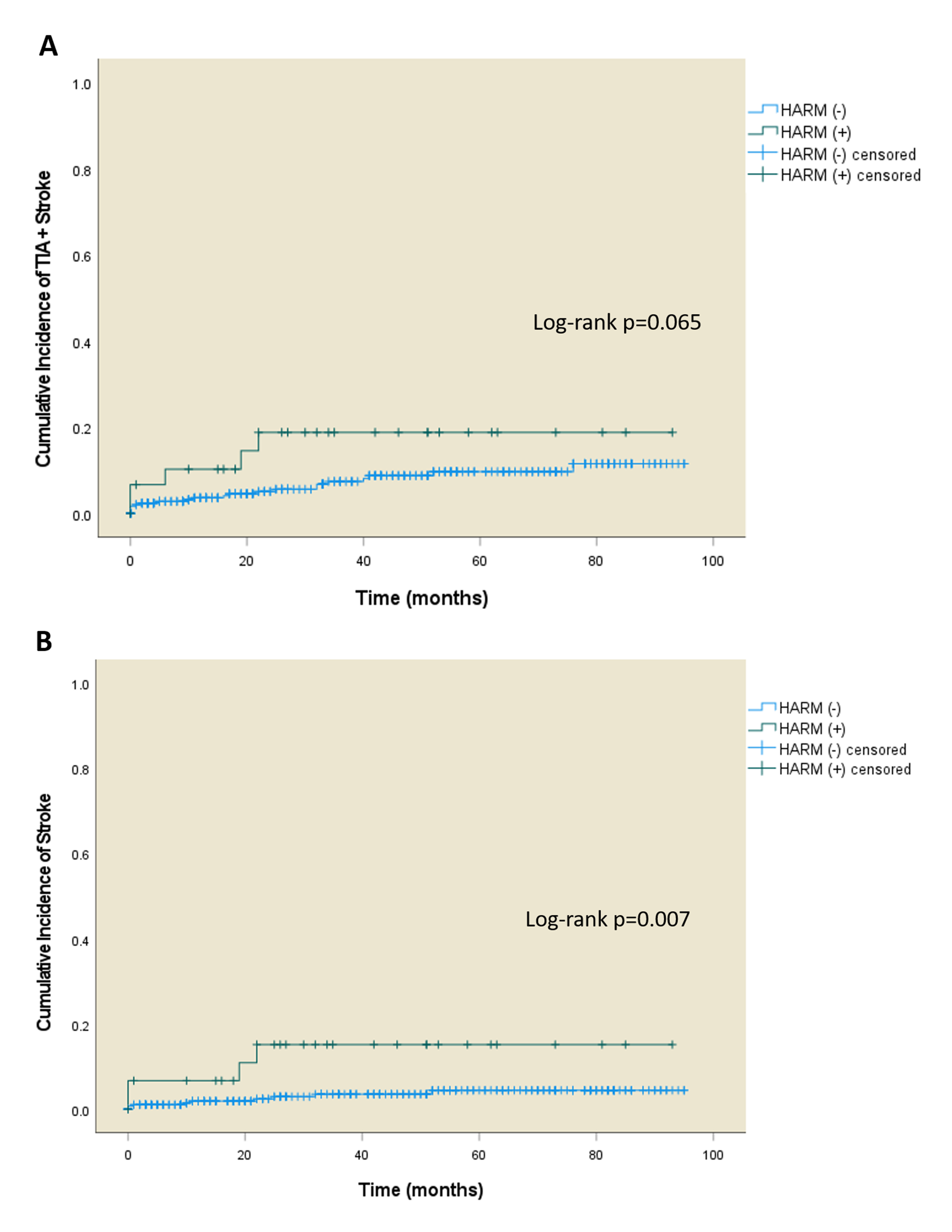
Results: The patients with HARM sign were older (70.7 vs. 64.4 years, p = 0.007), had more previous TIA or stroke history within 12 months (26.7% vs. 4.0%, p < 0.001), and had higher systolic blood pressure (154.3 vs. 144.1, p = 0.022). The HARM(+) group also had a shorter symptom duration of <1 hour (63.3% vs. 38.8%, p = 0.009) and more symptomatic stenosis (50–99%) or occlusion (60.0% vs. 14.0%, p < 0.001). Among the transient neurological symptoms, only cortical symptoms were more prevalent in the HARM(+) group (30.0% vs. 8.7%, p = 0.002). The total follow-up duration of both groups was similar, and the Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a higher cumulative incidence of recurrent stroke in the HARM(+) group (log-rank test, p = 0.007). However, multivariate Cox analysis indicated that symptomatic stenosis or occlusion, rather than the HARM sign, was independently associated with stroke recurrence.
Conclusion: The HARM sign in DWI-negative TIA patients is linked to older age, recent cerebrovascular events, shorter symptom duration, and large artery stenosis or occlusion. While the HARM sign correlates with higher recurrence of ischemic stroke, large artery stenosis or occlusion is the primary independent predictor.
More abstracts on this topic:
Sico Jason, Perkins Anthony, Daggy Joanne, Bravata Dawn, Rattray Nicholas, Burrone Laura, Sexson Ali, Miech Edward, Story Kristin, Koo Brian, Taylor Stanley, Myers Laura
A Novel Imaging Biomarker to Make Precise Outcome Predictions for Patients with Acute Ischemic StrokeMallavarapu Monica, Kim Hyun Woo, Iyyangar Ananya, Salazar-marioni Sergio, Yoo Albert, Giancardo Luca, Sheth Sunil, Jeevarajan Jerome
Readers' Comments
We encourage you to enter the discussion by posting your comments and questions below.
Presenters will be notified of your post so that they can respond as appropriate.
This discussion platform is provided to foster engagement, and simulate conversation and knowledge sharing.
You have to be authorized to post a comment. Please, Login or Signup.